Dexamethasone (DHAP)Glucocorticoidan;ti-inflammatory CAS# 50-02-2 |
- Vinblastine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2292
CAS No.:143-67-9
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- Pepstatin A
Catalog No.:BCC1218
CAS No.:26305-03-3
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- E 64d
Catalog No.:BCC1127
CAS No.:88321-09-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 50-02-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5743 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H29FO5 | M.Wt | 392.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | MK 125; NSC 34521; Prednisolone F | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 56 mg/mL (142.69 mM) Ethanol : 8.33 mg/mL (21.23 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
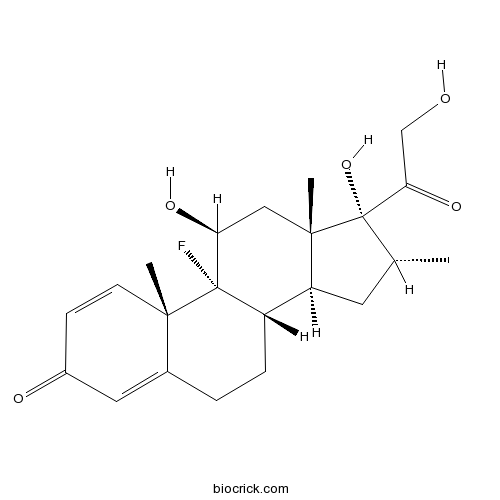
| Chemical Name | (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,16R,17R)-9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13,16-trimethyl-6,7,8,11,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CC2C3CCC4=CC(=O)C=CC4(C3(C(CC2(C1(C(=O)CO)O)C)O)F)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H29FO5/c1-12-8-16-15-5-4-13-9-14(25)6-7-19(13,2)21(15,23)17(26)10-20(16,3)22(12,28)18(27)11-24/h6-7,9,12,15-17,24,26,28H,4-5,8,10-11H2,1-3H3/t12-,15+,16+,17+,19+,20+,21+,22+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Glucocorticoid; anti-inflammatory. Reduces levels of activated NF-κB in immature dendritic cells (DCs) and inhibits differentiation into mature DCs. Induces differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Also induces autophagy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell lines. |

Dexamethasone (DHAP) Dilution Calculator

Dexamethasone (DHAP) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.548 mL | 12.7402 mL | 25.4803 mL | 50.9606 mL | 63.7008 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5096 mL | 2.548 mL | 5.0961 mL | 10.1921 mL | 12.7402 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2548 mL | 1.274 mL | 2.548 mL | 5.0961 mL | 6.3701 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.051 mL | 0.2548 mL | 0.5096 mL | 1.0192 mL | 1.274 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1274 mL | 0.2548 mL | 0.5096 mL | 0.637 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Glucocorticoid; anti-inflammatory. Reduces levels of activated NF-κB in immature dendritic cells (DCs) and inhibits differentiation into mature DCs. Induces differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Also induces autophagy in acute lymphoblas
- Guanidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4785
CAS No.:50-01-1
- Tioxolone
Catalog No.:BCC2316
CAS No.:4991-65-5
- 2,4-Pyridinedicarboxylic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC6483
CAS No.:499-80-9
- 5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN2633
CAS No.:499-75-2
- beta-Thujaplicin
Catalog No.:BCN3895
CAS No.:499-44-5
- IsoMaltose
Catalog No.:BCN8321
CAS No.:499-40-1
- Corydamine
Catalog No.:BCN3366
CAS No.:49870-84-0
- Erythroskyrin
Catalog No.:BCN1836
CAS No.:4987-27-3
- EX 527 (SEN0014196)
Catalog No.:BCC2223
CAS No.:49843-98-3
- Tobramycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC5633
CAS No.:49842-07-1
- Ethyl Nipecotate
Catalog No.:BCC3272
CAS No.:5006-62-2
- Scopine
Catalog No.:BCN1940
CAS No.:498-45-3
- Cortisone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4771
CAS No.:50-04-4
- Mitomycin C
Catalog No.:BCC2388
CAS No.:50-07-7
- Ergocalciferol
Catalog No.:BCN2208
CAS No.:50-14-6
- Cyclophosphamide
Catalog No.:BCC1185
CAS No.:50-18-0
- Corticosterone
Catalog No.:BCN2203
CAS No.:50-22-6
- Hydrocortisone
Catalog No.:BCN2192
CAS No.:50-23-7
- Prednisolone
Catalog No.:BCC4830
CAS No.:50-24-8
- Estriol
Catalog No.:BCN2235
CAS No.:50-27-1
- beta-Estradiol
Catalog No.:BCN2194
CAS No.:50-28-2
- Phenylbutazone
Catalog No.:BCC4822
CAS No.:50-33-9
- Thalidomide
Catalog No.:BCC2248
CAS No.:50-35-1
- Cocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1901
CAS No.:50-36-2
Effective salvage therapy for lymphoma with cisplatin in combination with high-dose Ara-C and dexamethasone (DHAP).[Pubmed:3334893]
Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):117-22.
Ninety patients with progressive recurrent lymphoma were treated with a combination of cisplatin 100 mg/m2 intravenously (IV) by continuous infusion over 24 hours, followed by cytosine arabinoside in two pulses each at a dose of 2 g/m2 given 12 hours apart. Dexamethasone, 40 mg orally or IV, was given on days 1 through 4. Vigorous hydration was reinforced by routine use of mannitol. Treatments were repeated at 3- to 4-week intervals for six to ten courses. Most patients had not achieved complete remission (CR) with prior therapies, which included Adriamycin (all patients) and methotrexate and VP-16 (58 patients). Median patient age was 55 years. Intermediate-grade lymphoma was the most frequent pathologic diagnosis. Seven patients died within two weeks of therapy; of the remaining 83 patients, 28 (34%) or 31% if all patients are considered, achieved CR, and 22 (26.5%) achieved partial remission (PR). Response was evident after the first two cycles of chemotherapy and appeared to be independent of the histopathologic type of lymphoma. To date, only eight of the complete responders have relapsed at a median follow-up of 11 months. The overall 2-year survival in 25%. Further analysis showed that patients with low tumor burden and normal lactic acid dehydrogenase (LDH) had a high CR response rate (67%) and a survival rate of 61% at 2 years. In contrast, patients with both high tumor burden and elevated serum LDH levels had a negligible CR rate, and only 5% are surviving at 1 year. Patients with either high tumor burden with normal LDH or low tumor burden with elevated LDH had an intermediate survival. Myelosuppression-related infection was the most frequent serious complication of this regimen (31%) and the cause of death of ten patients. Acute lysis syndrome was also observed in five patients with high tumor burden and was the cause of death in three of these patients. DHAP has proven to be an effective non-crossresistant regimen for patients with relapsing or refractory lymphoma, particularly for patients who have favorable prognostic characteristics.
Comparison of ICE (ifosfamide-carboplatin-etoposide) versus DHAP (cytosine arabinoside-cisplatin-dexamethasone) as salvage chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma.[Pubmed:18443961]
Cancer Invest. 2008 May;26(4):401-6.
BACKGROUND: High dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplantation is currently the treatment of choice for relapsed or refractory lymphoma patients. However, its applicability is mostly restricted to patients responding to salvage chemotherapy. Optimal salvage regimen for these patients is unclear. In this study, our aim was to compare the efficacy and toxicity profiles of DHAP (cytosine arabinoside, cisplatin and dexamethasone) and ICE (ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide) regimens in the salvage treatment of relapsed and refractory lymphoma. PATIENTS AND METHODS: In this retrospective analysis, 53 patients with primary refractory or relapsed Hodgkin's disease (HD) (n = 13) or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (n = 40) who received ICE or DHAP salvage regimen were included. RESULTS: Of 53 patients, 21 (39,6%) were female and the median age was 43 years. A total of 73 courses of ICE and 59 courses of DHAP were administered. Response could be evaluated in 49 patients (36 NHL and 13 HD). Of 49 patients, 11 (22.5%) achieved complete remission (CR) and 17 (35%) achieved partial remission (PR), leading to an overall response rate (ORR: CR + PR) of 57.5%. In the evaluable ICE group (n = 22) rates of CR, PR, and ORR were 27%, 41% and 68% and in the DHAP group (n = 27) rates of CR, PR, and ORR were 18%, 30% and 48% (p = 0.24, for ORR). Toxicity with both regimens was within acceptable limits. The major grade III-IV toxicities for both groups were hematological (neutopenia and thrombocytopenia). The main non-hematological toxicity was renal and observed in 8 patients. CONCLUSION: Although the toxicity profiles of both ICE and DHAP regimens were similar in the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory HD or NHL, ICE seems to have higher rates of response than DHAP regimen does.
Successful mobilization of peripheral blood stem cells with the DHAP regimen (dexamethasone, cytarabine, cisplatinum) plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with relapsed Hodgkin's disease.[Pubmed:16019552]
Leuk Lymphoma. 2005 Jul;46(7):1017-22.
High-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation can improve the outcome of relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's disease (HD) patients. The objective of the trial was to determine the mobilizing potential of the DHAP salvage regimen (dexamethasone, cytarabine, cisplatin) for the collection of peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC) in patients with relapsed HD. The target yield of harvesting CD34 + cells was > or =2 x 10(6)/kg in order to support the subsequent myeloablative chemotherapy. Most of the 105 patients included were intensively pre-treated with different combination chemotherapy regimens prior to mobilization. The use of DHAP followed by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF; 10 microg/kg) resulted in the successful collection of adequate numbers of PBSC in 97.1% of patients (102 of 105) with a median harvest of CD34+ cells of 13 x 10(6)/kg (range 2.6 - 85.1). More than 2.0 x 10(6) CD34+ cells/kg were achieved in 65 of 103 (63%) patients after 1 apheresis, the maximum number of aphereses for all patients was 3. It was found that the optimal time of PBSC harvest was at days 13 - 16 after initiating the mobilization regimen. These results demonstrate that the salvage chemotherapy regimen, such as DHAP combined with G-CSF, can be successfully used to mobilize PBSC in HD patients.
Short bouts of mechanical loading are as effective as dexamethasone at inducing matrix production by human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell.[Pubmed:20648425]
Eur Cell Mater. 2010 Jul 21;20:45-57.
Dexamethasone (Dex) is used widely to induce differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs); however, using a pharmaceutical agent to stimulate hMSC differentiation is not the best choice for engineered tissue transplantation due to potential side-effects. The goal of the present study was to investigate the effects of dynamic compressive loading on differentiation and mineralized matrix production of hMSCs in 3D polyurethane scaffolds, using a loading regimen previously shown to stimulate mineralised matrix production of mature bone cells (MLO-A5). hMSCs were seeded in polyurethane scaffolds and cultured in standard culture media with or without Dex. Cell-seeded scaffolds were compressed at 5% global strain for 2 h on day 9 and then every 5 days in a media-filled sterile chamber. Samples were tested for mRNA expression of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), osteopontin (OPN), collagen type 1 (col 1) and runt-related transcription factor-2 (RUNX-212 h) after the first loading, cell viability by MTS assay and alkaline phosphatase activity at day 12 of culture and cell viability, collagen content by Sirius red and calcium content by alizarin red at day 24 of culture. Neither Dex nor loading had significant effects on cell viability. Collagen content was significantly higher (p<0.01) in the loaded group compared with the non-loaded group in all conditions. There was no difference in ALP activity or the amount of collagen and calcium produced between the non-loaded group supplemented with Dex and the loaded group without Dex. We conclude that dynamic loading has the ability to stimulate osteogenic differentiation of hMSC in the absence of glucocorticoids.
Cell death induced by dexamethasone in lymphoid leukemia is mediated through initiation of autophagy.[Pubmed:19390558]
Cell Death Differ. 2009 Jul;16(7):1018-29.
Glucocorticoids are fundamental drugs used in the treatment of lymphoid malignancies with apoptotic cell death as the hitherto proposed mechanism of action. Recent studies, however, showed that an alternative mode of cell death, autophagy, is involved in the response to anticancer drugs. The specific role of autophagy and its relationship to apoptosis remains, nevertheless, controversial: it can either lead to cell survival or can function in cell death. We show that dexamethasone induced autophagy upstream of apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Inhibition of autophagy by siRNA-mediated repression of Beclin 1 expression inhibited apoptosis showing an important role of autophagy in dexamethasone-induced cell death. Dexamethasone treatment caused an upregulation of promyelocytic leukemia protein, PML, its complex formation with protein kinase B or Akt and a PML-dependent Akt dephosphorylation. Initiation of autophagy and the onset of apoptosis were both dependent on these events. PML knockout thymocytes were resistant to dexamethasone-induced death and upregulation of PML correlated with the ability of dexamethasone to kill primary leukemic cells. Our data reveal key mechanisms of dexamethasone-induced cell death that may inform the development of improved treatment protocols for lymphoid malignancies.
Dexamethasone inhibits dendritic cell maturation by redirecting differentiation of a subset of cells.[Pubmed:10614771]
J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Dec;66(6):909-14.
To investigate how corticosteroids affect differentiation of human dendritic cells (DC) in a defined inflammatory environment, we incubated immature DC with dexamethasone in the presence of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), and prostaglandin E2. Dexamethasone inhibited differentiation into mature DC, as indicated by the reduced expression of antigen-presenting molecules, costimulatory and adhesion molecules, a marker of mature DC, and IL-12. Dexamethasone increased expression of CD14, CD36, and CD68, molecules characteristic of monocytes/macrophages and induced CD14+CD83- cells, a subset distinct both from immature DC and mature DC. The effects were concentration-dependent, with ID50 values between 2 and 30 nM dexamethasone. Unlike T and B cells, in DC dexamethasone induced no apoptosis, although it suppressed activated nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB. Dexamethasone reduced the ability of DC to stimulate proliferation of allogeneic T cells in proportion to the level of CD14+CD83- cells in the population. CD83+ cells, isolated from dexamethasone-treated populations, retained the synthesis of IL-12 and the ability to stimulate proliferation of allogeneic T cells. Our data demonstrate that the dominant effect of the drug was redirecting differentiation of a subset of cells despite the presence of inflammatory cytokines. The observed ID50 values indicate that inhibition of DC differentiation might contribute significantly to in vivo immunosuppression by chronic administration of corticosteroids.
Effects of dexamethasone and cyclosporin A on the accumulation of eosinophils in acute cutaneous inflammation in the guinea-pig.[Pubmed:8735633]
Br J Pharmacol. 1996 May;118(2):317-24.
1. Eosinophils are thought to play an important role in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases and pharmacological suppression of their recruitment is considered to be of therapeutic benefit. In the present study we have assessed and compared the effects of treatment with dexamethasone and cyclosporin A on the accumulation of 111In-labelled eosinophils and local oedema formation in sites of acute inflammation in guinea-pig skin. 2. When injected locally 150 min prior to i.d. administration of antigen in a passive cutaneous anaphylactic (PCA) reaction, dexamethasone (10(-9) to 3 x 10(-7) mol per site) dose-dependently inhibited oedema formation by up to 50%. Similarly, oedema formation induced by PAF and lipopolysaccharide (LPS), but not by zymosan-activated plasma (ZAP), was significantly inhibited by dexamethasone. In contrast, 111In-eosinophil accumulation measured in response to i.d. injection of PAF, LPS and ZAP or in the PCA reaction was not altered. 3. Systemic treatment with dexamethasone (4 mg kg-1, i.v., 150 min pretreatment period) inhibited both oedema formation and 111In-eosinophil accumulation induced by PAF, ZAP, LPS and in the PCA reaction. 4. The effects of i.d. injection of cyclohexamide (2 x 10(-7) mol per site) on 111In-eosinophil accumulation and oedema formation induced by PAF, ZAP or in a PCA reaction were evaluated in order to assess the dependency of these responses on protein synthesis. Cycloheximide had no effect on the responses measured. In contrast, 111In-eosinophil accumulation, but oedema formation, induced by LPS was inhibited by 30%. 5. Acute (10 mg kg-1, i.v., 15 min pretreatment) or prolonged (10 mg kg-1, s.c. daily for 3 days) systemic treatment with cyclosporin A had no effect on 111In-eosinophil accumulation or oedema formation induced by PAF, ZAP, LPS or in the PCA reaction. 6. In conclusion, we demonstrate preferential inhibitory effects of dexamethasone on 111In-eosinophil accumulation according to its site of administration. In addition we show that dexamethasone inhibits protein synthesis-independent acute inflammation in guinea-pig skin. Finally, our results do not support the concept that eosinophils are an important cellular site of action for the inhibitory effects of cyclosporin A in a guinea-pig model of allergic inflammation.


