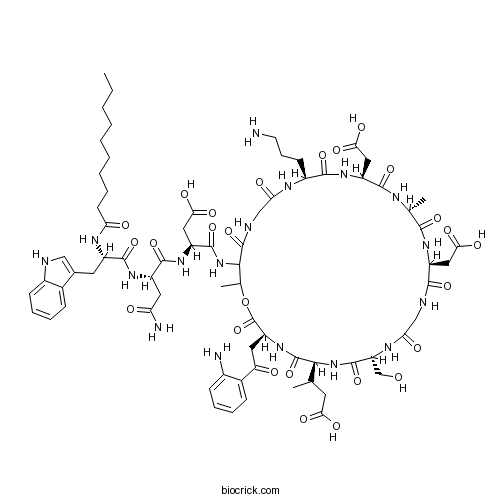
DaptomycinCalcium-dependent antibiotic CAS# 103060-53-3 |
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Clofarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1078
CAS No.:123318-82-1
- Ifosfamide
Catalog No.:BCC1164
CAS No.:3778-73-2
- Carboplatin
Catalog No.:BCC1170
CAS No.:41575-94-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 103060-53-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16129629 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C72H101N17O26 | M.Wt | 1620.67 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Cubicin; Cidecin; Deptomycin; Daptomycine | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 100 mg/mL (61.70 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (61.70 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCC(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)NC3C(OC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)CNC3=O)CCCN)CC(=O)O)C)CC(=O)O)CO)C(C)CC(=O)O)CC(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4N)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DOAKLVKFURWEDJ-OFNKPWESSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C72H101N17O26/c1-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-22-53(93)81-44(25-38-31-76-42-20-15-13-17-39(38)42)66(108)84-45(27-52(75)92)67(109)86-48(30-59(102)103)68(110)89-61-37(4)115-72(114)49(26-51(91)40-18-12-14-19-41(40)74)87-71(113)60(35(2)24-56(96)97)88-69(111)50(34-90)82-55(95)32-77-63(105)46(28-57(98)99)83-62(104)36(3)79-65(107)47(29-58(100)101)85-64(106)43(21-16-23-73)80-54(94)33-78-70(61)112/h12-15,17-20,31,35-37,43-50,60-61,76,90H,5-11,16,21-30,32-34,73-74H2,1-4H3,(H2,75,92)(H,77,105)(H,78,112)(H,79,107)(H,80,94)(H,81,93)(H,82,95)(H,83,104)(H,84,108)(H,85,106)(H,86,109)(H,87,113)(H,88,111)(H,89,110)(H,96,97)(H,98,99)(H,100,101)(H,102,103)/t35?,36-,37?,43+,44+,45+,46+,47+,48+,49+,50-,60+,61?/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Lipopeptide, calcium-dependent antibiotic. Exhibits potent bacteriocidal activity against most gram-positive bacteria in vitro and in vivo, including antibiotic-resistant strains such as MRSA and VRE. Disrupts plasma membrane function; activity results in membrane depolarization leading to inhibition of protein, DNA and RNA synthesis. |

Daptomycin Dilution Calculator

Daptomycin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.617 mL | 3.0851 mL | 6.1703 mL | 12.3406 mL | 15.4257 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1234 mL | 0.617 mL | 1.2341 mL | 2.4681 mL | 3.0851 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0617 mL | 0.3085 mL | 0.617 mL | 1.2341 mL | 1.5426 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0123 mL | 0.0617 mL | 0.1234 mL | 0.2468 mL | 0.3085 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0062 mL | 0.0309 mL | 0.0617 mL | 0.1234 mL | 0.1543 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Daptomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic which works against a broad spectrum of Gram-positive bacteria and it can work both in-vitro and in-vivo. It is a cyclic lipopeptide and many antibiotic resistant strains can be inhibited by daptomycin, such as meticillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (VISA) and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA).[1, 2]
The mode of action of Daptomycin would be through a calcium-dependent interaction with the cytoplasmic membrane, thus leading to the cell membrane depolarisation, ion loss and cell death.[2] Daptomycin can bind to the lipid tail of cell membrane of Gram-positive cells, then the following Ca2+ dependent insertion of daptomycin and oligomerization can cause a damage to the bacterial membrane potential, thus kills the cell very fast.[3]
References:
[1] Feng Wang, Ni-Ni Ren, Shuai Luo, Xiao-Xia Chen, Xu-Ming Mao, Yong-Quan Li. DptR2, a DeoR-type auto-regulator, is required for daptomycin production in Streptomyces roseosporus. Gene. 10 July 2014. 544(2): 208-215.
[2] Diixa Patel, Mashkur Husain, Celine Vidaillac, Molly E. Steed, Michael J. Rybak, Susan M. Seo, Glenn W. Kaatz. Mechanisms of in-vitro-selected daptomycin-non-susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. November 2011. 38(5): 442-446.
[3] Yong He, Jing Li, Nin Yin, Prudencio S. Herradura, Larry Martel, Yanzhi Zhang, Andre L. Pearson, Vidya Kulkarni, Carmela Mascio. Reduced pulmonary surfactant interaction of daptomycin analogs via tryptophan replacement with alternative amino acids. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 1 October 2012. 22(19): 6248-6251.
- Ethyl 3-(pyridin-2-ylamino)propanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8973
CAS No.:103041-38-9
- CTCE 9908
Catalog No.:BCC6366
CAS No.:1030384-98-5
- MK-4305
Catalog No.:BCC1760
CAS No.:1030377-33-3
- Alterlactone
Catalog No.:BCN7261
CAS No.:1030376-89-6
- Dehydroheliobuphthalmin
Catalog No.:BCN5844
CAS No.:103001-05-4
- Acetaminophen
Catalog No.:BCC5269
CAS No.:103-90-2
- 4'-Methylacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8714
CAS No.:103-89-9
- Phenylacetic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8349
CAS No.:103-82-2
- N-Methylbenzylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1790
CAS No.:103-67-3
- Scutebarbatine M
Catalog No.:BCN8327
CAS No.:960302-92-5
- Benzyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN5042
CAS No.:103-41-3
- Ethyl cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN5044
CAS No.:103-36-6
- MK-8245
Catalog No.:BCC2299
CAS No.:1030612-90-8
- AS 2034178
Catalog No.:BCC7996
CAS No.:1030846-42-4
- Bakuchiol
Catalog No.:BCN5845
CAS No.:10309-37-2
- 2-Amino-6-chloropurine
Catalog No.:BCC8540
CAS No.:10310-21-1
- Kinetensin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5845
CAS No.:103131-69-7
- ABT-046
Catalog No.:BCC1326
CAS No.:1031336-60-3
- 4-(4-(Dimethylamino)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxybutyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)benzonitrile hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC8648
CAS No.:103146-26-5
- UNC 3230
Catalog No.:BCC5618
CAS No.:1031602-63-7
- 14-Norpseurotin A
Catalog No.:BCN7262
CAS No.:1031727-34-0
- Pranlukast
Catalog No.:BCC4827
CAS No.:103177-37-3
- Fmoc-Tyr(3,5-I2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3264
CAS No.:103213-31-6
- Fmoc-Cys(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3479
CAS No.:103213-32-7
Effect of Daptomycin Dose on the Outcome of Vancomycin-Resistant, Daptomycin-Susceptible Enterococcus faecium Bacteremia.[Pubmed:28329222]
Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Apr 15;64(8):1026-1034.
Background: Treatment options for vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) bloodstream infection (BSI) are limited. Daptomycin, although not currently approved for this indication, is frequently used for the treatment of VRE-BSI. Its optimal dose still needs to be determined. Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational, cohort study during 2010-2015. We included patients who received a Daptomycin dose of >/=6 mg/kg for the treatment of VRE-BSI caused by Daptomycin-susceptible VRE. The primary endpoint was 14-day mortality, and multivariable logistic regression was performed for outcome analysis. Results: We included 112 patients treated with Daptomycin for VRE-BSI and with evaluable clinical outcomes. The Daptomycin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was 4 mg/L in 78 (69.6%) and Daptomycin dose of <7 mg/kg, 17/51 (33.3%) for a dose of 7-9 mg/kg, and 5/25 (20%) for a dose of >/=9 mg/kg (P = .05). The best outcomes were associated with a Daptomycin dose of >/=9 mg/kg compared to doses of <7 mg/kg (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 10.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.25-49.62; P=.003) and 7-9 mg/kg (aOR, 5.01; 95% CI, 1.14-21.98; P=.03). There was no significant difference in mortality with respect to the Daptomycin MIC. There was no association between Daptomycin dose and elevated creatinine kinase. Conclusion: Higher Daptomycin doses (>/=9 mg/kg) were associated with lower mortality in patients with VRE-BSI. Our results suggest that higher Daptomycin doses need to be considered for VRE-BSI treatment.
Effect of Continuous and Sequential Therapy among Veterans Receiving Daptomycin or Linezolid for Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Bacteremia.[Pubmed:28264856]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Apr 24;61(5). pii: AAC.02216-16.
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium bloodstream infections (VREF-BSI) cause significant mortality, highlighting the need to optimize their treatment. We compared the effectiveness and safety of Daptomycin (DAP) and linezolid (LZD) as continuous or sequential therapy for VREF-BSI in a national, retrospective, propensity score (PS)-matched cohort study of hospitalized Veterans Affairs patients (2004 to 2014). We compared clinical outcomes and adverse events among patients treated with continuous LZD, continuous DAP, or sequential LZD followed by DAP (LZD-to-DAP). Secondarily, we analyzed the impact of infectious diseases (ID) consultation and source of VREF-BSI. A total of 2,630 patients were included in the effectiveness analysis (LZD [n = 1,348], DAP [n = 1,055], LZD-to-DAP [n = 227]). LZD was associated with increased 30-day mortality versus DAP (risk ratio [RR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.22; P = 0.042). After PS matching, this relationship persisted (RR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.26; P = 0.015). LZD-to-DAP switchers had lower mortality than those remaining on LZD (RR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.63; P = 0.021), suggesting a benefit may still be derived with sequential therapy. LZD-treated patients experienced more adverse events, including a >/=50% reduction in platelets (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.11; P = 0.001). DAP was associated with lower mortality than was LZD in patients with endocarditis (RR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.41; P = 0.024); however, there was no statistically significant association between treatment group and mortality with regard to other sources of infection. Therefore, source of infection appears to be important in selection of patients most likely to benefit from DAP over LZD.
An Acyl-Linked Dimer of Daptomycin Is Strongly Inhibited by the Bacterial Cell Wall.[Pubmed:28350438]
ACS Infect Dis. 2017 Jul 14;3(7):462-466.
The lipopeptide antibiotic Daptomycin is active against Gram-positive pathogens. It permeabilizes bacterial cell membranes, which involves the formation of membrane-associated oligomers. We here studied a dimer of Daptomycin whose two subunits were linked through a bivalent aliphatic acyl chain. Unexpectedly, the dimer had very low activity on vegetative Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis cells. However, activity resembled that of monomeric Daptomycin on liposomes and on B. subtilis L-forms. These findings underscore the importance of the bacterial cell wall in Daptomycin resistance.
Targeted Antibiotic Delivery: Selective Siderophore Conjugation with Daptomycin Confers Potent Activity against Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Both in Vitro and in Vivo.[Pubmed:28287735]
J Med Chem. 2017 Jun 8;60(11):4577-4583.
In order to address the dire need for new antibiotics to treat specific strains of drug resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections, a mixed ligand analog of the natural Acinetobacter baumannii selective siderophore, fimsbactin, was coupled to Daptomycin, a Gram-positive only antibiotic. The resulting conjugate 11 has potent activity against multidrug resistant strains of A. baumannii both in vitro and in vivo. The study also indicates that conjugation of siderophores to "drugs" that are much larger than the siderophore (iron transport agent) itself facilitates active uptake that circumvents the normal permeability problems in Gram-negative bacteria. The results demonstrate the ability to extend activity of a normally Gram-positive only antibiotic to create a potent and targeted Gram-negative antibiotic using a bacterial iron transport based sideromycin Trojan horse strategy.
Daptomycin, a bacterial lipopeptide synthesized by a nonribosomal machinery.[Pubmed:20522545]
J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 3;285(36):27501-8.
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is a branched cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic of nonribosomal origin and the prototype of the acidic lipopeptide family. It was approved in 2003 for the nontopical treatment of skin structure infections caused by gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and in 2006 for the treatment of bacteremia. Understanding the ribosome-independent biosynthesis of Daptomycin assembly will provide opportunities for the generation of Daptomycin derivatives with an altered pharmaceutical spectrum to address upcoming Daptomycin-resistant pathogens. Herein, the structural properties of Daptomycin, its biosynthesis, recent efforts for the generation of structural diversity, and its proposed mode of action are discussed.
Daptomycin: a lipopeptide antibiotic for the treatment of serious Gram-positive infections.[Pubmed:15705644]
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Mar;55(3):283-8.
Infections caused by drug-resistant pathogens are on the rise. Daptomycin, a cyclic lipopeptide with activity against most Gram-positive pathogens, including vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, is a newly US-FDA approved antimicrobial for complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI). Daptomycin has a unique mechanism of action that results in destruction of the membrane potential. The rapid bactericidal activity of Daptomycin makes it an attractive antibiotic for serious Gram-positive infections.
Structural transitions as determinants of the action of the calcium-dependent antibiotic daptomycin.[Pubmed:15271353]
Chem Biol. 2004 Jul;11(7):949-57.
Daptomycin is a cyclic anionic lipopeptide antibiotic recently approved for the treatment of complicated skin infections (Cubicin). Its function is dependent on calcium (as Ca2+). Circular dichroism spectroscopy indicated that Daptomycin experienced two structural transitions: a transition upon interaction of Daptomycin with Ca2+, and a further transition upon interaction with Ca2+ and the bacterial acidic phospholipid, phosphatidyl glycerol. The Ca2+-dependent insertion of Daptomycin into model membranes promoted mild and more pronounced perturbations as assessed by the increase of lipid flip-flop and membrane leakage, respectively. The NMR structure of Daptomycin indicated that Ca2+ induced a conformational change in Daptomycin that increased its amphipathicity. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the association of Ca2+ with Daptomycin permits it to interact with bacterial membranes with effects that are similar to those of the cationic antimicrobial peptides.


