SMI-4aPotent Pim inhibitor CAS# 438190-29-5 |
- SGI-1776 free base
Catalog No.:BCC2232
CAS No.:1025065-69-3
- LKB1 (AAK1 dual inhibitor)
Catalog No.:BCC1705
CAS No.:1093222-27-5
- CX-6258
Catalog No.:BCC1504
CAS No.:1202916-90-2
- CX-6258 hydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1505
CAS No.:1353858-99-7
- PIM-1 Inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC2446
CAS No.:477845-12-8
- TCS PIM-1 1
Catalog No.:BCC2447
CAS No.:491871-58-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 438190-29-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1361334 | Appearance | Powder |
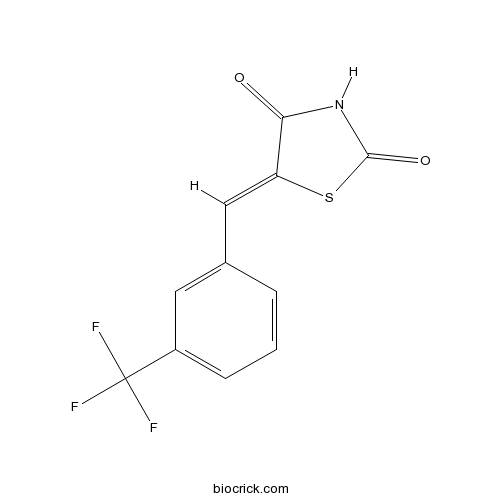
| Formula | C11H6F3NO2S | M.Wt | 273.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SMI-4a | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | (5Z)-5-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylidene]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC(=C1)C(F)(F)F)C=C2C(=O)NC(=O)S2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGJLOFCOEOHFKQ-YVMONPNESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H6F3NO2S/c12-11(13,14)7-3-1-2-6(4-7)5-8-9(16)15-10(17)18-8/h1-5H,(H,15,16,17)/b8-5- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective, ATP-competitive Pim kinase inhibitor (IC50 values are 24 and 100 nM for Pim-1 and Pim-2 respectively). Displays selectivity over a panel of ~50 other kinases tested. Exhibits cytotoxicity in PC3 prostate carcinoma cells in vitro (IC50 = 17 μM). |

SMI-4a Dilution Calculator

SMI-4a Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6599 mL | 18.2996 mL | 36.5992 mL | 73.1984 mL | 91.498 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.732 mL | 3.6599 mL | 7.3198 mL | 14.6397 mL | 18.2996 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.366 mL | 1.83 mL | 3.6599 mL | 7.3198 mL | 9.1498 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0732 mL | 0.366 mL | 0.732 mL | 1.464 mL | 1.83 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0366 mL | 0.183 mL | 0.366 mL | 0.732 mL | 0.915 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SMI-4a is a selective inhibitor of Pim1 with IC50 value of 17 nM [1] [2].
Pim-1 is an enzyme that is encoded by human PIM1 gene and it has been revealed that Pim-1 directly involved in the regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis and many studies have shown that Pim were over-expressed and promote cell growth and survival in a veraity of solid cancers and hematologic malignancies [3, 4].
SMI-4a is a selective Pim inhibitor and more active than the reported SMI-16a. When tested with human erythroleukemia cell line K562 cells, SIM-4a treatment modulated cell growth and activated AMPK which inhibited mTORC1 activity by inhibiting Pim activity [5]. In 25 leukemic cell lines, administration of SMI-4a induced cell-cycle arrest, elevated cell apoptosis, and pre–T-LBL/T-ALL being the highly sensitive cell line through mitochondrial pathway and inhibition of the mTORC1 pathway [2].
In Nu/nu nude mice model with 2 × 106 6812/2 cells subcutaneous xenograft, oral administration of SMI-4a from the third day for 5 of 7 days per week until day 21 on twice daily schedule significantly reduced tumor sizse [2].
References:
[1]. Beharry, Z., et al., Novel benzylidene-thiazolidine-2,4-diones inhibit Pim protein kinase activity and induce cell cycle arrest in leukemia and prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther, 2009. 8(6): p. 1473-83.
[2]. Lin, Y.W., et al., A small molecule inhibitor of Pim protein kinases blocks the growth of precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Blood, 2010. 115(4): p. 824-33.
[3]. Liu, Z., et al., Computational prediction and experimental validation of a novel synthesized pan-PIM inhibitor PI003 and its apoptosis-inducing mechanisms in cervical cancer. Oncotarget, 2015.
[4]. Warfel, N.A. and A.S. Kraft, PIM kinase (and Akt) biology and signaling in tumors. Pharmacol Ther, 2015.
[5]. Beharry, Z., et al., The Pim protein kinases regulate energy metabolism and cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(2): p. 528-33.
- 4-(4-Aminophenyl)morpholin-3-one
Catalog No.:BCC8650
CAS No.:438056-69-0
- H-Thr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3106
CAS No.:4378-13-6
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)
Catalog No.:BCC2094
CAS No.:437742-34-2
- Crategolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5487
CAS No.:4373-41-5
- Xanthinol nicotinate
Catalog No.:BCC9191
CAS No.:437-74-1
- Genkwanin
Catalog No.:BCN5488
CAS No.:437-64-9
- Gentisin
Catalog No.:BCN7518
CAS No.:437-50-3
- MRS 2365
Catalog No.:BCC5879
CAS No.:436847-09-5
- Tetrodotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1035
CAS No.:4368-28-9
- Kobe0065
Catalog No.:BCC5290
CAS No.:436133-68-5
- JKC 363
Catalog No.:BCC6022
CAS No.:436083-30-6
- Ajmaline
Catalog No.:BCN3867
CAS No.:4360-12-7
- Quercetin 3,3'-dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7781
CAS No.:4382-17-6
- Dihydrorobinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5489
CAS No.:4382-33-6
- Robtin
Catalog No.:BCN5490
CAS No.:4382-34-7
- Perakine
Catalog No.:BCN5491
CAS No.:4382-56-3
- PFK-015
Catalog No.:BCC5280
CAS No.:4382-63-2
- 3(20)-Phytene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6589
CAS No.:438536-34-6
- JIP-1 (153-163)
Catalog No.:BCC5777
CAS No.:438567-88-5
- 2-Amino-3-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8528
CAS No.:4389-45-1
- Gentianine
Catalog No.:BCN5492
CAS No.:439-89-4
- O-2093
Catalog No.:BCC7070
CAS No.:439080-01-0
- Afatinib
Catalog No.:BCC3656
CAS No.:439081-18-2
- Bay 60-7550
Catalog No.:BCC1405
CAS No.:439083-90-6
PIM-1 kinase inhibitor SMI-4a exerts antitumor effects in chronic myeloid leukemia cells by enhancing the activity of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta.[Pubmed:28849186]
Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4603-4612.
The development of targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has succeeded in altering the course of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). However, a number of patients have failed to respond or experienced disease relapse following TKI treatment. Proviral integration site for moloney murine leukemia virus1 (PIM1) is a serine/threonine kinase that participates in regulating apoptosis, cell cycle, signal transduction and transcriptional pathways, which are associated with tumor progression, and poor prognosis. SMI4a is a selective PIM1 kinase inhibitor that inhibits PIM1 kinase activity in vivo and in vitro. The present study aimed to explore the mechanism underlying the antitumor effect of SMI4a in K562 and imatinibresistant K562 (K562/G) cell lines. It was demonstrated that SMI4a inhibited the proliferation of K562 and K562/G cells using a WST8 assay. The Annexin Vpropidium iodide assay demonstrated that SMI4a induced apoptosis of K562 and K562/G cells in a dose, and timedependent manner. Furthermore, Hoechst 33342 staining was used to verify the apoptosis rate. The clone formation assay revealed that SMI4a significantly inhibited the colony formation capacity of K562 and K562/G cells. Western blot analysis demonstrated that SMI4a decreased phosphorylated (p)Ser9glycogen synthase kinase (GSK) 3beta/pGSK3beta and inhibited the translocation of betacatenin. In addition, the downstream gene expression of apoptosis regulator Bax and poly(ADPribose) polymerase1 was upregulated, and apoptosis regulator Bcl2 and Myc protooncogene protein expression levels were downregulated. Immunofluorescence results demonstrated changes in the expression level of betacatenin in the plasma and nucleus. The results of the present study suggest that SMI4a is an effective drug to use in combination with current chemotherapeutics for the treatment of imatinib-resistant CML.
Constitutive activation of Pim1 kinase is a therapeutic target for adult T-cell leukemia.[Pubmed:26813676]
Blood. 2016 May 19;127(20):2439-50.
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-associated adult T-cell leukemia and T-cell lymphoma (ATL) are aggressive diseases with poor prognoses, limited therapeutic options, and no curative treatment. In this study, we used a mouse model of ATL and restored expression of the microRNA, miR-124a, to identify in vivo downstream effectors responsible for its tumor-suppressive functions in ATL cells. Our results revealed that STAT3, a direct target of miR-124a, is constitutively activated in HTLV-I-transformed cells and ATL cells, and activating STAT3 mutations were detected in 25.5% of primary ATL patients. Interestingly, we found that the STAT3 downstream kinase effector, Pim1, is constitutively activated in ATL cells. The dependence of ATL cells to Pim1 activity was demonstrated using 2 Pim1 small inhibitors, SMI-4a and AZD1208. These studies indicated that HTLV-I-transformed and ATL cells, but not normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells, are highly sensitive to AZD1208, and the inhibition of Pim1 signaling triggers an apoptotic signal in leukemic cells. Finally, preclinical testing of AZD1208 in a mouse model of ATL resulted in significant prevention of tumor growth in vivo. In conclusion, our studies suggest that constitutive activation of the STAT3-Pim1 pathway represents a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of ATL.
Placental Pim-1 expression is increased in obesity and regulates cytokine- and toll-like receptor-mediated inflammation.[Pubmed:28487013]
Placenta. 2017 May;53:101-112.
INTRODUCTION: Obesity is a growing epidemic, and as a consequence the number of obese pregnancies has also increased. Pregnancy is characterised by maternal and placental inflammation which is intensified with maternal obesity. The proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemic virus (Pim)-1 protein is a serine/threonine kinase involved in a wide range of inflammatory diseases. In relation to obesity, however, its role has not been elucidated in human placenta. The aims were to determine the placental expression of Pim-1 with pre-existing maternal obesity and its role in regulating placental inflammation associated with obesity. METHODS: Human placenta was obtained at the time of term Caesarean section from lean and pre-existing obese pregnant women to determine the effect of maternal obesity on Pim-1 expression. To determine the effect of Pim-1 on the inflammatory response induced by bacterial endotoxin LPS and pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha or IL-1beta, the chemical inhibitor SMI-4a and siRNA were used. RESULTS: Pim-1 protein and mRNA expression was significantly increased in placenta of obese women. SMI-4a significantly suppressed the expression and release of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and chemokines GRO-alpha and MCP-1 when stimulated with LPS or TNF-alpha in placenta. Primary trophoblast cells transfected with Pim-1 siRNA had decreased expression and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, chemokines GRO-alpha and MCP-1, when stimulated with LPS, TNF-alpha or IL-1beta. DISCUSSION: The findings from this study implicate Pim-1 may contribute to placental inflammation in pregnancies complicated by maternal obesity. Thus, therapeutic targets for Pim-1 may improve fetal outcomes complicated by obese pregnancies.
Cytoplasmic Irradiation Induces Metabolic Shift in Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells via Activation of Pim-1 Kinase.[Pubmed:28170315]
Radiat Res. 2017 Apr;187(4):441-453.
The unique cellular and molecular consequences of cytoplasmic damage caused by ionizing radiation were studied using a precision microbeam irradiator. Our results indicated that targeted cytoplasmic irradiation induced metabolic shift from an oxidative to glycolytic phenotype in human small airway epithelial cells (SAE). At 24 h postirradiation, there was an increase in the mRNA expression level of key glycolytic enzymes as well as lactate secretion in SAE cells. Using RNA-sequencing analysis to compare genes that were responsive to cytoplasmic versus nuclear irradiation, we found a glycolysis related gene, Pim-1, was significantly upregulated only in cytoplasmic irradiated SAE cells. Inhibition of Pim-1 activity using the selective pharmaceutic inhibitor SMI-4a significantly reduced the level of lactate production and glucose uptake after cytoplasmic irradiation. In addition, Pim-1 also inhibited AMPK activity, which is a well-characterized negative regulator of glycolysis. Distinct from the glycolysis induced by cytoplasmic irradiation, targeted nuclear irradiation also induced a transient and minimal increase in glycolysis that correlated with increased expression of Hif-1alpha. In an effort to explore the underline mechanism, we found that inhibition of mitochondria fission using the cell-permeable inhibitor mdivi-1 suppressed the induction of Pim-1, thus confirming Pim-1 upregulation as a downstream effect of mitochondrial dysfunction. Our data show and, for the first time, that cytoplasmic irradiation mediate expression level of Pim-1, which lead to glycolytic shift in SAE cells. Additionally, since glycolysis is frequently linked to cancer cell metabolism, our findings further suggest a role of cytoplasmic damage in promoting neoplastic changes.
Inhibition of PIM1 kinase attenuates inflammation-induced pro-labour mediators in human foetal membranes in vitro.[Pubmed:28333279]
Mol Hum Reprod. 2017 Jun 1;23(6):428-440.
STUDY QUESTION: Does proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukaemic virus (PIM)1 kinase play a role in regulating the inflammatory processes of human labour and delivery? SUMMARY ANSWER: PIM1 kinase plays a critical role in foetal membranes in regulating pro-inflammatory and pro-labour mediators. WHAT IS KNOWN ALREADY: Infection and inflammation have strong causal links to preterm delivery by stimulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and collagen degrading enzymes, which can lead to rupture of membranes. PIM1 has been shown to have a role in immune regulation and inflammation in non-gestational tissues; however, its role has not been explored in the field of human labour. STUDY DESIGN, SIZE, DURATION: PIM1 expression was analysed in myometrium and/or foetal membranes obtained at term and preterm (n = 8-9 patients per group). Foetal membranes, freshly isolated amnion cells and primary myometrial cells were used to investigate the effect of PIM1 inhibition on pro-labour mediators (n = 5 patients per treatment group). PARTICIPANTS/MATERIALS, SETTING AND METHODS: Foetal membranes, from term and preterm, were obtained from non-labouring and labouring women, and from preterm pre-labour rupture of membranes (PPROM) (n = 9 per group). Amnion was collected from women with and without preterm chorioamnionitis (n = 8 per group). Expression of PIM1 kinase was determined by qRT-PCR and western blotting. To determine the effect of PIM1 kinase inhibition on the expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-labour mediators induced by bacterial products lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (10 mug/ml) and flagellin (1 mug/ml) and pro-inflammatory cytokine tumour necrosis factor (TNF) (10 ng/ml), chemical inhibitors SMI-4a (20 muM) and AZD1208 (50 muM) were used in foetal membrane explants and siRNA against PIM1 was used in primary amnion cells. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. MAIN RESULTS AND THE ROLE OF CHANCE: PIM1 expression was significantly increased in foetal membranes after spontaneous term labour compared to no labour at term and in amnion with preterm chorioamnionitis compared to preterm with no chorioamnionitis. There was no change in PIM1 expression with preterm labour or PPROM compared to preterm with no labour or PPROM. In human foetal membranes, PIM1 inhibitors SMI-4a and AZD1208 significantly decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL6) and chemokines CXCL8 and CCL2 mRNA and release, prostaglandin prostaglandin F2alpha (PGF2alpha) release, adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule 1 mRNA expression and release, and oxidative stress marker 8-isoprostane release after stimulation with either LPS or flagellin. Primary amnion cells transfected with PIM1 siRNA also showed decreased expression of IL6, CXCL8 and CCL2, PTGS2 mRNA and PGF2alpha release, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) expression, when stimulated with TNF. LARGE SCALE DATA: None. LIMITATIONS, REASONS FOR CAUTION: The conclusions were drawn from in vitro experiments using foetal membrane explants and primary cells isolated from amnion. Animal models are necessary to determine whether PIM1 kinase inhibitors can prevent spontaneous preterm birth in vivo. WIDER IMPLICATIONS OF THE FINDINGS: PIM1 kinase inhibitors may provide a novel therapeutic approach for preventing spontaneous preterm birth. STUDY FUNDING/COMPETING INTEREST(S): Associate Professor Martha Lappas is supported by a Career Development Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC; grant no. 1047025). Funding for this study was provided by the NHMRC (grant no. 1058786), Norman Beischer Medical Research Foundation and the Mercy Research Foundation. The authors have no conflict of interest.
Synthesis and evaluation of novel inhibitors of Pim-1 and Pim-2 protein kinases.[Pubmed:19072652]
J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 8;52(1):74-86.
The Pim protein kinases are frequently overexpressed in prostate cancer and certain forms of leukemia and lymphoma. 5-(3-Trifluoromethylbenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione (4a) was identified by screening to be a Pim-1 inhibitor and was found to attenuate the autophosphorylation of tagged Pim-1 in intact cells. Although 4a is a competitive inhibitor with respect to ATP, a screen of approximately 50 diverse protein kinases demonstrated that it has high selectivity for Pim kinases. Computational docking of 4a to Pim-1 provided a model for lead optimization, and a series of substituted thiazolidine-2,4-dione congeners was synthesized. The most potent new compounds exhibited IC(50)s of 13 nM for Pim-1 and 2.3 microM for Pim-2. Additional compounds in the series demonstrated selectivities of more than 2500-fold and 400-fold for Pim-1 or Pim-2, respectively, while other congeners were essentially equally potent toward the two isozymes. Overall, these compounds are new Pim kinase inhibitors that may provide leads to novel anticancer agents.


