AtractylodinCAS# 55290-63-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 55290-63-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5321047 | Appearance | Brown powder |
| Formula | C13H10O | M.Wt | 182.22 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Atractydin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 6 mg/mL (32.93 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
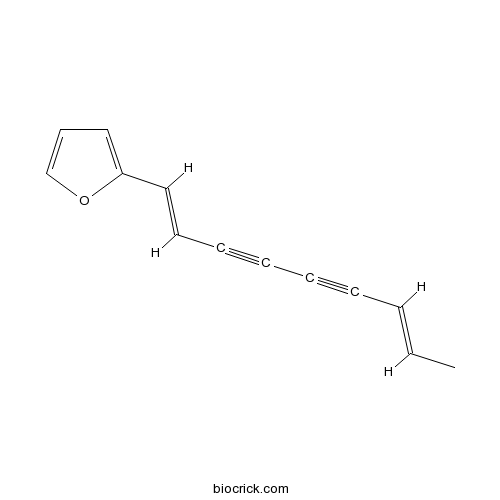
| Chemical Name | 2-[(1E,7E)-nona-1,7-dien-3,5-diynyl]furan | ||
| SMILES | CC=CC#CC#CC=CC1=CC=CO1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GRBKWAXRYIITKG-QFMFQGICSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Atractylodin has a good potential as a source for natural repellents, it could be developed as natural insecticide. Atractylodin has high lipase inhibitory activity with the IC50 of 39.12 μM. |
| Targets | Antifection |
| In vitro | Insecticidal and Repellant Activities of Polyacetylenes and Lactones Derived from Atractylodes lancea Rhizomes.[Pubmed: 25879503]Chem Biodivers. 2015 Apr;12(4):593-8.During a screening program for new agrochemicals from Chinese medicinal herbs and local wild plants, the petroleum ether (PE) extract of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) rhizomes was found to possess repellent and contact activities against Tribolium castaneum adults.
Signal transduction of atractylodin biosynthesis in Atractylodes lancea cell induced by endophytic fungal elicitor mediated with nitric oxide followed by salicylic acid[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2014, 45(5): 701-8.To investigate the signal molecules and signal transduction involved in endophytic fungal elicitor-induced Atractylodin biosynthesis and the effect of an endophytic fungal elicitor on the key enzyme activity in Atractylodes lancea.
|
| Animal Research | Lipase inhibition and antiobesity effect of Atractylodes lancea.[Pubmed: 24687739]Planta Med. 2014 May;80(7):577-82.The ethanol extract of Atractylodes lancea rhizome displayed significant lipase inhibition with an IC50 value of 9.06 μg/mL in a human pancreatic lipase assay from high-throughput screening.
|

Atractylodin Dilution Calculator

Atractylodin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4879 mL | 27.4394 mL | 54.8787 mL | 109.7574 mL | 137.1968 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0976 mL | 5.4879 mL | 10.9757 mL | 21.9515 mL | 27.4394 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5488 mL | 2.7439 mL | 5.4879 mL | 10.9757 mL | 13.7197 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1098 mL | 0.5488 mL | 1.0976 mL | 2.1951 mL | 2.7439 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0549 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5488 mL | 1.0976 mL | 1.372 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Atractylodin is an active component of the essential oil contained in the rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea and A.
References:
[1]. Takeda O, et al. A comparative study on essential oil components of wild and cultivated Atractylodes lancea and A. chinensis. Planta Med. 1996 Oct;62(5):444-9.
[2]. Nakai Y, et al. Effect of the rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea and its constituents on the delay of gastric emptying. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003 Jan;84(1):51-5.
- Praziquantel
Catalog No.:BCC4829
CAS No.:55268-74-1
- MnTBAP Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6477
CAS No.:55266-18-7
- Boc-Gln(Xan)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3385
CAS No.:55260-24-7
- A-674563
Catalog No.:BCC3903
CAS No.:552325-73-2
- A-443654
Catalog No.:BCC1321
CAS No.:552325-16-3
- T16Ainh - A01
Catalog No.:BCC6220
CAS No.:552309-42-9
- Vallesiachotamine
Catalog No.:BCN3548
CAS No.:5523-37-5
- Rolapitant
Catalog No.:BCC6441
CAS No.:552292-08-7
- AP 18
Catalog No.:BCC7634
CAS No.:55224-94-7
- Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4557
CAS No.:55203-24-2
- Sasapyrine
Catalog No.:BCC4714
CAS No.:552-94-3
- Daidzin
Catalog No.:BCN5891
CAS No.:552-66-9
- (Z)-Falcarindiol
Catalog No.:BCN8495
CAS No.:55297-87-5
- Tiamulin
Catalog No.:BCC9179
CAS No.:55297-95-5
- Thonzonium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC5636
CAS No.:553-08-2
- Xanthyletin
Catalog No.:BCN6722
CAS No.:553-19-5
- Costunolide
Catalog No.:BCN5740
CAS No.:553-21-9
- Atherosperminine
Catalog No.:BCN8208
CAS No.:5531-98-6
- Soyasaponin II
Catalog No.:BCN1418
CAS No.:55319-36-3
- Petasiphenone
Catalog No.:BCC8100
CAS No.:162616-81-1
- Beclomethasone dipropionate
Catalog No.:BCC4257
CAS No.:5534-09-8
- Vidarabine
Catalog No.:BCC4877
CAS No.:5536-17-4
- Baohuoside II
Catalog No.:BCN2888
CAS No.:55395-07-8
- Hydroxyisoleucine
Catalog No.:BCN8402
CAS No.:55399-93-4
A new 9-nor-atractylodin from Atractylodes lancea and the antibacterial activity of the atractylodin derivatives.[Pubmed:22061661]
Fitoterapia. 2012 Jan;83(1):199-203.
A new compound, namely, 9-nor-Atractylodin (1) and one known Atractylodin (2) were isolated from the rhizomes of Atractylodes lancea. The structural modifications of Atractylodin were carried out and a series of Atractylodin derivatives (3-10) were obtained. The antibacterial activities of 1-10 were examined against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and Candida albicans. Compounds 4 and 8, which contained the alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl fragment, were found to be active against E. coli and S. aureus.
Lipase inhibition and antiobesity effect of Atractylodes lancea.[Pubmed:24687739]
Planta Med. 2014 May;80(7):577-82.
The ethanol extract of Atractylodes lancea rhizome displayed significant lipase inhibition with an IC50 value of 9.06 microg/mL in a human pancreatic lipase assay from high-throughput screening. Bioassay-guided isolation led to the identification of one new polyacetylene, syn-(5E,11E)-3-acetoxy-4-O-(3-methylbutanoyl)-1,5,11-tridecatriene-7,9-diyne-3,4- diol (7), along with six known compounds (1-6). The structure of compound 7 was determined based on the analysis of NMR and MS data. Among these seven lipase inhibitors, the major compound Atractylodin (1) showed the highest lipase inhibitory activity (IC50 = 39.12 microM). The antiobesity effect of the ethanol extract of Atractylodes lancea rhizome was evaluated in a high-fat diet-induced obesity mice model at daily dosages of 250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg body weight for 4 weeks, and treatment with this extract demonstrated a moderate efficacy at the 500 mg/kg dose level.
Insecticidal and repellant activities of polyacetylenes and lactones derived from Atractylodes lancea rhizomes.[Pubmed:25879503]
Chem Biodivers. 2015 Apr;12(4):593-8.
During a screening program for new agrochemicals from Chinese medicinal herbs and local wild plants, the petroleum ether (PE) extract of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) rhizomes was found to possess repellent and contact activities against Tribolium castaneum adults. Bioactivity-directed chromatographic separation of PE extract on repeated silica-gel columns led to the isolation of two polyacetylenes, Atractylodin and Atractylodinol (1 and 2, resp.), and two lactones, atractylenolides II and III (3 and 4, resp.). The structures of the compounds were elucidated based on NMR spectra. The four isolated compounds were evaluated for their insecticidal and repellent activities against T. castaneum. Atractylodin exhibited strong contact activity against T. castaneum adults with a LD50 value of 1.83 mug/adult. Atractylodin and atractylenolide II also possessed strong repellenct activities against T. castaneum adults. After 4-h exposure, >90% repellency was achieved with Atractylodin at a low concentration of 0.63 mug/cm(2) . The results indicated that Atractylodin (1) and atractylenolide II (3) have a good potential as a source for natural repellents, and 1 has the potential to be developed as natural insecticide.
[Effect of endophytic fungal elicitors on growth and atractylodin accumulation of cell suspension cultures of Atractylodes lancea].[Pubmed:21473147]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Jan;36(1):27-31.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of endophytic fungal elicitors on the growth and Atractylodin accumulation of cell suspension cultures of Atractylodes lancea. METHOD: The endophytic fungal elicitors were added to the medium with different concentrations and culture period. Their effects on biomass, Atractylodin content and relevant enzyme activities in suspension cultured cells were studied. RESULT: The cell growth was not affected by elicitors at low concentration and obviously inhibited at high concentration. Inhibition rate reached 46.7% by 100 mg L(-1) elicitor. In addition, six strains from A. lancea, among which Rhizoctonia SP1 activity was higher, had distinctly promoted the accumulation of Atractylodin. Atractylodin biosynthesis was notably promoted by 20-60 mg L(-1) Rhizoctonia SP1 elicitor. When 40 mg L(-1) Rhizoctonia SP1 elicitor was added in the medium at the 12 day, the maximum content of Atractylodin was 28.06 microg L(-1) at the 21 day with 48.3% higher than that of the control and PPO, POD and CAT activities remarkably increased. CONCLUSION: Adding the endophytic elicitors to the medium is able to be effective approaches to enhance Atractylodin yield in the suspension culture cell of A. lancea.


