MLN9708Proteasome inhibitor CAS# 1201902-80-8 |
- Dihydroeponemycin
Catalog No.:BCC3596
CAS No.:126463-64-7
- Clasto-Lactacystin β-lactone
Catalog No.:BCC1224
CAS No.:154226-60-5
- Bortezomib (PS-341)
Catalog No.:BCC1238
CAS No.:179324-69-7
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)
Catalog No.:BCC2094
CAS No.:437742-34-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1201902-80-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 49867936 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H23BCl2N2O9 | M.Wt | 517.1 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
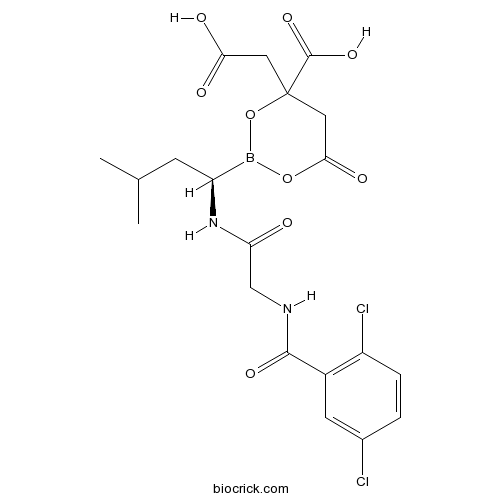
| Chemical Name | 4-(carboxymethyl)-2-[(1R)-1-[[2-[(2,5-dichlorobenzoyl)amino]acetyl]amino]-3-methylbutyl]-6-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaborinane-4-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | B1(OC(=O)CC(O1)(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YTXSYWAKVMZICI-PVCZSOGJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H23BCl2N2O9/c1-10(2)5-14(21-33-17(29)8-20(34-21,19(31)32)7-16(27)28)25-15(26)9-24-18(30)12-6-11(22)3-4-13(12)23/h3-4,6,10,14H,5,7-9H2,1-2H3,(H,24,30)(H,25,26)(H,27,28)(H,31,32)/t14-,20?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
| Cell lines | MM.1S (Dexamethasone sensitive) cells |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 100 nM, 3 hours for CT-L proteasome inhibition 100 nm, 3 hours for C-L proteasome inhibition 10 μM, 3 hours for T-L proteasome inhibition |
| Applications | MLN9708 significantly inhibited CT-L proteasome activity with an IC50 at 5 nM. Higher concentrations of MLN9708 showed inhibitory activity against C-L and T-L proteasome activities. |
| Animal experiment: | |
| Animal models | Female CB17-SCID mice bearing WSU-DLCL2 xenografts |
| Dosage form | Intravenous injection, 14 mg/kg, twice weekly or subcutaneous injection, 4 mg/kg, once daily |
| Application | Both intermittent and continuous MLN2238 dosing regimens showed strong antitumor activity (T/C = 0.44 and 0.29 for 14 mg/kg i.v. and 4 mg/kg s.c., respectively) and generated a greater apoptotic response in tumor tissue asmeasured by levels of cleaved caspase-3. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Chauhan D, Tian Z, Zhou B, et al. In vitro and in vivo selective antitumor activity of a novel orally bioavailable proteasome inhibitor MLN9708 against multiple myeloma cells. Clinical Cancer Research, 2011, 17(16): 5311-5321. [2] Kupperman E, Lee E C, Cao Y, et al. Evaluation of the proteasome inhibitor MLN9708 in preclinical models of human cancer. Cancer research, 2010, 70(5): 1970-1980. | |

MLN9708 Dilution Calculator

MLN9708 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9339 mL | 9.6693 mL | 19.3386 mL | 38.6772 mL | 48.3465 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3868 mL | 1.9339 mL | 3.8677 mL | 7.7354 mL | 9.6693 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1934 mL | 0.9669 mL | 1.9339 mL | 3.8677 mL | 4.8347 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0387 mL | 0.1934 mL | 0.3868 mL | 0.7735 mL | 0.9669 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0193 mL | 0.0967 mL | 0.1934 mL | 0.3868 mL | 0.4835 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
Radiolabeled MLN9708, a proteasome inhibitor with antitumor activity, were synthesized and evaluated for its stability.
Abstract
MLN9708 is a proteasome inhibitor with improved pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and antitumor activity in comparison to bortezomib.
Abstract
MLN2238, a proteasome inhibitor, induced the expression of miR33b predominantly through transcriptional regulation and negatively regulated oncogene PIM-1 blocking wild-type PIM-1 in MM cells.
Abstract
MLN2238, an active form of MLN9708, inhibited in vitro osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast resorption and promoted in vitro osteoblastogensis and osteoblast activity at clinically achievable concentrations. Compared to bortezomib, oral administration of MLN2238 exhibited equivalent tumor burden controlling efficacy with a marked benefit in associated bone disease.
Abstract
MLN9708 drug substance contains DCBC, which is a genotoxic impurity and could be quantified by a UHPLC/HRQMS method.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MLN9708, also known as ixazomib, is a second-generation small-molecule proteasome inhibitor. It is a citrate ester that immediately hydrolyzes to its biologically active form MLN2238 upon exposure to aqueous solutions or plasma. MLN9708 was selected from a large pool of boron-containing proteasome inhibitors based on a physicochemical profile that was distinct from bortezomib. MLN9708 has a shorter 20S proteasome dissociation half-life than bortezomib, which is demonstrated to play an important role in its improved tissue distribution.
Reference
Erik Kupperman, Edmund C. Lee, Yueying Cao, Bret Bannerman, Michael Fitzgerald, Allison Berger, Jie Yu, Yu Yang, Paul Hales, Frank Bruzzese, Jane Liu, Jonathan Blank, Khristofer Garcia, Christopher Tsu, Larry Dick, Paul Fleming, Li Yu, Mark Manfredi, Mark Rolfe, and Joe Bolen. Evaluation of the Proteasome Inhibitor MLN9708 in Preclinical Models of Human Cancer. Cancer Res March 1, 2010 70; 1970.
Edmund C. Lee, Michael Fitzgerald, Bret Bannerman, Jill Donelan, Kristen Bano, Jennifer Terkelsen, Daniel P. Bradley, Ozlem Subakan, Matthew D. Silva, Ray Liu, Michael Pickard, Zhi Li, Olga Tayber, Ping Li, Paul Hales, Mary Carsillo, Vishala T. Neppalli, Allison J. Berger, Erik Kupperman, Mark Manfredi, Joseph B. Bolen, Brian Van Ness, Siegfried Janz. Antitumor Activity of the Investigational Proteasome Inhibitor MLN9708 in Mouse Models of B-cell and Plasma Cell Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res December 1, 2011 17; 7313.
- Vinflunine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4602
CAS No.:1201898-17-0
- Crotaleschenine
Catalog No.:BCN2077
CAS No.:120154-95-2
- IPI-145 (INK1197)
Catalog No.:BCC1104
CAS No.:1201438-56-3
- Flavanthrin
Catalog No.:BCN3687
CAS No.:120090-80-4
- Fmoc-D-Arg(Mtr)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3078
CAS No.:120075-24-3
- CRF (6-33)
Catalog No.:BCC5791
CAS No.:120066-38-8
- Shizukanolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6411
CAS No.:120061-96-3
- Meridinol
Catalog No.:BCN6087
CAS No.:120051-54-9
- Edgeworin
Catalog No.:BCN6561
CAS No.:120028-43-5
- VCH-916
Catalog No.:BCC2031
CAS No.:1200133-34-1
- Donepezil HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4569
CAS No.:120011-70-3
- Dichlorphenamide
Catalog No.:BCC3761
CAS No.:120-97-8
- TCS 2210
Catalog No.:BCC7798
CAS No.:1201916-31-5
- Cynoglossamine
Catalog No.:BCN1970
CAS No.:120193-39-7
- 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamamide
Catalog No.:BCN6090
CAS No.:1202-41-1
- Clopidogrel
Catalog No.:BCC2497
CAS No.:120202-66-6
- Clopidogrel Related Compound C
Catalog No.:BCN2689
CAS No.:120202-71-3
- NMS-P715
Catalog No.:BCC6373
CAS No.:1202055-34-2
- Tenidap
Catalog No.:BCC7419
CAS No.:120210-48-2
- 1beta-Hydroxyeuscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3517
CAS No.:120211-98-5
- CGS 21680
Catalog No.:BCC1475
CAS No.:120225-54-9
- AVL-292
Catalog No.:BCC1385
CAS No.:1202757-89-8
- CNX-774
Catalog No.:BCC4394
CAS No.:1202759-32-7
- Salvinolone
Catalog No.:BCN3215
CAS No.:120278-22-0
A New Perspective for Osteosarcoma Therapy: Proteasome Inhibition by MLN9708/2238 Successfully Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest and Attenuates the Invasion Ability of Osteosarcoma Cells in Vitro.[Pubmed:28214890]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(2):451-465.
BACKGROUND: The proteasome exists in all eukaryotic cells and provides the main route of intracellular proteins degradation involved in cell growth and apoptosis. Proteasome inhibition could block protein degradation pathways and disturb regulatory networks, possibly leading to profound effects on cell growth, particularly in cancer cells. A proteasome inhibitor with an appropriate toxicity index for malignant cells rather than normal cells would be an attractive anticancer therapy. METHODS: The human osteosarcoma (OS) cell lines MG-63 and Saos-2 and normal osteoblast cells were used to study the antitumour activity of the proteasome inhibitor MLN9708/2238. RESULTS: MLN2238 inhibited cell growth, induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and attenuated the invasion abilities of MG-63 and Saos-2 cells, with little cytotoxicity to normal cells. In addition, MLN2238 promoted antitumour mechanisms including the accumulation of E2F1, P53, P21 and other negative G2/M checkpoint proteins; up-regulated the relative expression ratio of BAX/BCL-2, APAF-1 and pro-apoptotic proteins of the BCL-2 family; triggered mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP); down-regulated BCL-2 and XIAP; activated caspase3/8/9; and suppressed MMP2/9 expression and secretion levels. CONCLUSIONS: The proteasome may be a novel biochemical target for OS treatment in vitro. Our study provides a promising mechanistic framework for MLN9708/2238 in OS treatment, supporting its clinical development.
Next-generation proteasome inhibitor MLN9708 sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis.[Pubmed:27217076]
Sci Rep. 2016 May 24;6:26456.
Doxorubicin (Dox), one of the most effective chemotherapy drug for cancer treatment, is limited by its severe side effects and chemoresistance. Dox induces DNA damage and leads to significant proteomic changes in the cancer cells, which makes the ubiquitin-proteasome system a potential target to enhance the efficacy of Dox therapy. The unsuccessful clinical trials of proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib) in solid tumors led to the invention of MLN9708 (ixazomib), an orally bioavailable next-generation proteasome inhibitor with improved pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic features. In this preclinical study, we used eight human breast cancer cell lines, which represent the major molecular subtypes of breast cancer, to validate the cytotoxic effects of MLN9708, alone and in combination with Dox. We found that MLN9708 had cytotoxic effects, induced autophagy and MKP-1 expression, and enhanced Dox-induced apoptosis in these cell lines. MLN9708 also enhanced Dox-induced JNK and p38 phosphorylation and inhibited Dox-induced IkappaBalpha degradation. Our in vitro results suggest that MLN9708 has antitumor effects in breast cancer and can sensitize breast cancer cells to Dox treatment. This promising combination may be an effective and feasible therapeutic option for treating breast cancer and warrants clinical validation.
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution quantitation mass spectrometry method development and validation for determining genotoxic 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl chloride in MLN9708 drug substance.[Pubmed:24309557]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Feb;89:233-9.
A novel reversed-phase ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution quantitation mass spectrometry (UHPLC/HRQMS) method was developed to quantify 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl chloride (DCBC), a genotoxic impurity, in MLN9708 drug substance. A surrogate strategy was utilized whereby DCBC was intentionally hydrolyzed to 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid (DCBA) to provide a stable and reliable detection target. The hydrolysis approach was conservative since the measured signal represented the sum of DCBC and DCBA in MLN9708 drug substance, and such approach was acknowledged and accepted by food and drug administration (FDA). HRQMS was used as the detection method since conventional MS/MS methodology gave poor sensitivity and selectivity due to non-specific fragmentation of carbon dioxide loss upon collision activation dissociation. Profile algorithm mass spectrometry data were acquired with mass resolving power (MRP) of 60,000. Quantitation was based on the extracted ion chromatography (EIC) peak area signal, which was extracted at m/z 188.9515 with a mass extraction window (MEW) of 5ppm. The UHPLC/HRQMS method was validated based on International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines, which included selectivity, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantitation (LOQ), repeatability, linearity, accuracy, and stability.
Preclinical activity of the oral proteasome inhibitor MLN9708 in Myeloma bone disease.[Pubmed:24486586]
Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Mar 15;20(6):1542-54.
PURPOSE: MLN9708 (ixazomib citrate), which hydrolyzes to pharmacologically active MLN2238 (ixazomib), is a next-generation proteasome inhibitor with demonstrated preclinical and clinical antimyeloma activity, but yet with an unknown effect on myeloma bone disease. Here, we investigated its bone anabolic and antiresorptive effects in the myeloma setting and in comparison with bortezomib in preclinical models. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: The in vitro effect of MLN2238 was tested on osteoclasts and osteoclast precursors from healthy donors and patients with myeloma, and on osteoprogenitors derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells also from both origins. We used an in vivo model of bone marrow-disseminated human myeloma to evaluate MLN2238 antimyeloma and bone activities. RESULTS: Clinically achievable concentrations of MLN2238 markedly inhibited in vitro osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast resorption; these effects involved blockade of RANKL (receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand)-induced NF-kappaB activation, F-actin ring disruption, and diminished expression of alphaVbeta3 integrin. A similar range of MLN2238 concentrations promoted in vitro osteoblastogenesis and osteoblast activity (even in osteoprogenitors from patients with myeloma), partly mediated by activation of TCF/beta-catenin signaling and upregulation of the IRE1 component of the unfolded protein response. In a mouse model of bone marrow-disseminated human multiple myeloma, orally administered MLN2238 was equally effective as bortezomib to control tumor burden and also provided a marked benefit in associated bone disease (sustained by both bone anabolic and anticatabolic activities). CONCLUSION: Given favorable data on pharmacologic properties and emerging clinical safety profile of MLN9708, it is conceivable that this proteasome inhibitor may achieve bone beneficial effects in addition to its antimyeloma activity in patients with myeloma.


