NMS-P715MPS1 kinase inhibitor CAS# 1202055-34-2 |
- DBeQ
Catalog No.:BCC3916
CAS No.:177355-84-9
- Xanthohumol
Catalog No.:BCN5768
CAS No.:569-83-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1202055-34-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44556162 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C35H39F3N8O3 | M.Wt | 676.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
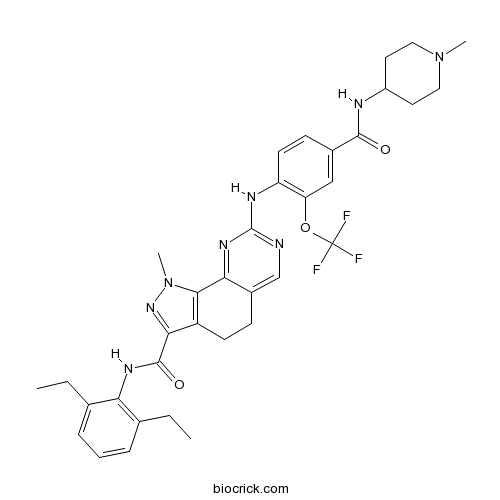
| Chemical Name | N-(2,6-diethylphenyl)-1-methyl-8-[4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)carbamoyl]-2-(trifluoromethoxy)anilino]-4,5-dihydropyrazolo[4,3-h]quinazoline-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CCC1=C(C(=CC=C1)CC)NC(=O)C2=NN(C3=C2CCC4=CN=C(N=C43)NC5=C(C=C(C=C5)C(=O)NC6CCN(CC6)C)OC(F)(F)F)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JFOAJUGFHDCBJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H39F3N8O3/c1-5-20-8-7-9-21(6-2)28(20)42-33(48)30-25-12-10-23-19-39-34(43-29(23)31(25)46(4)44-30)41-26-13-11-22(18-27(26)49-35(36,37)38)32(47)40-24-14-16-45(3)17-15-24/h7-9,11,13,18-19,24H,5-6,10,12,14-17H2,1-4H3,(H,40,47)(H,42,48)(H,39,41,43) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | NMS-P715 analog is an inhibitor of MPS1, with an IC50 of 84 nM.In Vitro:NMS-P715 analog (Compound 14) is an inhibitor of MPS1, with an IC50 of 84 nM; also less active on Aur-A, CDK2/A and PLK1 (IC50, 1.45, >10, 0.237 μM). In addition, NMS-P715 analog shows inhibitory effect on human tumor cell line (A2780) with an IC50 of 150 nM. References: | |||||

NMS-P715 Dilution Calculator

NMS-P715 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4777 mL | 7.3885 mL | 14.7769 mL | 29.5539 mL | 36.9424 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2955 mL | 1.4777 mL | 2.9554 mL | 5.9108 mL | 7.3885 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1478 mL | 0.7388 mL | 1.4777 mL | 2.9554 mL | 3.6942 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0296 mL | 0.1478 mL | 0.2955 mL | 0.5911 mL | 0.7388 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0148 mL | 0.0739 mL | 0.1478 mL | 0.2955 mL | 0.3694 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NMS-P715 is a potent and selective inhibitor of MPS1 kinase with IC50 value of 8 nM [1].
Human monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1) kinase is a serine/threonine kinase that plays an important role in spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) signaling by influencing the stability of the kinetochore-microtubule interaction and controlling chromosome alignment [1].
NMS-P715 is an orally available, selective and ATP-competitive MPS1 kinase inhibitor. In nocodazole-arrested U2OS cells, NMS-P715 promoted massive SAC override with EC50 value of
65 nM. In U2OS cells overexpressing YFP-α-tubulin, NMS-P715 induced mitotic acceleration and reduced mitotic cells. In nocodazole-arrested HeLa cells with MG132, NMS-P715 leads to complete delocalization of MAD1, MAD2, BUB1, BUB3 and Borealin and also reduced MPS1. In A2780 ovarian cancer cells, NMS-P715 reduced G1 phase, caused a flattening in G2/M phase of the cell cycle and subsequently induced apoptosis [1]. In human and murine pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells, NMS-P715 inhibited cell growth [2]. In glioblastoma (GBM) cells, NMS-P715 increased the radiosensitivity of GBM cells by induction of post-radiation mitotic catastrophe and reduced repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) [3].
In nude mice bearing human A2780 ovary carcinoma xenograft model, NMS-P715 (90 mg/kg for 7 days) inhibited tumor growth by 53%. In the A375 melanoma xenograft model, NMS-P715 (100 mg/kg for 10 days) inhibited tumor growth by 43% [1].
References:
[1]. Colombo R, Caldarelli M, Mennecozzi M, et al. Targeting the mitotic checkpoint for cancer therapy with NMS-P715, an inhibitor of MPS1 kinase. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(24): 10255-10264.
[2]. Slee RB, Grimes BR, Bansal R, et al. Selective inhibition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell growth by the mitotic MPS1 kinase inhibitor NMS-P715. Mol Cancer Ther, 2014, 13(2): 307-315.
[3]. Maachani UB, Kramp T, Hanson R, et al. Targeting MPS1 Enhances Radiosensitization of Human Glioblastoma by Modulating DNA Repair Proteins. Mol Cancer Res, 2015, 13(5): 852-862.
- Clopidogrel Related Compound C
Catalog No.:BCN2689
CAS No.:120202-71-3
- Clopidogrel
Catalog No.:BCC2497
CAS No.:120202-66-6
- 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamamide
Catalog No.:BCN6090
CAS No.:1202-41-1
- Cynoglossamine
Catalog No.:BCN1970
CAS No.:120193-39-7
- TCS 2210
Catalog No.:BCC7798
CAS No.:1201916-31-5
- MLN9708
Catalog No.:BCC2091
CAS No.:1201902-80-8
- Vinflunine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4602
CAS No.:1201898-17-0
- Crotaleschenine
Catalog No.:BCN2077
CAS No.:120154-95-2
- IPI-145 (INK1197)
Catalog No.:BCC1104
CAS No.:1201438-56-3
- Flavanthrin
Catalog No.:BCN3687
CAS No.:120090-80-4
- Fmoc-D-Arg(Mtr)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3078
CAS No.:120075-24-3
- CRF (6-33)
Catalog No.:BCC5791
CAS No.:120066-38-8
- Tenidap
Catalog No.:BCC7419
CAS No.:120210-48-2
- 1beta-Hydroxyeuscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3517
CAS No.:120211-98-5
- CGS 21680
Catalog No.:BCC1475
CAS No.:120225-54-9
- AVL-292
Catalog No.:BCC1385
CAS No.:1202757-89-8
- CNX-774
Catalog No.:BCC4394
CAS No.:1202759-32-7
- Salvinolone
Catalog No.:BCN3215
CAS No.:120278-22-0
- 4-Hydroxysapriparaquinone
Catalog No.:BCN4806
CAS No.:120278-25-3
- Dorzolamide
Catalog No.:BCC4287
CAS No.:120279-96-1
- CX-6258
Catalog No.:BCC1504
CAS No.:1202916-90-2
- Citroside A
Catalog No.:BCN7294
CAS No.:120330-44-1
- DASA-58
Catalog No.:BCC6522
CAS No.:1203494-49-8
- Cyclotraxin B
Catalog No.:BCC6357
CAS No.:1203586-72-4
Selective inhibition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell growth by the mitotic MPS1 kinase inhibitor NMS-P715.[Pubmed:24282275]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Feb;13(2):307-315.
Most solid tumors, including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), exhibit structural and numerical chromosome instability (CIN). Although often implicated as a driver of tumor progression and drug resistance, CIN also reduces cell fitness and poses a vulnerability that can be exploited therapeutically. The spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) ensures correct chromosome-microtubule attachment, thereby minimizing chromosome segregation errors. Many tumors exhibit upregulation of SAC components such as MPS1, which may help contain CIN within survivable limits. Prior studies showed that MPS1 inhibition with the small molecule NMS-P715 limits tumor growth in xenograft models. In cancer cell lines, NMS-P715 causes cell death associated with impaired SAC function and increased chromosome missegregation. Although normal cells appeared more resistant, effects on stem cells, which are the dose-limiting toxicity of most chemotherapeutics, were not examined. Elevated expression of 70 genes (CIN70), including MPS1, provides a surrogate measure of CIN and predicts poor patient survival in multiple tumor types. Our new findings show that the degree of CIN70 upregulation varies considerably among PDAC tumors, with higher CIN70 gene expression predictive of poor outcome. We identified a 25 gene subset (PDAC CIN25) whose overexpression was most strongly correlated with poor survival and included MPS1. In vitro, growth of human and murine PDAC cells is inhibited by NMS-P715 treatment, whereas adipose-derived human mesenchymal stem cells are relatively resistant and maintain chromosome stability upon exposure to NMS-P715. These studies suggest that NMS-P715 could have a favorable therapeutic index and warrant further investigation of MPS1 inhibition as a new PDAC treatment strategy.
Targeting the mitotic checkpoint for cancer therapy with NMS-P715, an inhibitor of MPS1 kinase.[Pubmed:21159646]
Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 15;70(24):10255-64.
MPS1 kinase is a key regulator of the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), a mitotic mechanism specifically required for proper chromosomal alignment and segregation. It has been found aberrantly overexpressed in a wide range of human tumors and is necessary for tumoral cell proliferation. Here we report the identification and characterization of NMS-P715, a selective and orally bioavailable MPS1 small-molecule inhibitor, which selectively reduces cancer cell proliferation, leaving normal cells almost unaffected. NMS-P715 accelerates mitosis and affects kinetochore components localization causing massive aneuploidy and cell death in a variety of tumoral cell lines and inhibits tumor growth in preclinical cancer models. Inhibiting the SAC could represent a promising new approach to selectively target cancer cells.


