BMS-509744Itk inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 439575-02-7 |
- ITK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1662
CAS No.:439574-61-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 439575-02-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11467730 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C32H41N5O4S2 | M.Wt | 623.83 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 21.9 mg/mL (35.11 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
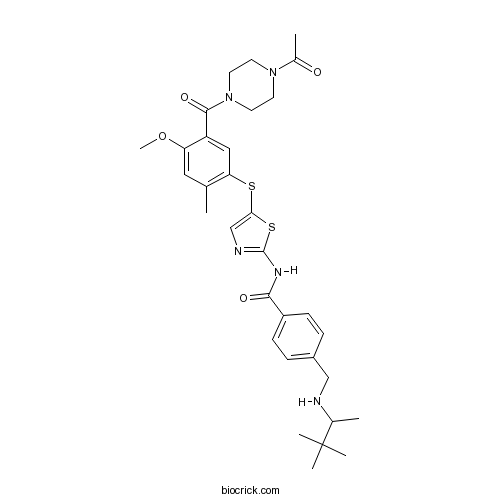
| Chemical Name | N-[5-[5-(4-acetylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-methoxy-2-methylphenyl]sulfanyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-4-[(3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ylamino)methyl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=C(C(=C1)OC)C(=O)N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C)SC3=CN=C(S3)NC(=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)CNC(C)C(C)(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZHXNIYGJAOPMSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H41N5O4S2/c1-20-16-26(41-7)25(30(40)37-14-12-36(13-15-37)22(3)38)17-27(20)42-28-19-34-31(43-28)35-29(39)24-10-8-23(9-11-24)18-33-21(2)32(4,5)6/h8-11,16-17,19,21,33H,12-15,18H2,1-7H3,(H,34,35,39) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective interleukin-2 inducible T cell kinase (ITK) inhibitor (IC50 = 19 nM). Displays 200-fold selectivity over Tec family kinases and 55-fold selectivity over other kinases tested. Reduces HIV infection of primary CD4+ T cells and attenuates the establishment of HIV infection in vitro. Reduces T cell proliferation and IL-2 production in vitro. Reduces lung inflammation in a mouse model of ovalbumin-induced allergy/asthma. |

BMS-509744 Dilution Calculator

BMS-509744 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.603 mL | 8.015 mL | 16.03 mL | 32.06 mL | 40.075 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3206 mL | 1.603 mL | 3.206 mL | 6.412 mL | 8.015 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1603 mL | 0.8015 mL | 1.603 mL | 3.206 mL | 4.0075 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0321 mL | 0.1603 mL | 0.3206 mL | 0.6412 mL | 0.8015 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.016 mL | 0.0802 mL | 0.1603 mL | 0.3206 mL | 0.4008 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
BMS-509744 is a selective inhibitor of ITK with IC50 value of 15 nM [1].
ITK (IL-2-inducible T cell kinase) is an enzyme and plays an important role in T cell receptor signaling. It has been reported that ITK involves in the Th2-mediated inflammatory process and thus be regarded as a promising target for Th2-mediated inflammatory/immunosuppressive diseases treatment, such as asthma, rhinitis, allergies and atopic dermatitis [2].
BMS-509744 is a potent ITK inhibitor and is different from the reported ITK inhibitor RO5191614. When tested with human and murine cells, administration of BMS-509744 reduced TCR-induced functions by functioning on PLCgamma1 tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium mobilization, IL-2 secretion and T-cell proliferation [2]. In wild-typr HIV1 infected cells, BMS-509744 treatment blocked its infectivity and replication by inhibiting ITK, while has no effect on Nef-defective HIV1 infected cells [3].
In mouse model of ovalbuim-induced allergy/asthma, administration of BMS-509744 suppressed the production of IL-2 and significantly diminished lung inflammation by inhibiting ITK activity [2].
References:
[1].Kutach, A.K., et al., Crystal structures of IL-2-inducible T cell kinase complexed with inhibitors: insights into rational drug design and activity regulation. Chem Biol Drug Des, 2010. 76(2): p. 154-63.
[2].Lin, T.A., et al., Selective Itk inhibitors block T-cell activation and murine lung inflammation. Biochemistry, 2004. 43(34): p. 11056-62.
[3].Tarafdar, S., J.A. Poe, and T.E. Smithgall, The accessory factor Nef links HIV-1 to Tec/Btk kinases in an Src homology 3 domain-dependent manner. J Biol Chem, 2014. 289(22): p. 15718-28.
- ITK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1662
CAS No.:439574-61-5
- GW 627368
Catalog No.:BCC7961
CAS No.:439288-66-1
- Lasmiditan
Catalog No.:BCC4077
CAS No.:439239-90-4
- Bay 60-7550
Catalog No.:BCC1405
CAS No.:439083-90-6
- Afatinib
Catalog No.:BCC3656
CAS No.:439081-18-2
- O-2093
Catalog No.:BCC7070
CAS No.:439080-01-0
- Gentianine
Catalog No.:BCN5492
CAS No.:439-89-4
- 2-Amino-3-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8528
CAS No.:4389-45-1
- JIP-1 (153-163)
Catalog No.:BCC5777
CAS No.:438567-88-5
- 3(20)-Phytene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6589
CAS No.:438536-34-6
- PFK-015
Catalog No.:BCC5280
CAS No.:4382-63-2
- Perakine
Catalog No.:BCN5491
CAS No.:4382-56-3
- NPY 5RA972
Catalog No.:BCC7747
CAS No.:439861-56-0
- Gnetifolin M
Catalog No.:BCN3394
CAS No.:439900-84-2
- Isoscabertopin
Catalog No.:BCN4634
CAS No.:439923-16-7
- Trifluoperazine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4384
CAS No.:440-17-5
- K 579
Catalog No.:BCC2364
CAS No.:440100-64-1
- WAY 200070
Catalog No.:BCC7669
CAS No.:440122-66-7
- 3-Phenyl-2-propen-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN5493
CAS No.:4407-36-7
- Benzoin oxime
Catalog No.:BCC8858
CAS No.:441-38-3
- Eribulin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC5173
CAS No.:441045-17-6
- 2-(Cyanomethyl)benzimidazole
Catalog No.:BCC8483
CAS No.:4414-88-4
- 6-Acetylacteoside
Catalog No.:BCC8109
CAS No.:441769-43-3
- Macitentan
Catalog No.:BCC1142
CAS No.:441798-33-0
ITK inhibition induced in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity through downregulating TCR signaling pathway in malignant T cell lymphoma.[Pubmed:30814910]
Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Feb 14;19:32.
Background: Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is a distinct subtype of peripheral T cell lymphoma and associated with poor outcomes. The activation status of T cell receptor (TCR) signaling has recently become a focus of attention in terms of the therapeutic targets. However, the molecular pathogenesis mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets are largely unknown. Methods: Antibodies specific to phosphorylated ZAP70, ITK and PLCgamma1 were used to identify the activation status of intracellular proteins involved in TCR signaling in AITL patients. Malignant T cell lymphoma cells were transduced with a lentiviral construct containing ITK shRNA for cellular and functional assays. The antitumor effects of the selective ITK inhibitor BMS-509744 were determined in vitro and in vivo. Results: Immunohistochemistry staining showed that more than half of the AITL patients (n = 38) exhibited continuously activated intracellular TCR signaling pathway. Patients positive for phosphorylated ITK showed a lower rate of complete response (20% vs. 75%, P = 0.004) and a shorter progression-free survival (5.17 months vs. 25.1 months, P = 0.022) than patients negative for phosphorylated ITK. Genetic and pharmacological cellular ITK inhibition significantly compromised the proliferation, invasion and migration of malignant T cells. The selective ITK inhibitor BMS-509744 also induced the pro-apoptotic effects and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in vitro and in vivo. Finally, inhibition of ITK synergistically enhanced the antitumor effect of vincristine and doxorubicin on malignant T cell lymphoma cell lines. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that ITK may be a novel candidate therapeutic target for the treatment of patients with ITK-expressing malignant T-cell lymphomas.
The accessory factor Nef links HIV-1 to Tec/Btk kinases in an Src homology 3 domain-dependent manner.[Pubmed:24722985]
J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15718-28.
The HIV-1 Nef virulence factor interacts with multiple host cell-signaling proteins. Nef binds to the Src homology 3 domains of Src family kinases, resulting in kinase activation important for viral infectivity, replication, and MHC-I down-regulation. Itk and other Tec family kinases are also present in HIV target cells, and Itk has been linked to HIV-1 infectivity and replication. However, the molecular mechanism linking Itk to HIV-1 is unknown. In this study, we explored the interaction of Nef with Tec family kinases using a cell-based bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay. In this approach, interaction of Nef with a partner kinase juxtaposes nonfluorescent YFP fragments fused to the C terminus of each protein, resulting in YFP complementation and a bright fluorescent signal. Using bimolecular fluorescence complementation, we observed that Nef interacts with the Tec family members Bmx, Btk, and Itk but not Tec or Txk. Interaction with Nef occurs through the kinase Src homology 3 domains and localizes to the plasma membrane. Allelic variants of Nef from all major HIV-1 subtypes interacted strongly with Itk in this assay, demonstrating the highly conserved nature of this interaction. A selective small molecule inhibitor of Itk kinase activity (BMS-509744) potently blocked wild-type HIV-1 infectivity and replication, but not that of a Nef-defective mutant. Nef induced constitutive Itk activation in transfected cells that was sensitive to inhibitor treatment. Taken together, these results provide the first evidence that Nef interacts with cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases of the Tec family and suggest that Nef provides a mechanistic link between HIV-1 and Itk signaling in the viral life cycle.
Crystal structures of IL-2-inducible T cell kinase complexed with inhibitors: insights into rational drug design and activity regulation.[Pubmed:20545945]
Chem Biol Drug Des. 2010 Aug;76(2):154-63.
IL-2-inducible T cell kinase plays an essential role in T cell receptor signaling and is considered a drug target for the treatment of Th2-mediated inflammatory diseases. By applying high-throughput protein engineering and crystallization, we have determined the X-ray crystal structures of IL-2-inducible T cell kinase in complex with its selective inhibitor BMS-509744 and the broad-spectrum kinase inhibitors sunitinib and RO5191614. Sunitinib uniquely stabilizes IL-2-inducible T cell kinase in the helix C-in conformation by inducing side chain conformational changes in the ATP-binding site. This preference of sunitinib to bind to an active kinase conformation is reflective of its broad-spectrum kinase activity. BMS-509744 uniquely stabilizes the activation loop in a substrate-blocking inactive conformation, indicating that structural changes described for Src family kinases are also involved in the regulation of IL-2-inducible T cell kinase activity. The observed BMS-509744 binding mode allows rationalization of structure-activity relationships reported for this inhibitor class and facilitates further structure-based drug design. Sequence-based analysis of this binding mode provides guidance for the rational design of inhibitor selectivity.
Selective Itk inhibitors block T-cell activation and murine lung inflammation.[Pubmed:15323564]
Biochemistry. 2004 Aug 31;43(34):11056-62.
Nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases including Lck, ZAP-70, and Itk play essential roles in T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Gene knockout studies have revealed that mice lacking these individual kinases exhibit various degrees of immunodeficiency; however, highly selective small molecule inhibitors of these kinases as potential immunosuppressive agents have not been identified. Here we discovered two novel compounds, BMS-488516 and BMS-509744, that potently and selectively inhibit Itk kinase activity. The compounds reduce TCR-induced functions including PLCgamma1 tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium mobilization, IL-2 secretion, and T-cell proliferation in vitro in both human and mouse cells. The inhibitors suppress the production of IL-2 induced by anti-TCR antibody administered to mice. BMS-509744 also significantly diminishes lung inflammation in a mouse model of ovalbumin-induced allergy/asthma. Our findings represent the first description of selective inhibitors to probe human Itk function and its associated pathway, and support the hypothesis that Itk is a therapeutic target for immunosuppressive and inflammatory diseases.
Selective targeting of ITK blocks multiple steps of HIV replication.[Pubmed:18443296]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 May 6;105(18):6684-9.
Treatment for HIV has relied on the use of antiretroviral agents that can be subject to the development of resistant viruses. The study of inhibitors directed against cellular proteins required for HIV replication is therefore of growing interest. Inducible T cell kinase (ITK) is a Tec family tyrosine kinase that regulates T cell receptor (TCR)-induced activation of PLCgamma-1, Ca(2+) mobilization and transcription factor activation, and actin rearrangement downstream of both TCR and chemokine receptors. Because productive infection of T cells with HIV requires T cell activation, chemokine receptors and actin reorganization, we asked whether ITK affects HIV infection using ITK-specific siRNA, a kinase-inactive ITK mutant or an ITK inhibitor. We demonstrate that loss of ITK function resulted in marked reductions in intracellular p24 levels upon HIV infection. Loss of ITK function after establishment of HIV infection also decreased virus spread within the culture. Inhibition of ITK did not affect expression of the HIV coreceptors CD4 or CXCR4 but partially blocked HIV viral entry, an effect that correlated with decreased actin polarization to gp120. Additionally, ITK was required for efficient HIV transcription, and overexpression of ITK increased both viral transcription and virus-like particle formation. Our data suggest that inhibition of ITK blocks HIV infection by affecting multiple steps of HIV replication.
Discovery and SAR of 2-amino-5-(thioaryl)thiazoles as potent and selective Itk inhibitors.[Pubmed:16682193]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Jul 15;16(14):3706-12.
A series of structurally novel aminothiazole based small molecule inhibitors of Itk were prepared to elucidate their structure-activity relationships (SARs), selectivity, and cell activity in inhibiting IL-2 secretion in a Jurkat T-cell assay. Compound 3 is identified as a potent and selective Itk inhibitor which inhibits anti-TCR antibody induced IL-2 production in mice in vivo and was previously reported to reduce lung inflammation in a mouse model of ovalbumin induced allergy/asthma.


