CyclophosphamideNitrogen mustard alkylating agent and prodrug. CAS# 50-18-0 |
- Daptomycin
Catalog No.:BCC1057
CAS No.:103060-53-3
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Clofarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1078
CAS No.:123318-82-1
- Ifosfamide
Catalog No.:BCC1164
CAS No.:3778-73-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 50-18-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2907 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H15Cl2N2O2P | M.Wt | 261.09 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 38 mg/mL (145.54 mM) H2O : 33.33 mg/mL (127.66 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
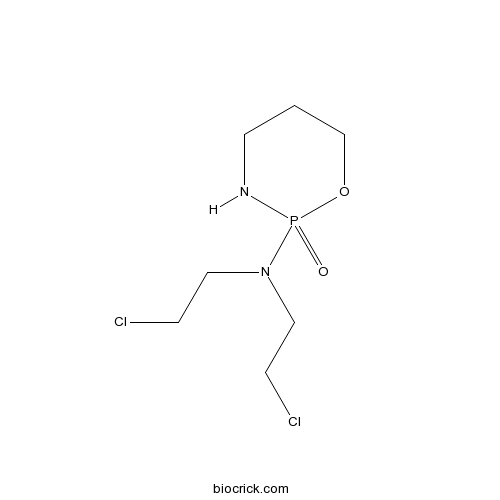
| Chemical Name | N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)-2-oxo-1,3,2$l^{5}-oxazaphosphinan-2-amine | ||
| SMILES | C1CNP(=O)(OC1)N(CCCl)CCCl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CMSMOCZEIVJLDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H15Cl2N2O2P/c8-2-5-11(6-3-9)14(12)10-4-1-7-13-14/h1-7H2,(H,10,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nitrogen mustard alkylating agent and prodrug. Phosphoramide mustard (active metabolite) forms DNA cross-links leading to cell death. Inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) through its degradation product acrolein. Chemotherapeutic for the treatment of breast cancer; regulates Bax and Bcl-2 expression when administered with etoposide in breast cancer cell lines. |

Cyclophosphamide Dilution Calculator

Cyclophosphamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8301 mL | 19.1505 mL | 38.301 mL | 76.6019 mL | 95.7524 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.766 mL | 3.8301 mL | 7.6602 mL | 15.3204 mL | 19.1505 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.383 mL | 1.915 mL | 3.8301 mL | 7.6602 mL | 9.5752 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0766 mL | 0.383 mL | 0.766 mL | 1.532 mL | 1.915 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0383 mL | 0.1915 mL | 0.383 mL | 0.766 mL | 0.9575 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Nitrogen mustard alkylating agent and prodrug. Phosphoramide mustard (active metabolite) forms DNA cross-links leading to cell death. Inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) through its degradation product acrolein. Chemotherapeutic for the treatment of
- Ergocalciferol
Catalog No.:BCN2208
CAS No.:50-14-6
- Mitomycin C
Catalog No.:BCC2388
CAS No.:50-07-7
- Cortisone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4771
CAS No.:50-04-4
- Dexamethasone (DHAP)
Catalog No.:BCC1184
CAS No.:50-02-2
- Guanidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4785
CAS No.:50-01-1
- Tioxolone
Catalog No.:BCC2316
CAS No.:4991-65-5
- 2,4-Pyridinedicarboxylic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC6483
CAS No.:499-80-9
- 5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN2633
CAS No.:499-75-2
- beta-Thujaplicin
Catalog No.:BCN3895
CAS No.:499-44-5
- IsoMaltose
Catalog No.:BCN8321
CAS No.:499-40-1
- Corydamine
Catalog No.:BCN3366
CAS No.:49870-84-0
- Erythroskyrin
Catalog No.:BCN1836
CAS No.:4987-27-3
- Corticosterone
Catalog No.:BCN2203
CAS No.:50-22-6
- Hydrocortisone
Catalog No.:BCN2192
CAS No.:50-23-7
- Prednisolone
Catalog No.:BCC4830
CAS No.:50-24-8
- Estriol
Catalog No.:BCN2235
CAS No.:50-27-1
- beta-Estradiol
Catalog No.:BCN2194
CAS No.:50-28-2
- Phenylbutazone
Catalog No.:BCC4822
CAS No.:50-33-9
- Thalidomide
Catalog No.:BCC2248
CAS No.:50-35-1
- Cocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1901
CAS No.:50-36-2
- Clomiphene citrate
Catalog No.:BCC4480
CAS No.:50-41-9
- Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
Catalog No.:BCC1186
CAS No.:50-44-2
- Estradiol Benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC4779
CAS No.:50-50-0
- Reserpine
Catalog No.:BCN4960
CAS No.:50-55-5
High-dose chemotherapy with thiotepa, busulfan, and cyclophosphamide and autologous stem cell transplantation for patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma in first complete remission.[Pubmed:28369839]
Cancer. 2017 Aug 15;123(16):3073-3079.
BACKGROUND: High-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (HDC-ASCT) is a therapeutic option for patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). To the authors' knowledge, data are limited regarding its use among patients in first complete remission (CR1) with the CNS-directed conditioning regimen of thiotepa, busulfan, and Cyclophosphamide (TBC). METHODS: A retrospective analysis of patients with PCNSL in CR1 who underwent transplantation using a TBC-based conditioning regimen at 2 academic institutions was performed. RESULTS: Forty-six consecutive patients who underwent HDC-ASCT while in CR1 were identified. The most common induction regimen was high-dose methotrexate plus temozolomide and rituximab (59%). No patients received whole-brain radiotherapy. A total of 40 patients (87%) received cytarabine before undergoing ASCT as either induction intensification, early consolidation therapy, or mobilization. The median time from diagnosis to transplantation was 6 months (range, 4-15 months). The median age of the patients at the time of transplantation was 59 years (range, 27-69 years). With a median follow-up of 2.7 years after ASCT (range, 6 months-7.5 years), the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 2-year overall survival and progression-free survival were 95% (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 80%-99%) and 92% (95% CI, 77%-97%), respectively. The most common toxicities were severe mucositis (35%) and bacterial infections occurring within 100 days of transplantation (35%). The estimated 2-year nonrecurrence mortality rate was 2.9% (95% CI, 0.2%-13.4%). CONCLUSIONS: HDC-ASCT with a CNS-directed conditioning regimen such as TBC should be considered for patients with PCNSL who are in CR1 because this approach is associated with encouraging disease control and survival in this select patient population. Cancer 2017;123:3073-79. (c) 2017 American Cancer Society.
Toxicity profile differences of adjuvant docetaxel/cyclophosphamide (TC) between Asian and Caucasian breast cancer patients.[Pubmed:28371190]
Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;13(6):372-378.
AIM: For early-stage breast cancer, four cycles of docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide (TC) was proven superior to doxorubicin plus Cyclophosphamide in the US Oncology 9375 trial. Given primary prophylactic antibiotics, 5% febrile neutropenia was recorded in a population comprising 75.5% Caucasians. Smaller trials and retrospective studies reviewing TC use in Asian patients did not produce similar incidence rates. This study aims to discover the variable hematological toxicities with TC use in Caucasian and Asian patients. METHODS: Breast cancer data was retrospectively reviewed for patients receiving adjuvant docetaxel 60-75 mg/m(2) plus Cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m(2) from six countries (China, Hong Kong, Japan, Taiwan, Italy, and United States). Similar number of patients with relatively balanced baseline characteristics were chosen for analysis of hematological and nonhematological toxicities and survival data. RESULTS: From March 2004 to July 2013, data of 227 patients (127 Asians and 100 Caucasian) patients were analyzed for treatment-related toxicities. During the four cycles of TC, Asians had a significantly higher rate of grade >/=2 neutropenia than Caucasians (45.7% vs 6.0%; P <0.001) and significantly more grade >/=3 neutropenia events were documented (respectively 30.7% vs 4.0%, P <0.001). The prophylactic use of G-CSF was similar; 26.0% in Asians and 28.0% in Caucasian (P = 0.764). There were no differences in nonhematological toxicities. No significant difference in disease-free survival was observed between Asians and Caucasians (log-rank P = 0.910). CONCLUSIONS: Ethnic differences in toxicity profile exist between Asian and Caucasian patients given adjuvant TC. Over 30% Asians but less than 5% Caucasians experienced grade >/=3 neutropenia.
Cyclophosphamide-based stem cell mobilization in relapsed multiple myeloma patients: A subgroup analysis from the phase III trial ReLApsE.[Pubmed:28370401]
Eur J Haematol. 2017 Jul;99(1):42-50.
OBJECTIVE: Analysis of the efficiency and toxicity of Cyclophosphamide-based stem cell mobilization in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma (RMM). METHODS: Peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) were mobilized with high dose Cyclophosphamide (2 g/m(2) daily on days 1 and 2) and G-CSF plus pre-emptive/rescue plerixafor in RMM patients (first to third relapse) treated within the ReLApsE trial of the German-Speaking Myeloma Multicenter Group (GMMG). RESULTS: Mobilization was initiated with high-dose Cyclophosphamide (HD-CY) and G-CSF in 30 patients. Fifteen patients received additional pre-emptive/rescue administration of plerixafor. Stem cell collection was successful (>/=2x10(6) CD34+ cells per kg bw) in 77% (23/30 patients). Patients with prior high-dose melphalan collected a significantly lower median total number of PBSCs than patients without prior high-dose melphalan (3.3x10(6) vs 17x10(6) CD34+ cells/kg bw). Toxicity of HD-CY was frequent with 12 serious adverse events (SAE) in 37% of patients (11/30 patients). Infections accounted for the majority of SAE reports. In two patients, SAEs were lethal (septic shock). CONCLUSIONS: These data proof feasibility of PBSC collection at relapse but emphasize the importance of collection and storage of additional PBSC transplants during first-line treatment when mobilization is more efficient and less toxic.
Regulation of BAX and BCL-2 expression in breast cancer cells by chemotherapy.[Pubmed:10481938]
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1999 May;55(2):107-17.
Optimizing chemotherapeutic drug delivery strategies relies, in part, on identification of the most clinically effective sequence, dose, and duration of drug exposure. The combination of dose intensive etoposide (VP-16) followed by Cyclophosphamide has clinical efficacy in the treatment of advanced breast cancer. However, molecular mechanisms that underlie the effectiveness of this combination of chemotherapeutic agents have not been investigated. In this study we investigated regulation of BAX and BCL-2 expression by VP-16 and Cyclophosphamide as a potential mechanism for the induction of breast cancer cell death induced by this regimen. There was a dose and time dependent increase in BAX expression in the breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, MDA-MB-435S, and MDA-MB-A231 following in vitro treatment with 50-100 microM VP-16. Elevation of BAX protein expression in the presence of VP-16 alone did not correlate with reduced viability or induction of apoptosis in MCF-7, MDA-MB-435S, or MDA-MB-A231. VP-16 did effectively block the breast cancer cell lines evaluated (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435S) at G2/M phase of the cell cycle, confirming activity of the drug in vitro. MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435S cells that were pre-treated with VP-16 and subsequently exposed to 1.0-12.0 microg/ml 4-hydroperoxyCyclophosphamide (4HC), an active metabolite of Cyclophosphamide, had markedly reduced viability when compared to matched controls treated with either VP-16 or 4HC individually. Consistent with this loss of viability, exposure of all three cell lines to the combination of VP-16 and 4HC resulted in higher BAX protein levels than those observed following treatment with either single agent. This combination of chemotherapeutic agents also resulted in reduced BCL-2 expression. These observations suggest that combination chemotherapy may derive its efficacy, in part, through coordinated regulation of specific gene products associated with apoptosis. Characterization of molecular events that underlie susceptibility of specific tumor cells to combination chemotherapeutic regimens may lead to additional improvements in treatment strategies for this disease.


