DoxorubicinTopo II inhibitor,immunosuppresive antineoplastic antibiotic CAS# 23214-92-8 |
- Amrubicin
Catalog No.:BCC3640
CAS No.:110267-81-7
- (S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN1225
CAS No.:19685-09-7
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Beta-Lapachone
Catalog No.:BCC5088
CAS No.:4707-32-8
- Genz-644282
Catalog No.:BCC1592
CAS No.:529488-28-6
- Amonafide
Catalog No.:BCC1249
CAS No.:69408-81-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23214-92-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 31703 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H29NO11 | M.Wt | 543.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Adriamycin; Hydroxydaunorubicin | ||
| Solubility | >27.2mg/mL in DMSO | ||
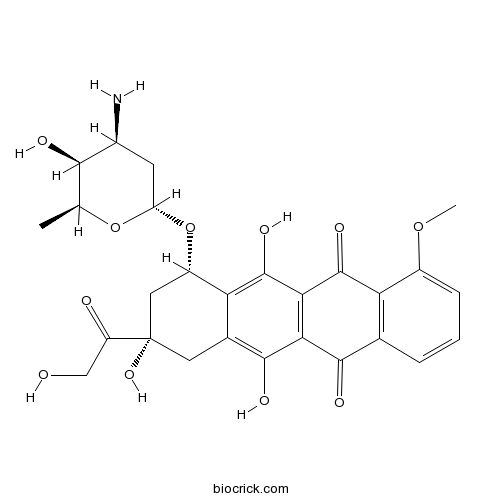
| Chemical Name | (7S,9S)-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-9-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2CC(CC3=C(C4=C(C(=C23)O)C(=O)C5=C(C4=O)C=CC=C5OC)O)(C(=O)CO)O)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H29NO11/c1-10-22(31)13(28)6-17(38-10)39-15-8-27(36,16(30)9-29)7-12-19(15)26(35)21-20(24(12)33)23(32)11-4-3-5-14(37-2)18(11)25(21)34/h3-5,10,13,15,17,22,29,31,33,35-36H,6-9,28H2,1-2H3/t10-,13-,15-,17-,22+,27-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) is an antibiotic agent, inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II and inducer of DNA damage and apoptosis. | |||||
| Targets | Autophagy | |||||

Doxorubicin Dilution Calculator

Doxorubicin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8399 mL | 9.1993 mL | 18.3986 mL | 36.7972 mL | 45.9965 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.368 mL | 1.8399 mL | 3.6797 mL | 7.3594 mL | 9.1993 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.184 mL | 0.9199 mL | 1.8399 mL | 3.6797 mL | 4.5996 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0368 mL | 0.184 mL | 0.368 mL | 0.7359 mL | 0.9199 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0184 mL | 0.092 mL | 0.184 mL | 0.368 mL | 0.46 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
Doxorubicin down-regulates HDAC1 expression and up-regulates miR-520h to induce DNA damage in cancer cells.
Abstract
Doxorubicin is an anti-neoplastic agent with cardiotoxicity.
Abstract
GC7 enhanced doxorubicin cytotoxicity and inhibited doxorubicin-induced EMT in epithelial HCC cells.
Abstract
Doxorubicin enhanced tumor infiltration by IFN-γ-secreting Tcells and decreased the content of TAMs in MMTV-neu mice.
Abstract
Although a few factors, including body composition, age, gender, changes in monocyte count and repeated dosing, have impacts on pharmacokinetic properties of PLD, clinical risk factors of ovarian cancer patients who have PPE and receive PLD are rarely identified.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Doxorubicin is a semi-synthesized anticancer agent derived from bacterial culture. [1] It is an anthracycline antibiotic. It is been widely used in blood cancers, solid tumors and sarcomas.
Doxorubicin intercalates into DNA double strand and inhibits the progression of DNA topoisomerase II, stopping replication process. [2] Doxorubicin also induces histone eviction from open chromatin, causing DNA damage and epigenetic deregulation. [3]
Doxorubicin is administrated intravenously. Approximately 75% of doxorubicin and its metabolites bind to plasma protein. Doxorubicin does not cross blood brain barrier. 50% of the drug is eliminated unchanged from the body mainly though bile excretion. The remaining undergoes one-electron reduction, two-electron reduction, and deglycosidation. The major metabolite is a potent membrane ion pump inhibitor, which is associated with cardiomyopathy. [4]
References:
[1]Brayfield, A, ed. (2013). Doxorubicin. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 15 April 2014.
[2]Pommier Y., et al. (2010). DNA topoisomerases and their poisoning by anticancer and antibacterial drugs. Chemistry & Biology 17 (5): 421–433.
[3]Pang, B., et al. (2013). Drug-induced histone eviction from open chromatin contributes to the chemotherapeutic effects of doxorubicin. Nature Communications 4 (5): 1908
[4]Boucek RJ., et al. (1987). The major metabolite of doxorubicin is a potent inhibitor of membrane-associated ion pumps. A correlative study of cardiac muscle with isolated membrane fractions. J of Biol Chem 262: 15851-15856.
- Ifenprodil Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4589
CAS No.:23210-58-4
- Ifenprodil hemitartrate
Catalog No.:BCC6688
CAS No.:23210-56-2
- Matairesinoside
Catalog No.:BCN7583
CAS No.:23202-85-9
- (1R,2S)-2-Amino-1,2-diphenylethanol
Catalog No.:BCC8382
CAS No.:23190-16-1
- Columbianetin acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2652
CAS No.:23180-65-6
- Paeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCN6301
CAS No.:23180-57-6
- Simiarenone
Catalog No.:BCN5082
CAS No.:2318-78-7
- Senkirkine
Catalog No.:BCN2136
CAS No.:2318-18-5
- Songoramine
Catalog No.:BCN6474
CAS No.:23179-78-4
- Nervosine
Catalog No.:BCN2012
CAS No.:23179-26-2
- Pyrolatin
Catalog No.:BCN8439
CAS No.:23176-70-7
- 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5040
CAS No.:2316-26-9
- Methoxydienone
Catalog No.:BCC9030
CAS No.:2322-77-2
- 23-Hydroxymangiferonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4668
CAS No.:232266-08-9
- TR-14035
Catalog No.:BCC4266
CAS No.:232271-19-1
- Ritodrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4337
CAS No.:23239-51-2
- 5,7-Diacetoxy-8-methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5083
CAS No.:23246-80-2
- Riddelline
Catalog No.:BCN2133
CAS No.:23246-96-0
- Dimaprit dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6672
CAS No.:23256-33-9
- Guanabenz Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4327
CAS No.:23256-50-0
- 4'-O-Methylvitexin
Catalog No.:BCN2642
CAS No.:2326-34-3
- Bay 36-7620
Catalog No.:BCC5915
CAS No.:232605-26-4
- VAL-083
Catalog No.:BCC2024
CAS No.:23261-20-3
- m-NH2-Tyr-OH.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3340
CAS No.:23279-22-3
Development, characterization and evaluation of doxorubicin nanostructured lipid carriers for prostate cancer.[Pubmed:28365942]
J BUON. 2017 Jan-Feb;22(1):102-111.
PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to develop an optimised formulation for a nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) loaded with Doxorubicin. METHODS: A Doxorubicin-loaded NLC was prepared using an emulsification solidification method. The Box-Behnken design response surface methodology was used to optimise formulations of the Doxorubicin-loaded NLC. RESULTS: The drug entrapment efficiency, drug loading efficiency, particle size, and zeta potential of the Doxorubicin- loaded NLC were 74.18%, 13.28%, 170 nm, and -14.8 mV, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy of the optimised NLC showed spherical particles. Furthermore, the Doxorubicin-loaded NLC was found to exhibit good therapeutic efficacy with remarkably improved oral bioavailability of Doxorubicin. CONCLUSION: The NLC system demonstrated potential for the targeted delivery of Doxorubicin in prostate cancer.
One-step formation of lipid-polyacrylic acid-calcium carbonate nanoparticles for co-delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin.[Pubmed:28368667]
J Drug Target. 2017 Sep;25(8):704-714.
A Doxorubicin (Dox) and curcumin (Cur) combination treatment regimen has been widely studied in pre-clinical research. However, the nanoparticles developed for this combination therapy require a consecutive drug loading process because of the different water-solubility of these drugs. This study provides a strategy for the "one-step" formation of nanoparticles encapsulating both Dox and Cur. We took advantage of polyacrylic acid (PAA) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to realise a high drug entrapment efficiency (EE) and pH-sensitive drug release using a simplified preparation method. Optimisation of lipid ratios and concentrations of CaCO3 was conducted. Under optimal conditions, the mean diameter of PEGylated lipid/PAA/CaCO3 nanoparticles with encapsulated Cur and Dox (LPCCD) was less than 100 nm. An obvious pH-sensitive release of both drugs was observed, with different Dox and Cur release rates. Successful co-delivery of Cur and Dox was achieved via LPCCD on HepG2 cells. LPCCD altered the bio-distribution of Dox and Cur in vivo and decreased Dox-induced cardiotoxicity. The current investigation has developed an efficient ternary system for co-delivery of Dox and Cur to tumours, using a "one-step" formation resulting in nanoparticles possessing remarkable pH-sensitive drug release behaviour, which may be valuable for further clinical studies and eventual clinical application.
Co-delivery of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor specific siRNA and doxorubicin using chitosan-based nanoparticles enhanced anticancer efficacy in A549 lung cancer cell line.[Pubmed:28362176]
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Mar;46(2):293-302.
Here, we investigated the effects of dual delivery of IGF-1R siRNA and Doxorubicin by chitosan nanoparticles on viability of A549 lung cancer cells line by utilization of MTT and qRT-PCR. Furthermore apoptosis and migration of treated cells were assessed by Annexin-PI and wound healing assays, respectively. The chitosan nanoparticles had about 176 nm size with zeta potential and polydispersive index about 11 mV and 0.3, respectively. The IGF-1R siRNA had synergistic effect on DOX-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in tumour cells. In addition, siRNA/DOX-loaded chitosan nanoparticles could significantly decrease migration and expressions of mmp9, VEGF and STAT3 in A549 cells.
Alternating Rabacfosadine/Doxorubicin: Efficacy and Tolerability in Naive Canine Multicentric Lymphoma.[Pubmed:28370378]
J Vet Intern Med. 2017 May;31(3):872-878.
BACKGROUND: Standard of care treatment for multicentric lymphoma in dogs remains Doxorubicin (DOX)-based combination chemotherapy, but owners may hesitate to commit the time and financial resources to complete such a protocol, typically requiring 12-16 visits. Rabacfosadine (RAB), a double prodrug of the nucleotide analog 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) guanine, has substantial single-agent activity in dogs with lymphoma, and a different mechanism of action than DOX. HYPOTHESIS/OBJECTIVES: Our objective was to evaluate the efficacy and adverse effect (AE) profile of alternating doses of RAB and DOX in dogs with naive multicentric lymphoma. ANIMALS: Fifty-four dogs with previously untreated lymphoma. METHODS: Open-label, multicenter prospective clinical trial. Dogs received alternating RAB (1.0 mg/kg IV weeks 0, 6, 12) and DOX (30 mg/m(2) IV weeks 3, 9, 15). Dogs that achieved complete response (CR) were followed by monthly evaluations. Complete clinicopathological evaluation and assessment of remission and AEs were performed every 21 days. RESULTS: The overall response rate was 84% (68%; CR; 16%; partial response [PR)]. The overall median progression-free interval (PFI) was 194 days (216 for CR and 63 for PR). Most AEs were mild and self-limiting: gastrointestinal and hematologic AEs were most common. Thirteen dogs experienced dermatologic AEs, and 2 dogs developed grade 5 pulmonary fibrosis. CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL IMPORTANCE: Alternating RAB/DOX generally was well tolerated and resulted in PFIs comparable to standard DOX-based multi-agent protocols, with fewer treatment visits. Most adverse events were mild or moderate and self-limiting. Further studies are warranted to explore long-term outcome and other RAB chemotherapy combinations.


