Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)20S proteasome inhibitor CAS# 437742-34-2 |
- MLN9708
Catalog No.:BCC2091
CAS No.:1201902-80-8
- MG-115
Catalog No.:BCC1237
CAS No.:133407-86-0
- Clasto-Lactacystin β-lactone
Catalog No.:BCC1224
CAS No.:154226-60-5
- Bortezomib (PS-341)
Catalog No.:BCC1238
CAS No.:179324-69-7
- AM 114
Catalog No.:BCC3589
CAS No.:856849-35-9
- ONX-0914 (PR-957)
Catalog No.:BCC2095
CAS No.:960374-59-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 437742-34-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11347535 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H20ClNO4 | M.Wt | 313.78 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (318.69 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
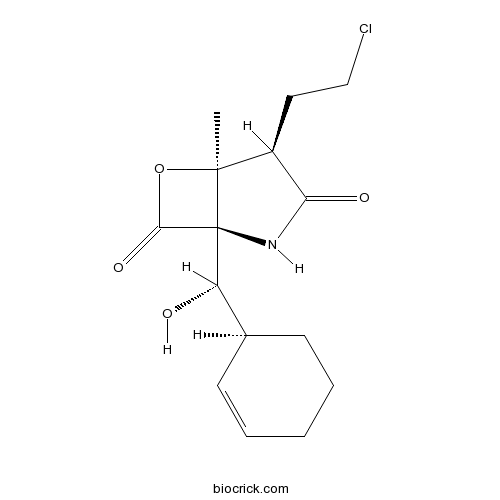
| Chemical Name | (1S,2R,5R)-2-(2-chloroethyl)-5-[(S)-[(1S)-cyclohex-2-en-1-yl]-hydroxymethyl]-1-methyl-7-oxa-4-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-3,6-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC12C(C(=O)NC1(C(=O)O2)C(C3CCCC=C3)O)CCCl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGWSFRIPKNWYAO-SHTIJGAHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H20ClNO4/c1-14-10(7-8-16)12(19)17-15(14,13(20)21-14)11(18)9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h3,5,9-11,18H,2,4,6-8H2,1H3,(H,17,19)/t9-,10+,11+,14+,15+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib) is a novel inhibitor of marine derived proteasome which inhibits CT-L, C-L, and T-L proteasome activities in human erythrocyte-derived 20S proteasomes with EC50 values of 3.5 nM, 430 nM, 28 nM, respectively. | |||||
| Targets | CT-L (EC50) | C-L (EC50) | T-L (EC50) | |||
| IC50 | 3.5 nM | 430 nM | 28 nM | |||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human MM-cell lines (MM.1S, INA-6, RPMI-8226, MM.1R,KMS12PE, and U266) |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 24 h; 2nM |
| Applications | Human MM-cell lines were pretreated with lenalidomide for 24 hours; NPI-0052 was then added for an additional 24 hours, followed by assessment for cell viability using MTT assays. A significant decrease in viability of all cell lines was observed in response to treatment with combined low doses of NPI-0052 and lenalidomide compared with either agent alone(P<0.05; n=3). These data demonstrate synergistic anti-MM activity of NPI-0052 plus lenalidomide. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | CB-17 SCID-male mice |
| Dosage form | 0.15 mg/kg; i.v. |
| Application | MM.1S-tumour bearing mice were injected with NPI-0052(0.15 mg/kg; i.v.) twice a week for 3 weeks, and tumour volume was measured. NPI-0052 treatment significantly decreased tumour growth relative to vehicle-treated control mice (P =0.005). NPI-0052 treatment was not associated with any toxicity, because no differences in body weight and overall appearance were noted. Importantly, the anti-MM activity of NPI-0052 was evident as early as day 5–7, when significant proteasome inhibition was observed in the tumours. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Chauhan D, Singh A V, Ciccarelli B, et al. Combination of novel proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 and lenalidomide trigger in vitro and in vivo synergistic cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma[J]. Blood, 2010, 115(4): 834-845. [2] Singh A V, Palladino M A, Lloyd G K, et al. Pharmacodynamic and efficacy studies of the novel proteasome inhibitor NPI‐0052 (marizomib) in a human plasmacytoma xenograft murine model[J]. British journal of haematology, 2010, 149(4): 550-559. | |

Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib) Dilution Calculator

Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1869 mL | 15.9347 mL | 31.8695 mL | 63.7389 mL | 79.6737 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6374 mL | 3.1869 mL | 6.3739 mL | 12.7478 mL | 15.9347 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3187 mL | 1.5935 mL | 3.1869 mL | 6.3739 mL | 7.9674 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0637 mL | 0.3187 mL | 0.6374 mL | 1.2748 mL | 1.5935 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0319 mL | 0.1593 mL | 0.3187 mL | 0.6374 mL | 0.7967 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Salinosporamide A is a potent inhibitor of 20S proteasome with IC50 value of 1.3 nM [1].
Salinosporamide A was isolated from the crude extract of a Salinospora strain CNB-392. It showed potent anti-tumor activity with an IC50 value of 11 ng/mL in HCT-116 cells. It also exerted a mean GI50 value of less than 10 nM in the NCI’s 60 cell line-panel. Among these cell lines, Salinosporamide A showed the greatest potent efficacies in NCI-H226, SF-539, SK-MEL-28 and MDA-MB-435 cells. Salinosporamide A inhibited the purified 20S proteasome with IC50 value of 1.3 nM. It was about 35-fold more potent than the first discovered specific proteasome inhibitor, omuralide [1].
References:
[1] Feling R H, Buchanan G O, Mincer T J, et al. Salinosporamide A: a highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus Salinospora. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2003, 42(3): 355-357.
- Crategolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5487
CAS No.:4373-41-5
- Xanthinol nicotinate
Catalog No.:BCC9191
CAS No.:437-74-1
- Genkwanin
Catalog No.:BCN5488
CAS No.:437-64-9
- Gentisin
Catalog No.:BCN7518
CAS No.:437-50-3
- MRS 2365
Catalog No.:BCC5879
CAS No.:436847-09-5
- Tetrodotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1035
CAS No.:4368-28-9
- Kobe0065
Catalog No.:BCC5290
CAS No.:436133-68-5
- JKC 363
Catalog No.:BCC6022
CAS No.:436083-30-6
- Ajmaline
Catalog No.:BCN3867
CAS No.:4360-12-7
- Fangchinoline
Catalog No.:BCN5956
CAS No.:436-77-1
- Diffractic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN8506
CAS No.:436-32-8
- (-)-Curine
Catalog No.:BCN2673
CAS No.:436-05-5
- H-Thr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3106
CAS No.:4378-13-6
- 4-(4-Aminophenyl)morpholin-3-one
Catalog No.:BCC8650
CAS No.:438056-69-0
- SMI-4a
Catalog No.:BCC2233
CAS No.:438190-29-5
- Quercetin 3,3'-dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7781
CAS No.:4382-17-6
- Dihydrorobinetin
Catalog No.:BCN5489
CAS No.:4382-33-6
- Robtin
Catalog No.:BCN5490
CAS No.:4382-34-7
- Perakine
Catalog No.:BCN5491
CAS No.:4382-56-3
- PFK-015
Catalog No.:BCC5280
CAS No.:4382-63-2
- 3(20)-Phytene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6589
CAS No.:438536-34-6
- JIP-1 (153-163)
Catalog No.:BCC5777
CAS No.:438567-88-5
- 2-Amino-3-methylbenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8528
CAS No.:4389-45-1
- Gentianine
Catalog No.:BCN5492
CAS No.:439-89-4
Coupled Biosynthesis of Volatiles and Salinosporamide A in Salinispora tropica.[Pubmed:27490971]
Chembiochem. 2016 Oct 17;17(20):1978-1985.
Terrestrial bacteria, especially actinomycetes, are known to be prolific producers of volatile compounds. We show here that bacteria from ocean sediments can also release complex bouquets of volatiles. The actinomycete Salinispora tropica produces cyclohexenyl compounds not previously known in nature, such as methyl cyclohex-2-ene-1-carboxylate (9), methyl 2-(cyclohex-2-en-1-yl)acetate (10), methyl (E/Z)-2-(cyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)acetate (11/12), and related alcohols 8 and 13. These compounds were identified by GC/MS and confirmed by synthesis. In addition, rare spiroacetals, aromatic compounds, short-chain acids and esters, alcohols, and various cyclic compounds were produced by the bacteria. The biosynthesis of the cyclohexenyl compounds is closely coupled to that of cyclohexenylalanine (4), a building block of salinosporamide A, a proteasome inhibitor produced by S. tropica. Analysis of S. tropica strains that harbor knockouts of the salinosporamide biosynthetic genes salX and salD, coupled with feeding experiments, revealed that 3-(cyclohex-2-en-1-yl)-2-oxopropanoic acid (60) and 3-(cyclohex-2-en-1-ylidene)-2-oxopropanoic acid (isomers 61 and 62) are important intermediates in the biosynthesis of salinosporamide A, 4, and 8-13.
Second Generation Proteasome Inhibitors in Multiple Myeloma.[Pubmed:27592543]
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(7):920-926.
Bortezomib was the first proteasome inhibitor (PI) discovered and demonstrated great efficacy in myeloma, both in vitro and in patients. However, still many patients ultimately relapse and there is the need for novel therapies. A second generation of PI have been discovered, potentially more effective ands some also orally administered. Carfilzomib is an irreversible proteasome inhibitor that showed great efficacy in clinical studies. Ixazomib is an oral compound that has been introduced recently in the therapeutic spectrum. Novel agents such as Marizomib seem promising in the fact that can also pass through the blood brain barrier and maybe effective also in CNS muyeloma. This review focus on all proteasome inhibitors available in clinics and the new ones coming soon.
The activity and safety of novel proteasome inhibitors strategies (single, doublet and triplet) for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.[Pubmed:28828905]
Acta Oncol. 2018 Feb;57(2):290-296.
PURPOSE: We sought to evaluate the activity and safety of these novel proteasome inhibitors (PIs) (carfilzomib, ixazomib, oprozomib and marizomib) containing regimens (single, doublet and triplet) for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (R/RMM). METHODS: We searched published reports including these novel PIs containing regimens for R/RMM. RESULTS: Finally, we identified 28 prospective studies that evaluated 4123 patients. Pooled analysis showed that novel PIs doublet combinations attained an impressive overall response rate (ORR) of 67%, which was higher than that of 22% from novel PIs single-agent (p < .001). And, the same trends favoring novel PIs doublet combinations were also shown in at least very good partial response (>/=VGPR) and clinical benefit rate (CBR) analysis. Meanwhile, the ORR of 70% from novel PIs triplet regimens seemed to be similar to that of 67% from novel PIs doublet combinations (p = .54). And, there were no difference between them in >/=VGPR and CBR analysis. Compared to standard therapy, novel PIs combinations clearly benefited patients with R/RMM in terms of overall survival (HR, 0.79; p= .01), progression free survival(HR, 0.64; p = .01), overall response rate (RR = 1.21 p < .001). CONCLUSIONS: Novel PIs doublet combinations attained superior response outcomes over novel PIs single-agent in patients with R/RMM. Meanwhile, novel PIs triplet combinations had similar response outcomes with novel PIs doublet combinations. Compared to standard therapy, novel PIs combinations clearly prolonged survival for patients with R/RMM.
Ligand Based-Pharmacophore Modeling and Extended Bi oactivity Prediction for Salinosporamide A, B and C from Marine Actino mycetes Salinispora tropica.[Pubmed:28000560]
Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2017;20(1):3-19.
AIM AND OBJECTIVE: Actinomycetes produce structurally unique secondary metabolites with pharmaceutically essential bioactivities. Salinispora, an obligate marine actinomycete, produces structurally varied and unique secondary metabolites. There is plenty of scope for development of drugs from the novel compounds isolated from Salinispora. Anticancer, antibacterial and anti-protozoa activities have been shown for Salinosporamides A, B and C, the secondary metabolites identified from Salinispora, which make them interesting subjects for further extended biological activity prediction. MATERIAL AND METHODS: An in silico ligand based-pharmacophore approach was used for the prediction of extended biological targets for salinosporamide A, B and C. Pharmacophore models of salinosporamide A, B and C were generated individually and screened against known drug databases. The drugs with best fitness score were shortlisted, and their respective targets pertaining to their bioactivity were retrieved. The predicted biological drug targets were docked with salinosporamide A, B and C for validation. RESULTS: The glucocorticoid receptor and methionine aminopeptidase 2 showed good docking score and binding energy with salinosporamide A, B and C. Molecular dynamics studies of the protein-ligand complexes showed stable interactions suggesting that the predicted new targets for salinosporamides might be promising. CONCLUSIONS: The glucocorticoid receptor and methionine aminopeptidase 2 could be possible new drug targets of bioactivity of salinosporamides. These proteins could be the druggable targets for antiinflammatory and anticancer activity of salinosporamides.
Marizomib for central nervous system-multiple myeloma.[Pubmed:28387460]
Br J Haematol. 2017 Apr;177(2):221-225.
Marizomib, a natural marine product, is an irreversible proteasome inhibitor currently under investigation in relapsed-refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) and malignant glioma. Central nervous system-multiple myeloma (CNS-MM) is a rare manifestation of extra-medullary disease with few therapeutic options, highlighting the unmet clinical need in these patients. Marizomib demonstrated encouraging activity in RRMM and has emerging clinical activity in glioma, making it a potential CNS-MM therapeutic intervention. Herein, we present two patients with RRMM and CNS involvement who benefited from marizomib-based therapy. These cases provide the first proof of principle for further exploring marizomib in CNS-MM patients.


