NLG919Potent IDO pathway inhibitor CAS# 1402836-58-1 |
- INCB024360 analogue
Catalog No.:BCC1647
CAS No.:914471-09-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1402836-58-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 66558287 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H22N2O | M.Wt | 282.38 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NLG-919 analogue; GDC-0919 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
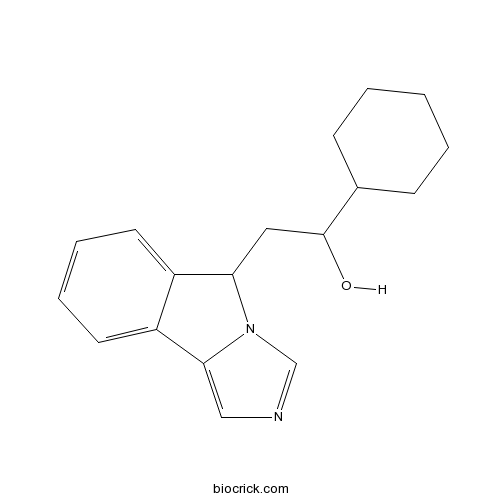
| Chemical Name | 1-cyclohexyl-2-(5H-imidazo[5,1-a]isoindol-5-yl)ethanol | ||
| SMILES | C1CCC(CC1)C(CC2C3=CC=CC=C3C4=CN=CN24)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YTRRAUACYORZLX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H22N2O/c21-18(13-6-2-1-3-7-13)10-16-14-8-4-5-9-15(14)17-11-19-12-20(16)17/h4-5,8-9,11-13,16,18,21H,1-3,6-7,10H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | NLG919 is a potent inhibitor of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-pathway with Ki value of 7 nM. | |||||
| Targets | IDO pathway | |||||
| IC50 | 7 nM (Ki) | |||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human and mouse IDO+ pDCs |
| Preparation method | Limited solubility. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 37oC |
| Applications | NLG919 potently blockes IDO-induced T cell suppression and restores robust T cell responses with an EC50=90 nM. NLG919 also abrogates IDO-induced suppression of antigen-specific T cells (OT-I or pmel-1) in vitro, (ED50=130 nM ) using mouse IDO+ pDCs from tumor-draining lymph nodes. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | Mice bearing large established B16F10 tumor |
| Dosage form | NLG919 was dosed either dissolved in the water at 3 mg/mL, plus a daily dose of 6 mg injected via IP, or administered subcutaneously at 1 mg/dose twice a day via injection plus 360 μg/day via an SC osmotic pump. |
| Application | NLG919 markedly enhances the antitumor responses of naive, resting pmel-1 cells to vaccination with cognate hgp100 peptide plus CpG-1826 in IFA. NLG919 plus pmel-1/vaccine produces a dramatic collapse of tumor size within 4 days of vaccination (~95% reduction in tumor volume compared to control animals receiving pmel-1/vaccine alone without NLG919). |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Mario R. Mautino, Firoz A et al. NLG919, a novel indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-pathway inhibitor drug candidate for cancer therapy. [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 104th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 2013 Apr 6-10; Washington, DC. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2013;73(8 Suppl):Abstract nr 491. | |

NLG919 Dilution Calculator

NLG919 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5413 mL | 17.7066 mL | 35.4133 mL | 70.8265 mL | 88.5332 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7083 mL | 3.5413 mL | 7.0827 mL | 14.1653 mL | 17.7066 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3541 mL | 1.7707 mL | 3.5413 mL | 7.0827 mL | 8.8533 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0708 mL | 0.3541 mL | 0.7083 mL | 1.4165 mL | 1.7707 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0354 mL | 0.1771 mL | 0.3541 mL | 0.7083 mL | 0.8853 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NLG919 is a novel and orally-bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) pathway, a crucial pathway involved in allergic inflammation that mediates immunosuppressive effects through metabolization of tryptophan (Trp) to kynurenine and affects differentiation and proliferation of T cells through inducing downstream signaling via GCN2, mTOR and AHR, with values of inhibition constant Ki and half maximal effective concentration EC50 of 7 nM and 75 nM respectively. Due to the established correlation of IDO pathway with various malignancies, the IDO pathway inhibition as well as its desirable pharmacological and biological properties potentiates NLG919 to be used for the treatment of immunosuppression associated with cancer.
Reference
Mario R. Mautino, Firoz A. Jaipuri, Jesse Waldo, Sanjeev Kumar, James Adams, Clarissa Van Allen, Agnieszka Marcinowicz-Flick, David Munn, Nicholas Vahanian, Charles J. Link. NLG919, a novel indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-pathway inhibitor drug candidate for cancer therapy. [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 104th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 2013 Apr 6-10; Washington, DC. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2013;73(8 Suppl):Abstract nr 491. doi:10.1158/1538-7445.AM2013-491
- N-Methyllindcarpine
Catalog No.:BCN6218
CAS No.:14028-97-8
- Amoxapine
Catalog No.:BCC4624
CAS No.:14028-44-5
- Boc-Lys(2-Cl-Z)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2581
CAS No.:14028-05-8
- TUG-770
Catalog No.:BCC2018
CAS No.:1402601-82-4
- Eupalinolide I
Catalog No.:BCN7367
CAS No.:1402067-84-8
- Psiguadial D
Catalog No.:BCN7086
CAS No.:1402066-95-8
- GSK2879552
Catalog No.:BCC6422
CAS No.:1401966-69-5
- Vc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC2032
CAS No.:1401963-17-4
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- (S)-(-)-5-Iodowillardiine
Catalog No.:BCC6597
CAS No.:140187-25-3
- (S)-(-)-5-Fluorowillardiine
Catalog No.:BCC6596
CAS No.:140187-23-1
- Monnieriside A
Catalog No.:BCN7892
CAS No.:1401807-73-5
- Chetomin
Catalog No.:BCC2432
CAS No.:1403-36-7
- Squalene-2,3-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6220
CAS No.:14031-37-9
- EPZ-6438
Catalog No.:BCC3634
CAS No.:1403254-99-8
- Macranthoidin A
Catalog No.:BCN2808
CAS No.:140360-29-8
- Heteroclitin D
Catalog No.:BCN8166
CAS No.:140369-76-2
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
- Nexturastat A
Catalog No.:BCC5345
CAS No.:1403783-31-2
- 6'-O-Cinnamoyl-8-epikingisidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7059
CAS No.:1403984-03-1
- Vancomycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4232
CAS No.:1404-93-9
- RSVA 405
Catalog No.:BCC8016
CAS No.:140405-36-3
- CCT244747
Catalog No.:BCC6423
CAS No.:1404095-34-6
- ON 146040
Catalog No.:BCC8058
CAS No.:1404231-34-0
Lymphoma Immunochemotherapy: Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin via a Dual Functional Nanocarrier.[Pubmed:28850241]
Mol Pharm. 2017 Nov 6;14(11):3888-3895.
Chemotherapy drug (paclitaxel, PTX) incorporated in a dual functional polymeric nanocarrier, PEG-Fmoc-NLG, has shown promise as an immunochemotherapy in a murine breast cancer model, 4T1.2. The formulation is composed of an amphiphilic polymer with a built-in immunotherapy drug NLG919 that exhibits the immunostimulatory ability through the inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1) in cancer cells. This work evaluates whether the PEG-derivatized NLG polymer can also be used for delivery of doxorubicin (Dox) in treatment of leukemia. The Dox-loaded micelles were self-assembled from PEG-Fmoc-NLG conjugate, which have a spherical shape with a uniform size of approximately 120 nm. In cultured murine lymphocytic leukemia cells (A20), Dox-loaded PEG-Fmoc-NLG micelles showed a cytotoxicity that was comparable to that of free Dox. For in vivo studies, significantly improved antitumor activity was observed for the Dox/PEG-Fmoc-NLG group compared to Doxil or the free Dox group in an A20 lymphoma mouse model. Flow cytometric analysis showed that treatment with Dox/PEG-Fmoc-NLG micelles led to significant increases in the numbers of both total CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cells and the functional CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cells with concomitant decreases in the numbers of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory T cells (Treg). Dox/PEG-Fmoc-NLG may represent a promising immunochemotherapy for lymphoma, which warrants more studies in the future.
Important Hydrogen Bond Networks in Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) Inhibitor Design Revealed by Crystal Structures of Imidazoleisoindole Derivatives with IDO1.[Pubmed:26642377]
J Med Chem. 2016 Jan 14;59(1):282-93.
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), promoting immune escape of tumors, is a therapeutic target for the cancer immunotherapy. A number of IDO1 inhibitors have been identified, but only limited structural biology studies of IDO1 inhibitors are available to provide insights on the binding mechanism of IDO1. In this study, we present the structure of IDO1 in complex with 24, a NLG919 analogue with potent activity. The complex structure revealed the imidazole nitrogen atom of 24 to coordinate with the heme iron, and the imidazoleisoindole core situated in pocket A with the 1-cyclohexylethanol moiety extended to pocket B to interact with the surrounding residues. Most interestingly, 24 formed an extensive hydrogen bond network with IDO1, which is a distinct feature of IDO1/24 complex structure and is not observed in the other IDO1 complex structures. Further structure-activity relationship, UV spectra, and structural biology studies of several analogues of 24 demonstrated that extensive hydrophobic interactions and the unique hydrogen bonding network contribute to the great potency of imidazoleisoindole derivatives. These results are expected to facilitate the structure-based drug design of new IDO inhibitors.
Programmable co-delivery of the immune checkpoint inhibitor NLG919 and chemotherapeutic doxorubicin via a redox-responsive immunostimulatory polymeric prodrug carrier.[Pubmed:28504251]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Jun;38(6):823-834.
To achieve synergistic therapeutic efficacy and prevent cancer relapse, chemotherapy and immunotherapy have been combined as a new modality for tumor treatment. In this work, we designed a redox-responsive immunostimulatory polymeric prodrug carrier, PSSN10, for programmable co-delivery of an immune checkpoint inhibitor NLG919 (NLG) and a chemotherapeutic doxorubicin (DOX). NLG-containing PSSN10 prodrug polymers were self-assembled into nano-sized micelles that served as a carrier to load DOX (DOX/PSSN10 micelles). DOX/PSSN10 micelles displayed spherical morphology with a size of approximately 170 nm. DOX was effectively loaded into PSSN10 micelles with a loading efficiency of 84.0%. In vitro DOX release studies showed that rapid drug release could be achieved in the highly redox environment after intracellular uptake by tumor cells. In 4T1.2 tumor-bearing mice, DOX/PSSN10 micelles exhibited greater accumulation of DOX and NLG in the tumor tissues compared with other organs. The PSSN10 carrier dose-dependently enhanced T-cell immune responses in the lymphocyte-Panc02 co-culture experiments, and significantly inhibited tumor growth in vivo. DOX/PSSN10 micelles showed potent cytotoxicity in vitro against 4T1.2 mouse breast cancer cells and PC-3 human prostate cancer cells comparable to that of DOX. In 4T1.2 tumor-bearing mice, DOX/PSSN10 mixed micelles (5 mg DOX/kg, iv) was more effective than DOXIL (a clinical formulation of liposomal DOX) or free DOX in inhibiting the tumor growth and prolonging the survival of the treated mice. In addition, a more immunoactive tumor microenvironment was observed in the mice treated with PSSN10 or DOX/PSSN10 micelles compared with the other treatment groups. In conclusion, systemic delivery of DOX via PSSN10 nanocarrier results in synergistic anti-tumor activity.
Combinatorial antitumor effects of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor NLG919 and paclitaxel in a murine B16-F10 melanoma model.[Pubmed:28604143]
Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2017 Sep;30(3):215-226.
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is involved in tumor immune escape and resistance to chemotherapy, and is clinically correlated with tumor progression. IDO inhibitors show marginal efficacy as single agents; therefore, combinations of these inhibitors with other therapies hold promise for cancer therapy. The aim of this study was to investigate the synergistic antitumor effects of IDO inhibitor NLG919 in combination with different regimens of paclitaxel in a murine B16-F10 melanoma model. NLG919 increased the cytotoxic activity of paclitaxel toward B16-F10 cells in the presence of pretreatment with interferon (IFN)-gamma in vitro. In B16-F10 tumor-bearing mice, NLG919 was uniformly distributed throughout tumors and decreased kynurenine levels and kynurenine/tryptophan ratios in tumors and plasma for 6-12 h. NLG919 suppressed tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner and exhibited maximum efficacy at 100 mg/kg. In combination with different regimens of paclitaxel, NLG919 displayed synergistic antitumor effects, and NLG919 did not increase the side effects of paclitaxel. Within the tumors, the percentage of CD3(+), CD8(+), and CD4(+) T cells and secretion of IFN-gamma and interleukin-2 were synergistically increased, whereas the percentage of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells was decreased. NLG919 can potentiate the antitumor efficacy of paclitaxel without increasing its side effects, suggesting that the combination of IDO inhibitor-based immunotherapy with chemotherapy could be a potential strategy for cancer treatment.
An immunostimulatory dual-functional nanocarrier that improves cancer immunochemotherapy.[Pubmed:27819653]
Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 7;7:13443.
Immunochemotherapy combines a chemotherapeutic agent with an immune-modulating agent and represents an attractive approach to improve cancer therapy. However, the success of immunochemotherapy is hampered by the lack of a strategy to effectively co-deliver the two therapeutics to the tumours. Here we report the development of a dual-functional, immunostimulatory nanomicellar carrier that is based on a prodrug conjugate of PEG with NLG919, an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor currently used for reversing tumour immune suppression. An Fmoc group, an effective drug-interactive motif, is also introduced into the carrier to improve the drug loading capacity and formulation stability. We show that PEG2k-Fmoc-NLG alone is effective in enhancing T-cell immune responses and exhibits significant antitumour activity in vivo. More importantly, systemic delivery of paclitaxel (PTX) using the PEG2k-Fmoc-NLG nanocarrier leads to a significantly improved antitumour response in both breast cancer and melanoma mouse models.


