Ifenprodil hemitartrateCAS# 23210-56-2 |
- NLG919
Catalog No.:BCC2325
CAS No.:1402836-58-1
- INCB024360 analogue
Catalog No.:BCC1647
CAS No.:914471-09-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23210-56-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3689 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H27NO2 | M.Wt | 325.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 15 mM in water with gentle warming | ||
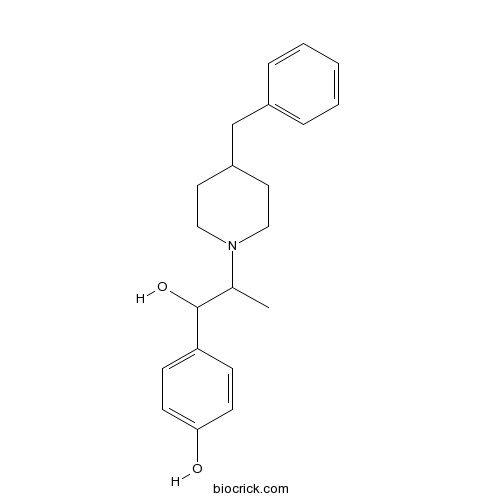
| Chemical Name | 4-[2-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-1-hydroxypropyl]phenol | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(C1=CC=C(C=C1)O)O)N2CCC(CC2)CC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UYNVMODNBIQBMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H27NO2/c1-16(21(24)19-7-9-20(23)10-8-19)22-13-11-18(12-14-22)15-17-5-3-2-4-6-17/h2-10,16,18,21,23-24H,11-15H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | NMDA receptor antagonist, acting at the polyamine site. Also an α-adrenergic vasodilator. σ2 ligand displaying about 3-fold selectivity over σ1 sites. |

Ifenprodil hemitartrate Dilution Calculator

Ifenprodil hemitartrate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0731 mL | 15.3657 mL | 30.7314 mL | 61.4628 mL | 76.8285 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6146 mL | 3.0731 mL | 6.1463 mL | 12.2926 mL | 15.3657 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3073 mL | 1.5366 mL | 3.0731 mL | 6.1463 mL | 7.6829 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0615 mL | 0.3073 mL | 0.6146 mL | 1.2293 mL | 1.5366 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0307 mL | 0.1537 mL | 0.3073 mL | 0.6146 mL | 0.7683 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Matairesinoside
Catalog No.:BCN7583
CAS No.:23202-85-9
- (1R,2S)-2-Amino-1,2-diphenylethanol
Catalog No.:BCC8382
CAS No.:23190-16-1
- Columbianetin acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2652
CAS No.:23180-65-6
- Paeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCN6301
CAS No.:23180-57-6
- Simiarenone
Catalog No.:BCN5082
CAS No.:2318-78-7
- Senkirkine
Catalog No.:BCN2136
CAS No.:2318-18-5
- Songoramine
Catalog No.:BCN6474
CAS No.:23179-78-4
- Nervosine
Catalog No.:BCN2012
CAS No.:23179-26-2
- Pyrolatin
Catalog No.:BCN8439
CAS No.:23176-70-7
- 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5040
CAS No.:2316-26-9
- H-Glu(OMe)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2932
CAS No.:23150-65-4
- Oxymetazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4333
CAS No.:2315-02-8
- Ifenprodil Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4589
CAS No.:23210-58-4
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- Methoxydienone
Catalog No.:BCC9030
CAS No.:2322-77-2
- 23-Hydroxymangiferonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4668
CAS No.:232266-08-9
- TR-14035
Catalog No.:BCC4266
CAS No.:232271-19-1
- Ritodrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4337
CAS No.:23239-51-2
- 5,7-Diacetoxy-8-methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5083
CAS No.:23246-80-2
- Riddelline
Catalog No.:BCN2133
CAS No.:23246-96-0
- Dimaprit dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6672
CAS No.:23256-33-9
- Guanabenz Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4327
CAS No.:23256-50-0
- 4'-O-Methylvitexin
Catalog No.:BCN2642
CAS No.:2326-34-3
- Bay 36-7620
Catalog No.:BCC5915
CAS No.:232605-26-4
NMDA receptors are important regulators of pancreatic cancer and are potential targets for treatment.[Pubmed:28761381]
Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jul 17;9:79-86.
Pancreatic cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, is a common disease with a poor prognosis. In this study, the importance of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors for the growth and survival of pancreatic cancer was investigated. Immunohistochemistry performed with antibodies against GluN1 and GluN2B revealed that all invasive adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors likely express these two NMDA receptor proteins. These proteins were found to be membrane components of pancreatic cancer cell lines, and both channel-blocker antagonist and GluN2B antagonist significantly reduced cell viability in vitro. Both types of antagonists caused an internalization of the receptors. Dizocilpine maleate (MK-801) and Ifenprodil hemitartrate both significantly inhibited the growth of pancreatic tumor xenografts in nu/nu mice. These findings predict that, as for other solid tumors investigated by us, pancreatic cancer could be successfully treated, alone or in combination, with NMDA receptor antagonists or other receptor-inhibiting blocking agents.
Neuroprotective effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists ifenprodil and SL-82,0715 on hippocampal cells in culture.[Pubmed:1346650]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):925-32.
The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists ifenprodil and SL-82,0715 were examined for neuroprotective efficacy against glutamate toxicity of hippocampal neurons in culture. Hippocampal cells were grown on 96-well culture plates for 2 to 3 weeks and then exposed for a 15-min period to glutamate or NMDA. Neurodegeneration was quantified 24 hr after the excitotoxin exposure, by measuring the activity of lactate dehydrogenase leaked into the culture medium by the damaged cells. Glutamate induced a concentration-dependent increase in lactate dehydrogenase that reached 3-fold the activity of control cultures. The NMDA antagonists MK-801 and AP-7 blocked this neurotoxicity when added either during or after the glutamate exposure. Ifenprodil and SL-82,0715 blocked the neurotoxicity only when added during the excitotoxin exposure. Ifenprodil was 3 times more potent than SL-82,0715 in blocking glutamate or NMDA-induced neurotoxicity. Glycine did not reverse the neuroprotective effects of these antagonists. The neuroprotective effect of ifenprodil or SL-82,0715 did not appear to result from actions at alpha-1 adrenergic or sigma receptor sites because the alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist prazosin and the sigma ligands haloperidol, 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-propylpiperidine) and 1,3-di-o-tolylguanidine) showed no neuroprotective activity. We conclude that ifenprodil and SL-82,0715 protect cultured hippocampal neurons from excitotoxic damage by antagonizing NMDA receptors.
Ifenprodil is a novel type of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist: interaction with polyamines.[Pubmed:2555674]
Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;36(5):758-65.
We have investigated the interactions of polyamines and the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist ifenprodil with the binding of [3H]MK801 to the NMDA receptor. Spermine and spermidine but not putrescine substantially increase [3H]MK801 binding to well washed rat brain membranes in the absence or presence of saturating concentrations of glutamate and glycine. Spermine also increased the association and dissociation of [3H]MK801 from its binding site, suggesting that polyamines activate the NMDA receptor in a similar manner to glycine. Ifenprodil inhibited the binding of [3H]MK801 in a biphasic fashion. The high affinity phase of binding (Ki of approximately 15 nM) accounted for 50-60% of total [3H]MK801 binding in the nominal absence of glutamate, glycine, and polyamines or in the presence of 100 microM glutamate. This fraction was reduced to 20% by the addition of 30 microM glycine and could be abolished by the addition of 50 microM spermine. However, ifenprodil apparently did not act by binding to the polyamine recognition site. The low affinity phase (Ki of 20-40 microM) was insensitive to the presence of positive modulators and may represent binding to the Zn2+ regulatory site. Ifenprodil decreased NMDA and glycine-induced Ca2+ influx into cultured rat brain neurons. The potency of ifenprodil suggests that spermine may activate NMDA receptors in vivo. These data indicate that ifenprodil may bind to the NMDA receptor in a state-dependent fashion and preferentially stabilize an inactivated form of the channel.
Ifenprodil and SL 82.0715 as cerebral anti-ischemic agents. I. Evidence for efficacy in models of focal cerebral ischemia.[Pubmed:2849668]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1211-21.
Recent studies have strongly implicated the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate in the cascade of pathological mechanisms that cause neuronal loss after certain types of brain ischemia. The neurotoxic effects of glutamate are mediated, at least in global ischemia, via NMDA receptors. In the present study we have examined the effects of compounds that possess NMDA receptor antagonist properties (ifenprodil, SL 82.0715 [(+/-)-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]- 1-piperidineethanol] and 1-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine) on the histological consequences of focal, as opposed to global, cerebral ischemia in both the rat and the cat. Ifenprodil (0.3-3 mg/kg i.v.) administered as a perfusion over 3 hr after occlusion of the feline middle cerebral artery reduced the volume of infarcted tissue (measured 4 days after occlusion) in a dose-related manner. At the highest dose a 42% reduction of infarcted volume was noted, essentially in cortical tissue. In an identical protocol, a derivative of ifenprodil, SL 82.0715, reduced the volume of infarction in a manner comparable to that described for ifenprodil. As SL 82.0715 possesses better p.o. bioavailability, this compound was also evaluated in the rat, again after middle cerebral artery occlusion. First administered 30 min after the induction of ischemia, SL 82.0715 (1 and 10 mg/kg p.o.) reduced infarction volume by 34 and 48%, respectively. The quantitative histology was performed 2 days after middle cerebral artery occlusion. The noncompetitive receptor antagonist, 1-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine, administered (1 mg/kg i.p.) before the induction of focal ischemia, similarly and significantly decreased the final volume of infarction. As both ifenprodil and SL 82.0715 are noncompetitive antagonists of the NMDA receptor, two conclusions may be drawn from the present investigation. First, NMDA antagonism by ifenprodil and its derivative is an effective approach for tissue sparing in animal models of stroke and brain infarction. Second, these pharmacological observations provide evidence for the involvement of excitatory amino-acid induced-neurotoxicity in the evolution and consequences of focal cerebral ischemia.


