Guanabenz AcetateCAS# 23256-50-0 |
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- Cadherin Peptide, avian
Catalog No.:BCC1018
CAS No.:127650-08-2
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996)
Catalog No.:BCC1014
CAS No.:96249-43-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

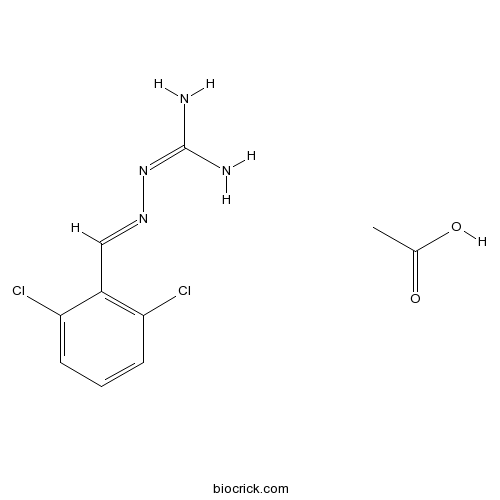
| Cas No. | 23256-50-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5702062 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H12Cl2N4O2 | M.Wt | 291.13 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 51 mg/mL (175.18 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2,6-Dichlorobenzylidene)amino]gua | ||
| SMILES | CC(O)=O.NC(N)=NN=Cc1c(Cl)cccc1Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MCSPBPXATWBACD-GAYQJXMFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H8Cl2N4.C2H4O2/c9-6-2-1-3-7(10)5(6)4-13-14-8(11)12;1-2(3)4/h1-4H,(H4,11,12,14);1H3,(H,3,4)/b13-4+; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | α2-adrenergic agonist and IGRS (imidazoline I2 binding site) selective ligand. |

Guanabenz Acetate Dilution Calculator

Guanabenz Acetate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4349 mL | 17.1745 mL | 34.3489 mL | 68.6978 mL | 85.8723 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.687 mL | 3.4349 mL | 6.8698 mL | 13.7396 mL | 17.1745 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3435 mL | 1.7174 mL | 3.4349 mL | 6.8698 mL | 8.5872 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0687 mL | 0.3435 mL | 0.687 mL | 1.374 mL | 1.7174 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0343 mL | 0.1717 mL | 0.3435 mL | 0.687 mL | 0.8587 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Guanabenz Acetate is an selective agonist of α2a-adrenergic receptor, α2b-adrenergic receptor and α2c-adrenergic receptor with pEC50 of 8.25, 7.01 and ~5, respectively.
- Dimaprit dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6672
CAS No.:23256-33-9
- Riddelline
Catalog No.:BCN2133
CAS No.:23246-96-0
- 5,7-Diacetoxy-8-methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5083
CAS No.:23246-80-2
- Ritodrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4337
CAS No.:23239-51-2
- TR-14035
Catalog No.:BCC4266
CAS No.:232271-19-1
- 23-Hydroxymangiferonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4668
CAS No.:232266-08-9
- Methoxydienone
Catalog No.:BCC9030
CAS No.:2322-77-2
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- Ifenprodil Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4589
CAS No.:23210-58-4
- Ifenprodil hemitartrate
Catalog No.:BCC6688
CAS No.:23210-56-2
- Matairesinoside
Catalog No.:BCN7583
CAS No.:23202-85-9
- (1R,2S)-2-Amino-1,2-diphenylethanol
Catalog No.:BCC8382
CAS No.:23190-16-1
- 4'-O-Methylvitexin
Catalog No.:BCN2642
CAS No.:2326-34-3
- Bay 36-7620
Catalog No.:BCC5915
CAS No.:232605-26-4
- VAL-083
Catalog No.:BCC2024
CAS No.:23261-20-3
- m-NH2-Tyr-OH.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3340
CAS No.:23279-22-3
- Probucol
Catalog No.:BCC4833
CAS No.:23288-49-5
- Delta 7-avenasterol
Catalog No.:BCN3212
CAS No.:23290-26-8
- Emodin-8-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6329
CAS No.:23313-21-5
- Cephalexin monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4096
CAS No.:23325-78-2
- Nefopam HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4681
CAS No.:23327-57-3
- MK 0343
Catalog No.:BCC6170
CAS No.:233275-76-8
- Glycoborinine
Catalog No.:BCN7462
CAS No.:233279-39-5
- L-Ser(Bzl)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2579
CAS No.:23356-96-9
Sinoatrial and atrioventricular dysfunction associated with the use of guanabenz acetate.[Pubmed:3378199]
Can J Cardiol. 1988 Apr;4(3):146-8.
Guanabenz Acetate is an antihypertensive drug that is closely related to clonidine hydrochloride. Clonidine is well known to potentiate atrioventricular (AV) node conduction disturbances, but to date that effect has not been attributed to guanabenz. A case of electrocardiographic and electrophysiologic studies in a patient with both sinus and AV node conduction disturbances associated with the use of Guanabenz Acetate is reported. The sinus cycle length was increased by 50% after guanabenz and the sinus node recovery time was prolonged by 42%. AV block occurred proximal to the His bundle and His-ventricular prolongation of 42% also occurred. This drug should be used cautiously in patients with evidence of sinus or AV node dysfunction.
Effects of guanabenz acetate on the pacemaker activity of rabbit sinoatrial node cells.[Pubmed:2619423]
Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1989 Jul-Aug;300:209-17.
The effects of Guanabenz Acetate on the electrophysiological properties of isolated rabbit sinoatrial node were studied using conventional microelectrode and double-microelectrode voltage clamp methods and were compared with those of clonidine and guanethidine. In spontaneously beating sinoatrial node preparations, guanabenz decreased the heart rate, the maximum rate of rise (Vmax), the action potential amplitude and the rate of diastolic depolarization in a dose-dependent fashion, whereas the action potential duration at 50% repolarization was prolonged. In comparison with clonidine and guanethidine, the inhibitory potency of guanethidine on the heart rate is weaker than that of guanabenz and clonidine. On the current systems, the voltage clamp experiments showed that guanabenz reduced the slow inward current and the time-dependent potassium outward current. These observations indicate that guanabenz acts directly on cardiac tissues and its bradycardic action can be mainly explained by a reduction of delayed current systems.
Renal effects of infusion of rilmenidine and guanabenz in conscious dogs: contribution of peripheral and central nervous system alpha 2-adrenoceptors.[Pubmed:8564219]
Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Sep;116(1):1557-70.
1. We tested the renal effects of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists, rilmenidine and guanabenz and the antagonists, 2-methoxyidazoxan and idazoxan, in conscious dogs. Our aim was to test the hypothesis that putative imidazoline (I) receptors influence renal function. We reasoned that since rilmenidine and guanabenz are selective for I1- and I2-binding sites respectively, an influence of one of these receptive sites on renal function would be reflected in qualitative differences between the effects of these agents. Moreover, effects mediated by putative I-receptors should be relatively resistant to antagonism by the selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist, 2-methoxyidazoxan. Since the effects of these drugs on renal function could be mediated in the central nervous system or periphery, the dogs were studied under both normal and ganglion-blocked conditions. 2. In dogs with intact autonomic reflexes, 2-methoxyidazoxan (15 micrograms kg-1 plus 0.6 micrograms kg-1 min-1) produced effects consistent with a generalized increase in sympathetic drive, including increases in mean arterial pressure and plasma renin activity, and a reduction in sodium excretion. In ganglion-blocked dogs, 2-methoxyidazoxan reduced sodium excretion but had no discernible effect on systemic or renal haemodynamics. We conclude that an alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated mechanism in the central nervous system tonically inhibits sympathetic drive in the conscious dog. 3. In ganglion-blocked dogs idazoxan (3-300 micrograms kg-1) dose-dependently increased arterial pressure. This was not abolished by concomitant administration of 2-methoxyidazoxan (0.3-30 micrograms kg-1). The pressor effect of idazoxan is therefore probably mediated by an agonist action at alpha 1-adrenoceptors. 4. The effects of infusions of rilmenidine (0.1-1.0 mg kg-1) and guanabenz (10-100 micrograms kg-1) were indistinguishable. They comprised dose-dependent increases in mean arterial pressure, urine excretion, and glomerular filtration rate (the latter in ganglion blocked dogs only), and dose-dependent reductions in heart rate, renal blood flow and sodium excretion (only in dogs with intact autonomic reflexes). All of these effects were antagonized by 2-methoxyidazoxan. 5. We conclude that the renal effects of rilmenidine and guanabenz infusions in conscious dogs are predominantly, if not completely, attributable to activation of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Our results do not support the hypothesis that putative I-receptors contribute towards the renal effects of these agents.
Guanabenz. A review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension.[Pubmed:6352237]
Drugs. 1983 Sep;26(3):212-29.
Guanabenz is an orally active central alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Its antihypertensive action is thought to result from a decrease in sympathetic outflow from the brain to the peripheral circulatory system as a result of stimulation of central alpha 2-adrenoceptors. In mild to moderate hypertension it is as effective as methyldopa and clonidine in lowering blood pressure when used as the sole treatment. As with these drugs, guanabenz may be combined with a diuretic to increase its blood pressure-lowering effect. The overall incidence of side effects seen with guanabenz was at least as high as with methyldopa or clonidine, and side effects such as drowsiness or dry mouth have been bothersome enough to lead to discontinuation of guanabenz therapy in some patients. However, particularly troublesome effects such as sodium retention, depression or sexual dysfunction which may occur with methyldopa or clonidine have not been reported with guanabenz.


