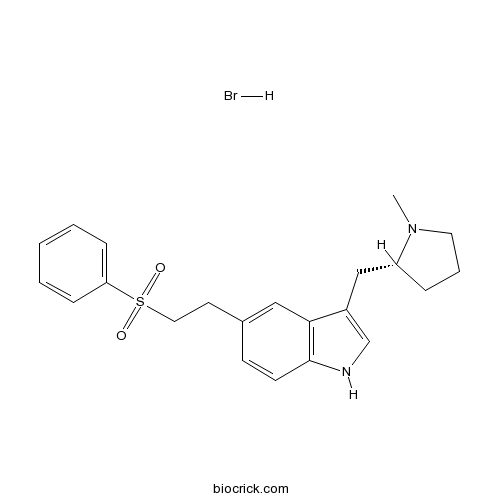
Eletriptan HBrOrally active, selective 5-HT1B/1D agonist CAS# 177834-92-3 |
- XL-888
Catalog No.:BCC2339
CAS No.:1149705-71-4
- MKT 077
Catalog No.:BCC6241
CAS No.:147366-41-4
- Alvespimycin
Catalog No.:BCC1346
CAS No.:467214-20-6
- NVP-BEP800
Catalog No.:BCC2129
CAS No.:847559-80-2
- BIIB021
Catalog No.:BCC2124
CAS No.:848695-25-0
- PF-04929113 (SNX-5422)
Catalog No.:BCC2130
CAS No.:908115-27-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 177834-92-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 656631 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H27BrN2O2S | M.Wt | 463.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-[2-(benzenesulfonyl)ethyl]-3-[[(2R)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl]-1H-indole;hydrobromide | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCCC1CC2=CNC3=C2C=C(C=C3)CCS(=O)(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4.Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UTINOWOSWSPFLJ-FSRHSHDFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H26N2O2S.BrH/c1-24-12-5-6-19(24)15-18-16-23-22-10-9-17(14-21(18)22)11-13-27(25,26)20-7-3-2-4-8-20;/h2-4,7-10,14,16,19,23H,5-6,11-13,15H2,1H3;1H/t19-;/m1./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Orally active, selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist. Produces a dose-dependent reduction in carotid artery blood flow in vivo. Displays antimigraine activity. |

Eletriptan HBr Dilution Calculator

Eletriptan HBr Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1578 mL | 10.7891 mL | 21.5782 mL | 43.1565 mL | 53.9456 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4316 mL | 2.1578 mL | 4.3156 mL | 8.6313 mL | 10.7891 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2158 mL | 1.0789 mL | 2.1578 mL | 4.3156 mL | 5.3946 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0432 mL | 0.2158 mL | 0.4316 mL | 0.8631 mL | 1.0789 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1079 mL | 0.2158 mL | 0.4316 mL | 0.5395 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Eletriptan hydrobromide is a orally active, selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist.
- Calystegine A6
Catalog No.:BCN1886
CAS No.:177794-04-6
- Calystegine N1
Catalog No.:BCN1866
CAS No.:177794-03-5
- Proxyfan oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7378
CAS No.:177708-09-7
- NKP608
Catalog No.:BCC1802
CAS No.:177707-12-9
- MNITMT
Catalog No.:BCC7382
CAS No.:177653-76-8
- Glycerol 1-(26-hydroxyhexacosanoate)
Catalog No.:BCN1131
CAS No.:177602-14-1
- ZK 164015
Catalog No.:BCC7272
CAS No.:177583-70-9
- Flavokawain B
Catalog No.:BCN3568
CAS No.:1775-97-9
- 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8537
CAS No.:1775-95-7
- Aglain C
Catalog No.:BCN6604
CAS No.:177468-85-8
- DBeQ
Catalog No.:BCC3916
CAS No.:177355-84-9
- Aglain B
Catalog No.:BCN6636
CAS No.:177262-32-7
- Boc-His-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3398
CAS No.:17791-52-5
- Clematichinenoside C
Catalog No.:BCN7850
CAS No.:177912-24-2
- Sauchinone
Catalog No.:BCN2299
CAS No.:177931-17-8
- Allopurinol Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4886
CAS No.:17795-21-0
- Fmoc-D-Phe(4-NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3278
CAS No.:177966-63-1
- Aescigenin
Catalog No.:BCC8293
CAS No.:17806-68-7
- Nociceptin (1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5749
CAS No.:178064-02-3
- Bacopasaponin C
Catalog No.:BCC8124
CAS No.:178064-13-6
- 3-Deoxyzinnolide
Catalog No.:BCN4799
CAS No.:17811-32-4
- H-Asp-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2884
CAS No.:17812-32-7
- 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2910
CAS No.:17817-31-1
- Hardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1132
CAS No.:1782-65-6
Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of eletriptan hydrobromide in healthy Korean subjects.[Pubmed:29497279]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Feb 19;12:331-337.
Background: Migraine is one of the most common headache disorders that greatly affect the quality of life. Selective serotonin (5-HT) receptor agonists such as triptamine-based drugs called triptans are used for treatment of migraine. Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetic (PK) and tolerability profiles of eletriptan hydrobromide (Eletriptan HBr), a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine (also known as serotonin) 1B/1D receptor agonist, in Koreans and compare the results to those observed in non-Koreans in a previously published study. Patients and methods: A randomized, open-label, single, and repeated-dose study was conducted in 16 healthy Korean male subjects using a four-treatment, four-period, and four-sequence crossover design (NCT01139515). The subjects received one of the following four treatments in each period: a single dose of 20, 40, 80 mg Eletriptan HBr or a repeated oral dose of 40 mg 2 h apart. Blood samples were collected before and up to 26 h after dosing for quantification of plasma eletriptan concentration by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry. The PK parameters were estimated using noncompartmental methods. Ethnicity differences between Korean and non-Korean subjects were identified using geometric mean ratios and 90% confidence intervals (CIs) of dose-normalized maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and dose-normalized area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from 0 h to the last measurable concentration (AUC0-t). Results: After single-dose administration of Eletriptan HBr to Korean subjects, the mean Cmax and AUC0-t increased linearly with dose. Comparable total systemic exposures were observed in the 2 h apart 40 mg repeated and single 80 mg dose. The geometric mean ratios (90% CIs) of the dose-normalized Cmax and AUC0-t of Korean subjects were similar to those of non-Korean subjects reported in the literature. The adverse events observed were transient and mild in severity. Conclusion: Eletriptan HBr showed linear PK and was well tolerated in Korean subjects. The PK and tolerability of Eletriptan HBr did not differ between Korean and non-Korean subjects.
The in vivo pharmacological profile of eletriptan (UK-116,044): a potent and novel 5-HT(1B/1D) receptor agonist.[Pubmed:10856450]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jun 9;398(1):73-81.
The anti-migraine drug, eletriptan [(R)-3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-5-[2-(phenylsulphonyl )ethyl]-1 H-indole; UK-116,044], is a novel 5-HT(1B/1D) receptor agonist. In this paper, the regional vasoconstrictor profile of eletriptan, in comparison with sumatriptan, was examined in the anaesthetised dog. The inhibitory actions of eletriptan on neurogenic inflammation in rat dura mater were also assessed. In the anaesthetised dog, eletriptan (1-1000 microg kg(-1) i.v.) produced a dose-dependent reduction of carotid arterial blood flow with a similar potency and maximum effect to sumatriptan (ED(50) values: eletriptan and sumatriptan, 12 and 9 microg kg(-1), i.v., respectively). However, eletriptan exhibited a significantly lower potency than sumatriptan in reducing coronary artery diameter (ED(50) values: 63 and 19 microg kg(-1), i.v., respectively, P<0.05). In the femoral circulation, sumatriptan caused a significant reduction in arterial blood flow (ED(50) 35 microg kg(-1) i.v.) whereas eletriptan (1-1000 microg kg(-1) i.v.) had no significant effect upon femoral arterial blood flow when compared to vehicle-treated animals. In rats, eletriptan (30-300 microg kg(-1) i.v.) administered prior to electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion produced a dose-related and complete inhibition of plasma protein extravasation in the dura mater (mean extravasation ratio: control 1.9; eletriptan 1.0, minimum effective dose 100 microg kg(-1), P<0.05). The potency and maximum effect of eletriptan was identical to that of sumatriptan in this model. When administered during a period of continual stimulation of the trigeminal nerve, eletriptan (100 microg kg(-1) i.v.) produced a complete inhibition of plasma protein extravasation. The ability to reduce canine carotid arterial blood flow and inhibit neurogenic inflammation in rat dura mater suggests that vascular and neurogenic mechanisms may contribute to eletriptan's clinical efficacy in migraine patients. In addition, eletriptan exhibits some selectivity for reducing carotid arterial blood flow when compared with femoral arterial blood flow and coronary artery diameter, in the anaesthetised dog.
Characterisation of the 5-HT receptor binding profile of eletriptan and kinetics of [3H]eletriptan binding at human 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors.[Pubmed:10193663]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Mar 5;368(2-3):259-68.
The affinity of eletriptan ((R)-3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-5-[2-(phenylsulphonyl )ethyl]-1H-indole) for a range of 5-HT receptors was compared to values obtained for other 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists known to be effective in the treatment of migraine. Eletriptan, like sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan and rizatriptan had highest affinity for the human 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D and putative 5-ht1f receptor. Kinetic studies comparing the binding of [3H]eletriptan and [3H]sumatriptan to the human recombinant 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors expressed in HeLa cells revealed that both radioligands bound with high specificity (>90%) and reached equilibrium within 10-15 min. However, [3H]eletriptan had over 6-fold higher affinity than [3H]sumatriptan at the 5-HT1D receptor (K(D)): 0.92 and 6.58 nM, respectively) and over 3-fold higher affinity than [3H]sumatriptan at the 5-HT1B receptor (K(D): 3.14 and 11.07 nM, respectively). Association and dissociation rates for both radioligands could only be accurately determined at the 5-HT1D receptor and then only at 4 degrees C. At this temperature, [3H]eletriptan had a significantly (P<0.05) faster association rate (K(on) 0.249 min(-1) nM(-1)) than [3H]sumatriptan (K(on) 0.024 min(-1) nM(-1)) and a significantly (P<0.05) slower off-rate (K(off) 0.027 min(-1) compared to 0.037 min(-1) for [3H]sumatriptan). These data indicate that eletriptan is a potent ligand at the human 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, and 5-ht1f receptors and are consistent with its potent vasoconstrictor activity and use as a drug for the acute treatment of migraine headache.


