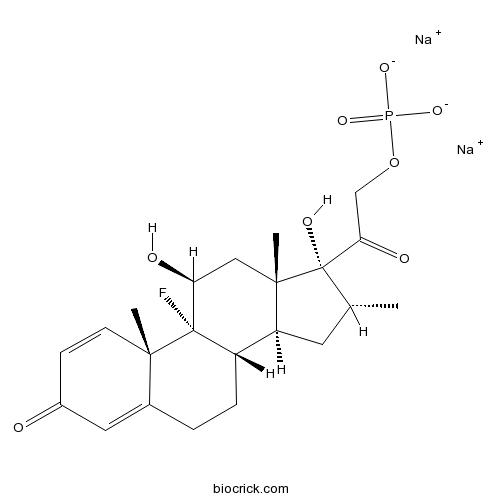
Dexamethasone Sodium PhosphateCAS# 55203-24-2 |
- Vinblastine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2292
CAS No.:143-67-9
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- Pepstatin A
Catalog No.:BCC1218
CAS No.:26305-03-3
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- E 64d
Catalog No.:BCC1127
CAS No.:88321-09-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 55203-24-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16961 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H28FNa2O8P | M.Wt | 516.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Dexamethasone 21-phosphate disodium salt;Dalalone;2392-39-4 | ||
| Solubility | <5.1mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming | ||
| Chemical Name | disodium;[2-[(8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,16R,17R)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-10,13,16-trimethyl-3-oxo-6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-oxoethyl] phosphate | ||
| SMILES | [Na+].[Na+].C[C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@H]3CCC4=CC(=O)C=C[C@]4(C)[C@@]3(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@]2(C)[C@@]1(O)C(=O)CO[P]([O-])([O-])=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PLCQGRYPOISRTQ-FCJDYXGNSA-L | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H30FO8P.2Na/c1-12-8-16-15-5-4-13-9-14(24)6-7-19(13,2)21(15,23)17(25)10-20(16,3)22(12,27)18(26)11-31-32(28,29)30;;/h6-7,9,12,15-17,25,27H,4-5,8,10-11H2,1-3H3,(H2,28,29,30);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t12-,15+,16+,17+,19+,20+,21+,22+;;/m1../s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate Dilution Calculator

Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9365 mL | 9.6824 mL | 19.3648 mL | 38.7297 mL | 48.4121 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3873 mL | 1.9365 mL | 3.873 mL | 7.7459 mL | 9.6824 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1936 mL | 0.9682 mL | 1.9365 mL | 3.873 mL | 4.8412 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0387 mL | 0.1936 mL | 0.3873 mL | 0.7746 mL | 0.9682 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0968 mL | 0.1936 mL | 0.3873 mL | 0.4841 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Dexamethasone is an interleukin receptor inhibitor and also suppresses COX-2.
- Sasapyrine
Catalog No.:BCC4714
CAS No.:552-94-3
- Daidzin
Catalog No.:BCN5891
CAS No.:552-66-9
- Prunetin
Catalog No.:BCN2335
CAS No.:552-59-0
- Eriodictyol
Catalog No.:BCN1209
CAS No.:552-58-9
- Isorhoifolin
Catalog No.:BCN5739
CAS No.:552-57-8
- Paeonol
Catalog No.:BCN5738
CAS No.:552-41-0
- Oxohydrastinine
Catalog No.:BCN3299
CAS No.:552-29-4
- Kaempferol 3-sophoroside-7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7825
CAS No.:55136-76-0
- (S)-3-Carboxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6607
CAS No.:55136-48-6
- 4beta-Carboxy-19-nortotarol
Catalog No.:BCN4065
CAS No.:55102-39-1
- 2'-Aminoacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1746
CAS No.:551-93-9
- Dimetridazole
Catalog No.:BCC8944
CAS No.:551-92-8
- AP 18
Catalog No.:BCC7634
CAS No.:55224-94-7
- Rolapitant
Catalog No.:BCC6441
CAS No.:552292-08-7
- Vallesiachotamine
Catalog No.:BCN3548
CAS No.:5523-37-5
- T16Ainh - A01
Catalog No.:BCC6220
CAS No.:552309-42-9
- A-443654
Catalog No.:BCC1321
CAS No.:552325-16-3
- A-674563
Catalog No.:BCC3903
CAS No.:552325-73-2
- Boc-Gln(Xan)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3385
CAS No.:55260-24-7
- MnTBAP Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC6477
CAS No.:55266-18-7
- Praziquantel
Catalog No.:BCC4829
CAS No.:55268-74-1
- Atractylodin
Catalog No.:BCN6292
CAS No.:55290-63-6
- (Z)-Falcarindiol
Catalog No.:BCN8495
CAS No.:55297-87-5
- Tiamulin
Catalog No.:BCC9179
CAS No.:55297-95-5
Compatibility and Stability of Rolapitant Injectable Emulsion Admixed with Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate.[Pubmed:28346199]
Int J Pharm Compd. 2017 Jan-Feb;21(1):66-75.
Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist, 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 receptor antagonist, and dexamethasone combination therapy is the standard of care for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Herein, we describe the physical and chemical stability of an injectable emulsion of the Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist rolapitant 185 mg in 92.5 mL (free base, 166.5 mg in 92.5 mL) admixed with either 2.5 mL of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate (10 mg) or 5 mL of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate (20 mg). Admixtures were prepared and stored in two types of container closures (glass and Crystal Zenith plastic bottles) and four types of intravenous administration tubing sets (or intravenous tubing sets). The assessment of the physical and chemical stability was conducted on admixtures packaged in bottled samples stored at room temperature (20 degrees C to 25 degrees C under fluorescent light) and evaluated at 0, 1, and 6 hours. For admixtures in intravenous tubing sets, the assessment of physicochemical stability was performed after 0 and 7 hours of storage at 20 degrees C to 25 degrees C, and then after 20 hours (total 27 hours) under refrigeration (2 degrees C to 8 degrees C) and protected from light. Physical stability was assessed by visually examining the bottle contents under normal room light and measuring turbidity and particulate matter. Chemical stability was assessed by measuring the pH of the admixture and determining drug concentrations through high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Results showed that all samples were physically compatible throughout the duration of the study. The admixtures stayed within narrow and acceptable ranges in pH, turbidity, and particulate matter. Admixtures of rolapitant and dexamethasone were chemically stable when stored in glass and Crystal Zenith bottles for at least 6 hours at room temperature, as well as in the four selected intravenous tubing sets for 7 hours at 20 degrees C to 25 degrees C and then for 20 (total 27 hours) hours at 2 degrees C to 8 degrees C. No loss of potency of any admixed component occurred in the samples stored at the temperature ranges studied.
Stability-Indicating HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Chloramphenicol, Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Tetrahydrozoline Hydrochloride in Ophthalmic Solution.[Pubmed:27123429]
Adv Pharm Bull. 2016 Mar;6(1):137-41.
PURPOSE: A simple stability-indicating RP-HPLC assay method was developed and validated for quantitative determination of Chloramphenicol, Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Tetrahydrozoline Hydrochloride in ophthalmic solution in the presence of 2-amino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)propane-1,3-diol, a degradation product of Chloramphenicol, and Dexamethasone, a degradation product of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate. METHODS: Effective chromatographic separation was achieved using C18 column (250 mm, 4.6 mm i.d., 5 mum) with isocratic mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile - phosphate buffer (pH 4.0; 0.05 M) (30:70, v/v) at a flow rate of 1 mL/minute. The column temperature was maintained at 40 degrees C and the detection wavelength was 230 nm. RESULTS: The proposed HPLC procedure was statistically validated according to the ICH guideline, and was proved to be stability-indicating by resolution of the APIs from their forced degradation products. CONCLUSION: The developed method is suitable for the routine analysis as well as stability studies.
Biomembranes from slaughterhouse blood erythrocytes as prolonged release systems for dexamethasone sodium phosphate.[Pubmed:27254304]
Biotechnol Prog. 2016 Jul 8;32(4):1046-55.
The present study investigated preparation of bovine and porcine erythrocyte membranes from slaughterhouse blood as bio-derived materials for delivery of dexamethasone-sodium phosphate (DexP). The obtained biomembranes, i.e., ghosts were characterized in vitro in terms of morphological properties, loading parameters, and release behavior. For the last two, an UHPLC/-HESI-MS/MS based analytical procedure for absolute drug identification and quantification was developed. The results revealed that loading of DexP into both type of ghosts was directly proportional to the increase of drug concentration in the incubation medium, while incubation at 37 degrees C had statistically significant effect on loaded amount of DexP (P < 0.05). The encapsulation efficiency was about fivefold higher in porcine compared to bovine ghosts. Insight into ghosts' surface morphology by field emission-scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy confirmed that besides inevitable effects of osmosis, DexP inclusion itself had no observable additional effect on the morphology of the ghosts carriers. DexP release profiles were dependent on erythrocyte ghost type and amount of residual hemoglobin. However, sustained DexP release was achieved and shown over 3 days from porcine ghosts and 5 days from bovine erythrocyte ghosts. (c) 2016 American Institute of Chemical Engineers Biotechnol. Prog., 32:1046-1055, 2016.
Ex vivo encapsulation of dexamethasone sodium phosphate into human autologous erythrocytes using fully automated biomedical equipment.[Pubmed:27939571]
Int J Pharm. 2017 Jan 30;517(1-2):175-184.
Erythrocyte-based drug delivery systems are emerging as potential new solutions for the release of drugs into the bloodstream. The aim of the present work was to assess the performance of a fully automated process (EDS) for the ex-vivo encapsulation of the pro-drug Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate (DSP) into autologous erythrocytes in compliance with regulatory requirements. The loading method was based on reversible hypotonic hemolysis, which allows the opening of transient pores in the cell membrane to be crossed by DSP. The efficiency of encapsulation and the biochemical and physiological characteristics of the processed erythrocytes were investigated in blood samples from 34 healthy donors. It was found that the processed erythrocytes maintained their fundamental properties and the encapsulation process was reproducible. The EDS under study showed greater loading efficiency and reduced variability compared to previous EDS versions. Notably, these results were confirmed using blood samples from Ataxia Telangiectasia (AT) patients, 9.33+/-1.40 and 19.41+/-2.10mg of DSP (mean+/-SD, n=134) by using 62.5 and 125mg DSP loading quantities, respectively. These results support the use of the new EDS version 3.2.0 to investigate the effect of erythrocyte-delivered dexamethasone in regulatory trials in patients with AT.


