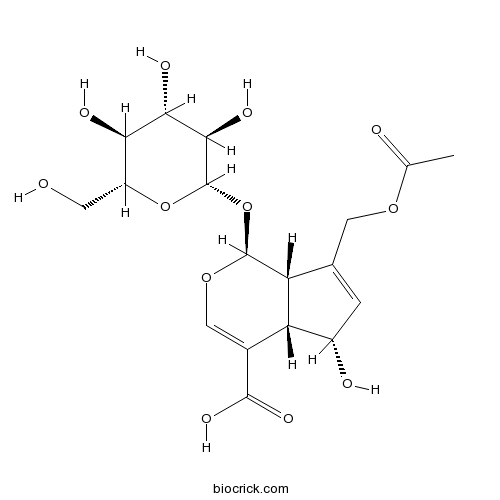
Asperulosidic acidCAS# 25368-11-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 25368-11-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11968867 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C18H24O12 | M.Wt | 432.4 |
| Type of Compound | Iridoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, methanol and pyridine | ||
| Chemical Name | (1S,4aS,5S,7aS)-7-(acetyloxymethyl)-5-hydroxy-1-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-1,4a,5,7a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OCC1=CC(C2C1C(OC=C2C(=O)O)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DGDWCRWJRNMRKX-DILZHRMZSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Asperulosidic acid has been recently used in chinese medicine as a useful drug against some tumors. 2. Asperulosidic acid has anticlastogenic activity, since the anticlastogenic irridoids have an alpha-unsaturated carbonyl group, this structure is considered to play an important role in the anticlastogenicity. 3. Asperulosidic acid, and 6-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-1-O-octanoyl-beta-D-glucopyranose are effective in suppressing 12-O-tedtradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)- or epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced cell transformation and associated AP-1 activity. 4. Asperulosidic acid can inhibit the seed germination and growth of seedlings of large crabgrass. |
| Targets | EGFR | AP-1 |

Asperulosidic acid Dilution Calculator

Asperulosidic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3127 mL | 11.5634 mL | 23.1267 mL | 46.2535 mL | 57.8168 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4625 mL | 2.3127 mL | 4.6253 mL | 9.2507 mL | 11.5634 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2313 mL | 1.1563 mL | 2.3127 mL | 4.6253 mL | 5.7817 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0463 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.9251 mL | 1.1563 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0231 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.5782 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Litseglutine B
Catalog No.:BCN5120
CAS No.:25368-01-8
- 2-Amino-6-methylbenzothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8543
CAS No.:2536-91-6
- 16-O-Acetylpolyporenic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN4058
CAS No.:2535-06-0
- Wiskostatin
Catalog No.:BCC7934
CAS No.:253449-04-6
- (+)-Corlumidine
Catalog No.:BCN2662
CAS No.:25344-54-1
- Viniferin
Catalog No.:BCN3757
CAS No.:253435-07-3
- Trazodone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5032
CAS No.:25332-39-2
- BMS 195614
Catalog No.:BCC7740
CAS No.:253310-42-8
- Isocalamendiol
Catalog No.:BCN5119
CAS No.:25330-21-6
- Tetrabromobisphenol A diallyl ether
Catalog No.:BCC9174
CAS No.:25327-89-3
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1117
CAS No.:25316-40-9
- Eribulin
Catalog No.:BCC5174
CAS No.:253128-41-5
- TRIM
Catalog No.:BCC6847
CAS No.:25371-96-4
- AR-C 102222
Catalog No.:BCC6092
CAS No.:253771-21-0
- Kanamycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1205
CAS No.:25389-94-0
- Morroniside
Catalog No.:BCN5009
CAS No.:25406-64-8
- Boc-ß-HoAsp(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3229
CAS No.:254101-10-5
- Phellopterin
Catalog No.:BCN2637
CAS No.:2543-94-4
- H-Cys(pMeOBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2909
CAS No.:2544-31-2
- Dehydropitavastatin ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8931
CAS No.:254452-91-0
- (+)-Afzelechin
Catalog No.:BCN5121
CAS No.:2545-00-8
- Felbamate
Catalog No.:BCC4904
CAS No.:25451-15-4
- H-D-Glu-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC2938
CAS No.:25456-76-2
- H-Asn-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC2877
CAS No.:25456-86-4
Two novel glycosides from the fruits of Morinda citrifolia (noni) inhibit AP-1 transactivation and cell transformation in the mouse epidermal JB6 cell line.[Pubmed:11479211]
Cancer Res. 2001 Aug 1;61(15):5749-56.
The fruit juice of Morinda citrifolia (noni), a plant originally grown in the Hawaiian and Tahitian islands, has long been used by islanders to treat diseases, including cancer. Two novel glycosides, 6-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-1-O-octanoyl-beta-D-glucopyranose and Asperulosidic acid, extracted from the juice of noni fruits, were used to examine their effects on 12-O-tedtradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)- and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced AP-1 transactivation and cell transformation in mouse epidermal JB6 cells. The results indicated that both compounds were effective in suppressing TPA- or EGF-induced cell transformation and associated AP-1 activity. TPA- or EGF-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun, but not extracellular signal-regulated kinases or p38 kinases, was also blocked by the compounds, indicating that c-Jun N-terminal kinases were critical in mediating TPA- or EGF-induced AP-1 activity and subsequent cell transformation in JB6 cells.


