DBeQP97 ATPase inhibitor CAS# 177355-84-9 |
- Vinblastine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2292
CAS No.:143-67-9
- Pepstatin A
Catalog No.:BCC1218
CAS No.:26305-03-3
- Dexamethasone (DHAP)
Catalog No.:BCC1184
CAS No.:50-02-2
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- E 64d
Catalog No.:BCC1127
CAS No.:88321-09-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 177355-84-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 676352 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H20N4 | M.Wt | 340.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | JRF 12 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 47 mg/mL (138.06 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
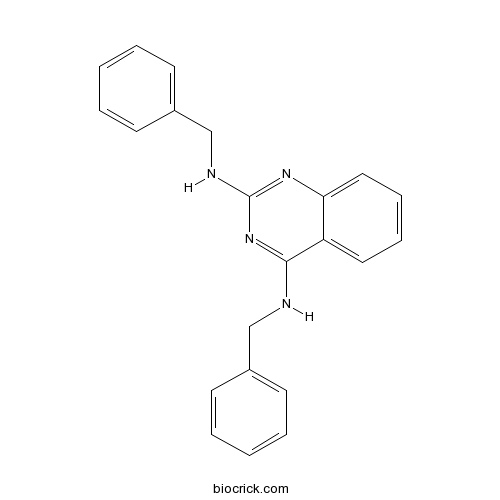
| Chemical Name | 2-N,4-N-dibenzylquinazoline-2,4-diamine | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CNC2=NC(=NC3=CC=CC=C32)NCC4=CC=CC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QAIMUUJJAJBPCL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H20N4/c1-3-9-17(10-4-1)15-23-21-19-13-7-8-14-20(19)25-22(26-21)24-16-18-11-5-2-6-12-18/h1-14H,15-16H2,(H2,23,24,25,26) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective and reversible inhibitor of p97 ATPase (IC50 = 1.5 μM). Induces executioner caspases (caspase-3 and caspase-7) rapidly. Blocks the degradation of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) reporters; also blocks autophagosome maturation and promotes accumulation of LC3-II. |

DBeQ Dilution Calculator

DBeQ Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9375 mL | 14.6877 mL | 29.3755 mL | 58.751 mL | 73.4387 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5875 mL | 2.9375 mL | 5.8751 mL | 11.7502 mL | 14.6877 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2938 mL | 1.4688 mL | 2.9375 mL | 5.8751 mL | 7.3439 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0588 mL | 0.2938 mL | 0.5875 mL | 1.175 mL | 1.4688 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0294 mL | 0.1469 mL | 0.2938 mL | 0.5875 mL | 0.7344 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
DBeQ is a selective and reversible inhibitor of p97 ATPase (IC50 = 1.5 μM) which induces caspase-3 and caspase-7 rapidly.
p97 knows also as VCP ( Cdc48 in yeast) is a hexameric ATPase of the AAA family which disassembles SNARE proteins after membrane fusion.[1] It is involved in a fusion of homotypic membranes, protein degradation, and activation of membrane-bound transcription factors.[2] p97 is one of the most abundant proteins in the eukaryotic cytosol and its segregase function has been linked to a large number of biological processes including endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation(ERAD), mitochondrial associated degradation, ubiquitin fusion degradation, homotypic membrane fusion, cell cycle regulation, autophagy and transcription factor regulation.[3]
DBeQ can block the degradation of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) reporters and also block autophagosome maturation,all of which are proven to be important in cancer therapy.[4,5] DBeQ is ATP-sensitive and selectively target D1and D2 domain with ODD-Luc IC50 56 μM, Luc-ODC IC50 45 μM,UbG76VGFP IC50 2.3 μM, much less affected by the presence of p47 than the other quinazolines.[6,7]
References:
1. Zhang, X. et al. "Structure of the AAA ATPase p97". Molecular cell 2000, 6 (6): 1473–84.
2. Madsen, L. et al. "New ATPase regulators--p97 goes to the PUB.". Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2009, 41 (12): 2380–8.
3. Eli Chapman. et al. “Inhibitors of the AAA+ Chaperone p97”. Molecules 2015, 20(2), 3027-3049.
4. Liu, Y. Et al. “VCP/p97,down-regulated by microRNA-129-5p, could regulate the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma”. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35800.
5. Laguë, M.N. et al. “Proteomic profiling of a mouse model for ovarian granulosa cell tumor identifies VCP as a highly sensitive serum tumor marker in several human cancers.” PLoS One 2012, 7, e42470.
6. Fang, C.J. et al. “Evaluating p97 inhibitor analogues for their domain selectivity and potency against the p97–p47 complex.” Chem. Med. Chem. 2014.
7. Chou, T.F. et al. “Specific inhibition of p97/VCP ATPase and kinetic analysis demonstrated interaction between D1 and D2 ATPase domains.” J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 2886–2899.
- Aglain B
Catalog No.:BCN6636
CAS No.:177262-32-7
- 26-O-Acetylsootepin A
Catalog No.:BCN7699
CAS No.:1772588-99-4
- R 568 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7781
CAS No.:177172-49-5
- Ambrisentan
Catalog No.:BCC4887
CAS No.:177036-94-1
- 2alpha,19alpha-Dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7406
CAS No.:176983-21-4
- LY 320135
Catalog No.:BCC7346
CAS No.:176977-56-3
- CCT007093
Catalog No.:BCC5147
CAS No.:176957-55-4
- Metergoline
Catalog No.:BCC6709
CAS No.:17692-51-2
- Homoplantaginin
Catalog No.:BCN2488
CAS No.:17680-84-1
- (RS)-3,4-DCPG
Catalog No.:BCC7045
CAS No.:176796-64-8
- Ageratochromene dimer
Catalog No.:BCN8110
CAS No.:17678-76-1
- Neoruscogenin
Catalog No.:BCN8168
CAS No.:17676-33-4
- Aglain C
Catalog No.:BCN6604
CAS No.:177468-85-8
- 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8537
CAS No.:1775-95-7
- Flavokawain B
Catalog No.:BCN3568
CAS No.:1775-97-9
- ZK 164015
Catalog No.:BCC7272
CAS No.:177583-70-9
- Glycerol 1-(26-hydroxyhexacosanoate)
Catalog No.:BCN1131
CAS No.:177602-14-1
- MNITMT
Catalog No.:BCC7382
CAS No.:177653-76-8
- NKP608
Catalog No.:BCC1802
CAS No.:177707-12-9
- Proxyfan oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7378
CAS No.:177708-09-7
- Calystegine N1
Catalog No.:BCN1866
CAS No.:177794-03-5
- Calystegine A6
Catalog No.:BCN1886
CAS No.:177794-04-6
- Eletriptan HBr
Catalog No.:BCC5039
CAS No.:177834-92-3
- Boc-His-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3398
CAS No.:17791-52-5
The AAA ATPase Vps4 Plays Important Roles in Candida albicans Hyphal Formation and is Inhibited by DBeQ.[Pubmed:26700222]
Mycopathologia. 2016 Jun;181(5-6):329-39.
Candida albicans is an opportunistic human pathogen, and its pathogenicity is associated with hyphal formation. Previous studies have shown that at neutral-to-alkaline pH, hyphal growth is dependent on the Rim101 pathway whose activation requires Snf7, a member of the ESCRT system. In this work, we described the purification and characterization of the C. albicans Vps4, an AAA ATPase required for recycling of the ESCRTs. Its role on hyphal growth has been investigated. Our data suggest deletion of Vps4 decreases overall hyphal growth at pH 7 and increases the growth of multiple hyphae induced by serum, which indicates that the ESCRTs may make a Rim101-independent contribution to hyphal growth. Furthermore, DBeQ, an inhibitor of the AAA ATPase p97, was shown to inhibit the ATPase activity of Vps4 with an IC50 of about 11.5 muM. To a less degree, it also inhibits hyphal growth. Our work may provide a new strategy to control C. albicans infection.
Reversible inhibitor of p97, DBeQ, impairs both ubiquitin-dependent and autophagic protein clearance pathways.[Pubmed:21383145]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 22;108(12):4834-9.
A specific small-molecule inhibitor of p97 would provide an important tool to investigate diverse functions of this essential ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA) ATPase and to evaluate its potential to be a therapeutic target in human disease. We carried out a high-throughput screen to identify inhibitors of p97 ATPase activity. Dual-reporter cell lines that simultaneously express p97-dependent and p97-independent proteasome substrates were used to stratify inhibitors that emerged from the screen. N2,N4-dibenzylquinazoline-2,4-diamine (DBeQ) was identified as a selective, potent, reversible, and ATP-competitive p97 inhibitor. DBeQ blocks multiple processes that have been shown by RNAi to depend on p97, including degradation of ubiquitin fusion degradation and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway reporters, as well as autophagosome maturation. DBeQ also potently inhibits cancer cell growth and is more rapid than a proteasome inhibitor at mobilizing the executioner caspases-3 and -7. Our results provide a rationale for targeting p97 in cancer therapy.
Development of p97 AAA ATPase inhibitors.[Pubmed:21606684]
Autophagy. 2011 Sep;7(9):1091-2. Epub 2011 Sep 1.
Specific p97 inhibitors are valuable research tools to carry out mechanistic and cellular investigations of p97 biology. p97 is an abundant, ubiquitin-selective chaperone that has multiple functions and is essential for life. Therefore, genetic methods that require long incubations like siRNA or expression of dominant-negative p97 mutants are likely to generate complicated outcomes due to secondary consequences that arise upon slow depletion of p97 activity. We recently identified a small molecule p97 inhibitor, N ( 2) ,N ( 4) -dibenzylquinazoline-2,4-diamine (DBeQ), and documented its effects on blocking autophagic degradation of LC3-II and proteasomal degradation of a p97-dependent ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) substrate. What distinguishes DBeQ from conventional proteasome inhibitors is that DBeQ affects both the UPS and autophagic protein degradation pathways and rapidly activates cell death. Whether DBeQ activates autophagic and/or apoptotic cell death will require further work to evaluate its detailed mechanism of action. An exciting goal for the future will be to generate p97 inhibitors that affect one or the other pathway. We propose that generation of 'separation of function' inhibitors will be a challenging adventure for chemical biologists but will yield extremely powerful tools to study p97 and enable evaluation of the therapeutic potential of targeting distinct p97 complexes.


