AfatinibIrreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor CAS# 439081-18-2 |
- Mutant EGFR inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4119
CAS No.:1421373-62-7
- Compound 56
Catalog No.:BCC3615
CAS No.:171745-13-4
- Gefitinib hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1591
CAS No.:184475-55-6
- BIBX 1382
Catalog No.:BCC1418
CAS No.:196612-93-8
- Pelitinib (EKB-569)
Catalog No.:BCC1118
CAS No.:257933-82-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 439081-18-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10184653 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H25ClFN5O3 | M.Wt | 485.94 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Afatinib;850140-72-6;BIBW 2992 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 97 mg/mL (199.61 mM) in DMSO | ||
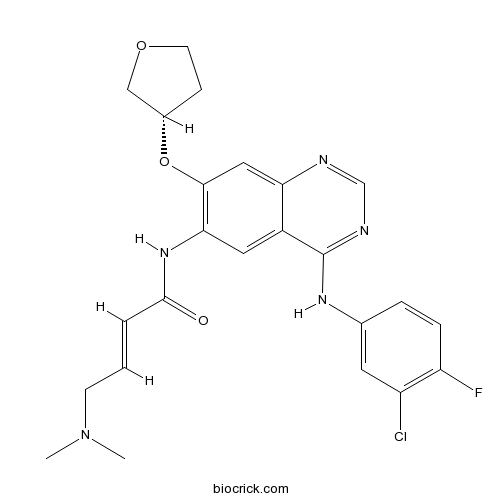
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-[4-(3-chloro-4-fluoroanilino)-7-[(3S)-oxolan-3-yl]oxyquinazolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)CC=CC(=O)NC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)F)Cl)OC4CCOC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ULXXDDBFHOBEHA-CWDCEQMOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H25ClFN5O3/c1-31(2)8-3-4-23(32)30-21-11-17-20(12-22(21)34-16-7-9-33-13-16)27-14-28-24(17)29-15-5-6-19(26)18(25)10-15/h3-6,10-12,14,16H,7-9,13H2,1-2H3,(H,30,32)(H,27,28,29)/b4-3+/t16-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Afatinib (BIBW2992) is an irreversible inhibitor of EGFR/HER2 for EGFR(wt), EGFR(L858R), EGFR(L858R/T790M) and HER2 with IC50 of 0.5 nM, 0.4 nM, 10 nM and 14 nM, respectively; 100-fold more active against Gefitinib-resistant L858R-T790M EGFR mutant. | ||||||
| Targets | EGFRwt | EGFRL858R | EGFR L858R/T790M | HER2 | |||
| IC50 | 0.5 nM | 0.4 nM | 10 nM | 14 nM | |||
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
| Cell lines | NCI-H1975 and BT474 cells |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | EC50: 92 nM for NCI-H1975 cells, 54 nM for BT474 cells; 96 hours |
| Applications | The effect of the inhibitor on cellular proliferation was tested in various assay formats including anchorage-dependent (BT474 cells grown on plastic; two-dimensional assays) and anchorage-independent (NCI-H1975 cells grown in soft agar; three-dimensional assays) assays. Afatinib dose-dependently inhibited cell proliferation and showed nanomolar activity. The EC50 values for NCI-H1975 and BT474 cells were 92 nM and 54 nM, respectively. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
| Animal models | Transgenic mice expressing the delE748-A752 version of mouse Egfr and the L858R version of human EGFR |
| Dosage form | Oral administration, 5 mg/kg, once daily, 5 days per week |
| Application | The transgenic mice received the oral administration of the drug until toxicity or death. All mice in the control group died, with a median survival time of 119 days. Afatinib treatment significantly enhanced the survival of transgenic mice with a median survival time of 456 days. No toxic death was observed in any mice. Four weeks after the initiation of treatment, body weight in the control group was significantly lower than in the afatinib group. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Solca F, Dahl G, Zoephel A, et al. Target binding properties and cellular activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992), an irreversible ErbB family blocker. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2012, 343(2): 342-350. [2] Ninomiya T, Takigawa N, Ichihara E, et al. Afatinib prolongs survival compared with gefitinib in an epidermal growth factor receptor-driven lung cancer model. Molecular cancer therapeutics, 2013, 12(5): 589-597. Kinase Assay
[1] Cell Assay
[2] Animal Administration
[2] References: | |

Afatinib Dilution Calculator

Afatinib Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0579 mL | 10.2893 mL | 20.5787 mL | 41.1573 mL | 51.4467 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4116 mL | 2.0579 mL | 4.1157 mL | 8.2315 mL | 10.2893 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2058 mL | 1.0289 mL | 2.0579 mL | 4.1157 mL | 5.1447 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0412 mL | 0.2058 mL | 0.4116 mL | 0.8231 mL | 1.0289 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0206 mL | 0.1029 mL | 0.2058 mL | 0.4116 mL | 0.5145 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Afatinib (BIBW2992), an irreversible inhibitor of the ErbB family of tyrosine kinases, downregulates ErbB signalling by binding to the kinase domains of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/ human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) with IC50 of 0.5 nM and 14nM, respectively.
The ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase family consists of four cell surface receptors: ErbB1/ EGFR/HER1, ErbB2/HER2, ErbB3/HER3, and ErbB4/HER4. It has been shown that EGFR and HER2 play important roles in the development and progression of certain aggressive types of cancers and inflammation-associated diseases.
Afatinib was shown to suppress EGF-induced phosphorylation of EGFR and cell proliferation in a variety of EGFR-overexpressing and HER2-expressing cell lines such as A431, NIH-3T3-HER2, NCI-N87 and BT-474 [1].
The component has also been used extensively in various animal models to study the role of EGFR/HER2. Oral administration of afatinib inhibited cancer cell growth and survival and suppress the tumor regression in xenograft and transgenic lung cancer models [2]. In addition, afatinib is identified as EGFR blocker which was approved for the treatment of patients with EGFR-mutated nonsmall cell lung cancer [3].
References:
1.Eskens FA, Mom CH, Planting AS, Gietema JA, Amelsberg A, Huisman H, et al. A phase I dose escalation study of BIBW 2992, an irreversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor 1 (EGFR) and 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase in a 2-week on, 2-week off schedule in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 2008,98:80-85.
2.Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, Kubo S, Takahashi M, Chirieac LR, et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene 2008,27:4702-4711.
3.Engle JA, Kolesar JM. Afatinib: A first-line treatment for selected patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2014,71:1933-1938.
Afatinib is an irreversible, dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitor, shows potent activity against wild-type and mutant forms of EGFR and HER2, with IC50 of 0.5 nM, 0.4 nM, 10 nM and 14 nM for EGFRwt, EGFRL858R, EGFRL858R/T790M and HER2, respectively.
In Vitro:In cell-free in vitro kinase assays, Afatinib (BIBW2992) dimaleate shows potent activity against wild-type and mutant forms of EGFR and HER2, similar to Gefitinib in potency for L858R EGFR, but about 100-fold more active against the Gefitinib-resistant L858R-T790M EGFR double mutant, with an IC50 of 10 nM. BIBW2992 is furthermore comparable to Lapatinib and Canertinib for in vitro potency against HER2, with an IC50 of 14 nM. The most sensitive kinase in this evaluation is lyn with an IC50 of 736 nM[1]. Afatinib is an irreversible inhibitor of these ErbB family receptors. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines are sensitive to Afatinib with IC50 concentrations at lower micro-molar range (at 48 hour incubation: HKESC-1=78 nM, HKESC-2=115 nM, KYSE510=3.182 μM, SLMT-1=4.625 μM and EC-1=1.489 μM; and at 72 hour incubation: HKESC-1=2 nM, HKESC-2=2 nM, KYSE510=1.090 μM, SLMT-1=1.161 μM and EC-1=109 nM) with a maximum growth inhibition over 95%. Afatinib can strongly induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in HKESC-2 and EC-1 in a dose- and time-dependent manner[2].
In Vivo:Afatinib (15 mg/kg) strongly inhibits the growth of HKESC-2 tumor once the treatment began. Average tumor sizes of vehicle and treatment at end point are 348±24 mm3 and 108±36 mm3 respectively, showing significantly difference between them. And apparently tumor size does not bounce back in a short period of time after the end of Afatinib administration. Without rapid change of body weight throughout the treatment shows that the toxicity of Afatinib is minimal and this drug is well tolerated[2].
References:
[1]. Li D, et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 2008 Aug 7;27(34):4702-11.
[2]. Wong CH, et al. Preclinical evaluation of afatinib (BIBW2992) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;5(12):3588-99.
[3]. Wang XK, et al. Afatinib circumvents multidrug resistance via dually inhibiting ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 2 in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 15;5(23):11971-85.
[4]. Yoshioka T, et al. Antitumor activity of pan-HER inhibitors in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018 Apr;109(4):1166-1176.
- O-2093
Catalog No.:BCC7070
CAS No.:439080-01-0
- Gentianine
Catalog No.:BCN5492
CAS No.:439-89-4
- 2-Amino-3-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8528
CAS No.:4389-45-1
- JIP-1 (153-163)
Catalog No.:BCC5777
CAS No.:438567-88-5
- 3(20)-Phytene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6589
CAS No.:438536-34-6
- PFK-015
Catalog No.:BCC5280
CAS No.:4382-63-2
- Perakine
Catalog No.:BCN5491
CAS No.:4382-56-3
- Robtin
Catalog No.:BCN5490
CAS No.:4382-34-7
- Dihydrorobinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5489
CAS No.:4382-33-6
- Quercetin 3,3'-dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7781
CAS No.:4382-17-6
- SMI-4a
Catalog No.:BCC2233
CAS No.:438190-29-5
- 4-(4-Aminophenyl)morpholin-3-one
Catalog No.:BCC8650
CAS No.:438056-69-0
- Bay 60-7550
Catalog No.:BCC1405
CAS No.:439083-90-6
- Lasmiditan
Catalog No.:BCC4077
CAS No.:439239-90-4
- GW 627368
Catalog No.:BCC7961
CAS No.:439288-66-1
- ITK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1662
CAS No.:439574-61-5
- BMS-509744
Catalog No.:BCC1424
CAS No.:439575-02-7
- NPY 5RA972
Catalog No.:BCC7747
CAS No.:439861-56-0
- Gnetifolin M
Catalog No.:BCN3394
CAS No.:439900-84-2
- Isoscabertopin
Catalog No.:BCN4634
CAS No.:439923-16-7
- Trifluoperazine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4384
CAS No.:440-17-5
- K 579
Catalog No.:BCC2364
CAS No.:440100-64-1
- WAY 200070
Catalog No.:BCC7669
CAS No.:440122-66-7
- 3-Phenyl-2-propen-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN5493
CAS No.:4407-36-7
Inhibition of IGF1R signaling abrogates resistance to afatinib (BIBW2992) in EGFR T790M mutant lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:26052929]
Mol Carcinog. 2016 May;55(5):991-1001.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation have benefited from treatment of reversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as gefitinib and erlotinib. Acquisition of a secondary mutation in EGFR T790M is the most common mechanism of resistance to first generation EGFR TKIs, resulting in therapeutic failure. Afatinib is a second generation of EGFR TKI that showed great efficacy against tumors bearing the EGFR T790M mutation, but it failed to show the improvement on overall survival of lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations possibly because of novel acquired resistance mechanisms. Currently, there are no therapeutic options available for lung cancer patients who develop acquired resistance to Afatinib. To identify novel resistance mechanism(s) to Afatinib, we developed Afatinib resistant cell lines from a parental human-derived NSCLC cell line, H1975, harboring both EGFR L858R and T790M mutations. We found that activation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) signaling pathway contributes to Afatinib resistance in NSCLC cells harboring the T790M mutation. IGF1R knockdown not only significantly sensitizes resistant cells to Afatinib, but also induces apoptosis in Afatinib resistance cells. In addition, combination treatment with Afatinib and linsitinib shows more than additive effects on tumor growth in in vivo H1975 xenograft. Therefore, these finding suggest that IGF1R inhibition or combination of EGFR-IGF1R inhibition strategies would be potential ways to prevent or potentiate the effects of current therapeutic options to lung cancer patients demonstrating resistance to either first or second generation EGFR TKIs.
Preclinical evaluation of afatinib (BIBW2992) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).[Pubmed:26885448]
Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;5(12):3588-99. eCollection 2015.
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the eighth most common cancer worldwide. Epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) are often overexpressed in esophageal cancers, thus anti-EGFR inhibitors have been evaluated in ESCC. Afatinib was an irreversible inhibitor of these ErbB family receptors. This study characterized the preclinical activity of Afatinib in five ESCC cell lines: HKESC-1, HKESC-2, KYSE510, SLMT-1 and EC-1. ESCC cell lines were sensitive to Afatinib with IC50 concentrations at lower micro-molar range (at 72 hour incubation: HKESC-1 = 0.002 muM, HKESC-2 = 0.002 muM, KYSE510 = 1.090 muM, SLMT-1 = 1.161 muM and EC-1 = 0.109 muM) with a maximum growth inhibition over 95%. Afatinib can strongly induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in HKESC-2 and EC-1 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The phosphorylation of ErbB family downstream effectors such as pAKT, pS6 and pMAPK were significantly inhibited in HKESC-2 and EC-1. Apoptosis was observed in both cell lines at 24 hours after exposure to Afatinib, as determined by the presence of cleaved PARP. Afatinib could effectively inhibit HKESC-2 tumor growth in mice without obvious toxicity. Afatinib alone has shown excellent growth inhibitory effect on ESCC in both in vitro and in vivo models, however, no synergistic effect was observed when it was combined with chemotherapeutic agents such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and cisplatin. In summary, Afatinib can inhibit cell proliferation effectively by arresting the cells in G0/G1 phase, as well as inducing apoptosis in ESCC. These findings warrant further studies of Afatinib as therapeutic agent in treating ESCC.
Growth response of human colorectal tumour cell lines to treatment with afatinib (BIBW2992), an irreversible erbB family blocker, and its association with expression of HER family members.[Pubmed:21617858]
Int J Oncol. 2011 Aug;39(2):483-91.
Despite the approval of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), cetuximab and panitumumab, for the treatment of colorectal cancer patients, there is currently no reliable predictive marker for response to therapy. In addition, the duration of response is often limited. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effect of Afatinib, an irreversible erbB family blocker, as a single agent or in combination with cytotoxic drugs (5-fluorouracil, irinotecan and oxaliplatin) or mAb ICR62 on the proliferation of a panel of human colorectal tumour cell lines and the association between the expression levels of the EGFR family members and response to treatment. Of the cells examined, EGFR-overexpressing DiFi cells were the most sensitive to treatment with both Afatinib (IC50=45 nM) and ICR62 (IC50=4.33 nM). Afatinib also inhibited the growth of other tumour cell lines with IC50 values which ranged from 0.33 microM (CCL-221) to 1.62 microM (HCT-116). A significant association was found between the co-expression of EGFR, human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)-2 and HER-3 and response to treatment with Afatinib (R=0.915, P=0.021). Treat-ment with Afatinib and cytotoxic drugs was accompanied by an increase in the proportion of these cells in the sub-G0/G1 and in the S and G2/M phase of the cell cycle, respectively. We conclude that Afatinib as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs shows activity in colorectal tumour cells and that determination of the co-expression of HER family members should be conducted in clinical trials using drugs targeting erbB signaling. This approach could lead to the identification of a specific subpopulation of cancer patients more likely to benefit from erbB-directed therapy.


