Columbianetin acetateCAS# 23180-65-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23180-65-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 161409 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H16O5 | M.Wt | 288.30 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
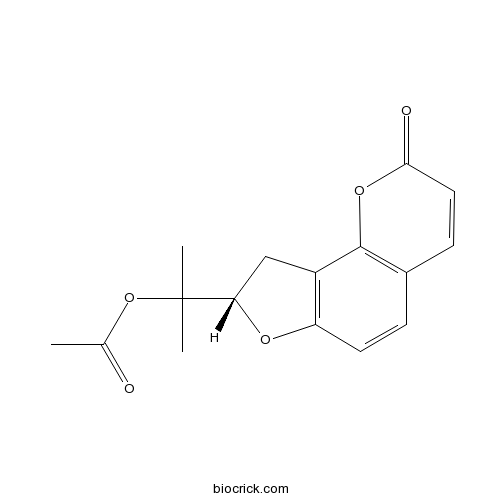
| Chemical Name | 2-[(8S)-2-oxo-8,9-dihydrofuro[2,3-h]chromen-8-yl]propan-2-yl acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C1CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2OC(=O)C=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IQTTZQQJJBEAIM-ZDUSSCGKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H16O5/c1-9(17)21-16(2,3)13-8-11-12(19-13)6-4-10-5-7-14(18)20-15(10)11/h4-7,13H,8H2,1-3H3/t13-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Columbianetin may be helpful in regulating mast cell-mediated allergic inflammatory responses, the absorption of columbianetin acetate is a passive diffusion process without pH-dependent. |
| Targets | Immunology & Inflammation related |
| In vitro | Absorption and transport of 6 coumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata in human Caco-2 cell monolayer model[Pubmed: 18405608]Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Apr;6(4):392-8.
To study the absorption and transepithelial transport of six coumarins (umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, Columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B, isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata) in the human Caco-2 cell monolayer model.
|
| In vivo | Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities from roots of Angelica pubescens.[Pubmed: 7700984]Planta Med. 1995 Feb;61(1):2-8.
|

Columbianetin acetate Dilution Calculator

Columbianetin acetate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4686 mL | 17.343 mL | 34.6861 mL | 69.3722 mL | 86.7152 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6937 mL | 3.4686 mL | 6.9372 mL | 13.8744 mL | 17.343 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3469 mL | 1.7343 mL | 3.4686 mL | 6.9372 mL | 8.6715 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0694 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.6937 mL | 1.3874 mL | 1.7343 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0347 mL | 0.1734 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.6937 mL | 0.8672 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Paeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCN6301
CAS No.:23180-57-6
- Simiarenone
Catalog No.:BCN5082
CAS No.:2318-78-7
- Senkirkine
Catalog No.:BCN2136
CAS No.:2318-18-5
- Songoramine
Catalog No.:BCN6474
CAS No.:23179-78-4
- Nervosine
Catalog No.:BCN2012
CAS No.:23179-26-2
- Pyrolatin
Catalog No.:BCN8439
CAS No.:23176-70-7
- 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5040
CAS No.:2316-26-9
- H-Glu(OMe)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2932
CAS No.:23150-65-4
- Oxymetazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4333
CAS No.:2315-02-8
- Pentoxyverine Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC4697
CAS No.:23142-01-0
- Vincosamide
Catalog No.:BCN5081
CAS No.:23141-27-7
- Strictosamide
Catalog No.:BCN5080
CAS No.:23141-25-5
- (1R,2S)-2-Amino-1,2-diphenylethanol
Catalog No.:BCC8382
CAS No.:23190-16-1
- Matairesinoside
Catalog No.:BCN7583
CAS No.:23202-85-9
- Ifenprodil hemitartrate
Catalog No.:BCC6688
CAS No.:23210-56-2
- Ifenprodil Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4589
CAS No.:23210-58-4
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- Methoxydienone
Catalog No.:BCC9030
CAS No.:2322-77-2
- 23-Hydroxymangiferonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4668
CAS No.:232266-08-9
- TR-14035
Catalog No.:BCC4266
CAS No.:232271-19-1
- Ritodrine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4337
CAS No.:23239-51-2
- 5,7-Diacetoxy-8-methoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5083
CAS No.:23246-80-2
- Riddelline
Catalog No.:BCN2133
CAS No.:23246-96-0
- Dimaprit dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6672
CAS No.:23256-33-9
[Absorption and transport of 6 coumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata in human Caco-2 cell monolayer model].[Pubmed:18405608]
Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Apr;6(4):392-8.
OBJECTIVE: To study the absorption and transepithelial transport of six coumarins (umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, Columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B, isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata) in the human Caco-2 cell monolayer model. METHODS: The in vitro cultured human colon carcinoma cell line, Caco-2 cell monolayer model, was applied to study the absorption and transport of the six coumarins from apical (AP) to basolateral (BL) side and from BL to AP side. The six coumarins were measured by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with ultraviolet absorption detector. Transport parameters and apparent permeability coefficients (P(app)) were calculated and compared with those of propranolol as a control substance of high permeability and atenolol as a control substance of poor permeability. The transport mechanism of angelol-B was assayed by using iodoacetamide as a reference standard to inhibit ATP-dependent transport and MK571 as a well-known inhibitor of MRP2. RESULTS: The absorption and transport of six coumarins were passive diffusion as the dominating process. The P(app) values of umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, Columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B from AP to BL side were (2.679+/-0.263) x 10(-5), (1.306+/-0.324) x 10(-5), (0.595+/-0.086) x 10(-6), (2.930+/-0.410) x 10(-6), (1.532+/-0.444) x 10(-5) and (1.413+/-0.243) x 10(-5) cm/s, and from BL to AP side were (3.381+/-0.410) x 10(-5), (0.898+/-0.134) x 10(-5), (0.510+/-0.183) x 10(-6), (0.222+/-0.025) x 10(-6), (1.203+/-0.280) x 10(-5) and (0.754+/-0.092) x 10(-5) cm/s, respectively. In this assay, the P(app) value of propranolol was 2.18 x 10(-5) cm/s and the P(app) value of atenolol was 2.77 x 10(-7) cm/s. Among the 6 coumarins, the P(app) values of umbelliferone, osthole, angelol-A and angelol-B from AP to BL side were identical with that of propranolol, and columbianadin and Columbianetin acetate lied between propranolol and atenolol. When replaced the HBSS with EBSS, and iodoacetamide or MK-591 were used in the experiment, the P(app) of angelol-B had no statistical difference as compared with the control group. In the mean total recoveries, umbelliferone was (83.31+/-3.52)%, angelol-A was (77.39+/-7.38)%, osthole, columbianadin and angelol-B were between 50% to 65%, and Columbianetin acetate was lower than 10%. The accumulation rates of osthole and columbianadin in the Caco-2 cells were (36.15+/-5.87)% and (53.90+/-4.39)%, respectively. CONCLUSION: The absorption and transport of umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, Columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B are passive diffusion as the dominating process in Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Umbelliferone, osthole, angelol-A and angelol-B are estimated to be highly absorbed compounds, and columbianadin and Columbianetin acetate are estimated to be moderately absorbed compounds. In the Caco-2 cells, osthol and columbianadin appear to accumulate, and Columbianetin acetate may be metabolized. The absorption and transport of angelol-B are not influenced by the change of pH and the presence of iodoacetamide or MK571.
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities from roots of Angelica pubescens.[Pubmed:7700984]
Planta Med. 1995 Feb;61(1):2-8.
In the present study, we extracted Angelica pubescens (AP) with various solvents in order to find the bioactive constituents that demonstrated analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The results were obtained as follows: (1) Methanol-, chloroform-, and ethyl acetate-extracts effectively reduced the pain that was induced by 1% acetic acid and a hot plate. (2) Methanol-, chloroform-, and ethyl acetate-extracts reduced the edema that was induced by 3% formalin or 1.5% carrageenan. (3) Sixteen compounds have been isolated and identified from the roots of AP. Among these compounds, columbianadin, Columbianetin acetate, bergapten, umbelliferone, and caffeic acid significantly demonstrated anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities at 10 mg/kg. However, only osthole and xanthotoxin revealed anti-inflammatory activity. Isoimperatorin only demonstrated an analgesic effect. These results revealed that the anti-inflammatory and analgesic constituents from roots of AP were related to peripheral inhibition of inflammatory substances and to the influence on the central nervous system.


