ZK 164015Potent estrogen receptor antagonist CAS# 177583-70-9 |
- Zoledronic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC1067
CAS No.:118072-93-8
- Go 6976
Catalog No.:BCC3703
CAS No.:136194-77-9
- Enzastaurin (LY317615)
Catalog No.:BCC1100
CAS No.:170364-57-5
- Chelerythrine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN8322
CAS No.:3895-92-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 177583-70-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9806489 | Appearance | Powder |
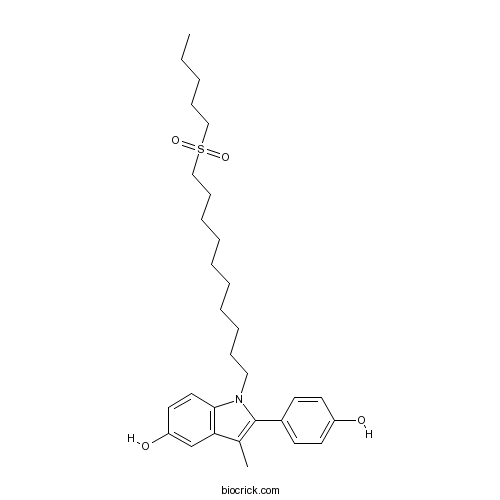
| Formula | C30H43NO4S | M.Wt | 513.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in ethanol and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1-(10-pentylsulfonyldecyl)indol-5-ol | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCS(=O)(=O)CCCCCCCCCCN1C2=C(C=C(C=C2)O)C(=C1C3=CC=C(C=C3)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LYJSJVYJLZOMCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H43NO4S/c1-3-4-12-21-36(34,35)22-13-10-8-6-5-7-9-11-20-31-29-19-18-27(33)23-28(29)24(2)30(31)25-14-16-26(32)17-15-25/h14-19,23,32-33H,3-13,20-22H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent estrogen receptor silent antagonist. Inhibits 17β-estradiol stimulation of luciferase activity (IC50 = 0.025 μM); potently inhibits the growth of estrogen-sensitive human MCF-7 breast cancer cells in vitro (IC50 ~ 1 nM). |

ZK 164015 Dilution Calculator

ZK 164015 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9465 mL | 9.7327 mL | 19.4655 mL | 38.931 mL | 48.6637 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3893 mL | 1.9465 mL | 3.8931 mL | 7.7862 mL | 9.7327 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1947 mL | 0.9733 mL | 1.9465 mL | 3.8931 mL | 4.8664 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1947 mL | 0.3893 mL | 0.7786 mL | 0.9733 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0195 mL | 0.0973 mL | 0.1947 mL | 0.3893 mL | 0.4866 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Flavokawain B
Catalog No.:BCN3568
CAS No.:1775-97-9
- 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8537
CAS No.:1775-95-7
- Aglain C
Catalog No.:BCN6604
CAS No.:177468-85-8
- DBeQ
Catalog No.:BCC3916
CAS No.:177355-84-9
- Aglain B
Catalog No.:BCN6636
CAS No.:177262-32-7
- 26-O-Acetylsootepin A
Catalog No.:BCN7699
CAS No.:1772588-99-4
- R 568 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7781
CAS No.:177172-49-5
- Ambrisentan
Catalog No.:BCC4887
CAS No.:177036-94-1
- 2alpha,19alpha-Dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7406
CAS No.:176983-21-4
- LY 320135
Catalog No.:BCC7346
CAS No.:176977-56-3
- CCT007093
Catalog No.:BCC5147
CAS No.:176957-55-4
- Metergoline
Catalog No.:BCC6709
CAS No.:17692-51-2
- Glycerol 1-(26-hydroxyhexacosanoate)
Catalog No.:BCN1131
CAS No.:177602-14-1
- MNITMT
Catalog No.:BCC7382
CAS No.:177653-76-8
- NKP608
Catalog No.:BCC1802
CAS No.:177707-12-9
- Proxyfan oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7378
CAS No.:177708-09-7
- Calystegine N1
Catalog No.:BCN1866
CAS No.:177794-03-5
- Calystegine A6
Catalog No.:BCN1886
CAS No.:177794-04-6
- Eletriptan HBr
Catalog No.:BCC5039
CAS No.:177834-92-3
- Boc-His-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3398
CAS No.:17791-52-5
- Clematichinenoside C
Catalog No.:BCN7850
CAS No.:177912-24-2
- Sauchinone
Catalog No.:BCN2299
CAS No.:177931-17-8
- Allopurinol Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4886
CAS No.:17795-21-0
- Fmoc-D-Phe(4-NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3278
CAS No.:177966-63-1
On the Structure-Property Relationships of Cation-Exchanged ZK-5 Zeolites for CO2 Adsorption.[Pubmed:28067993]
ChemSusChem. 2017 Mar 9;10(5):946-957.
The CO2 adsorption properties of cation-exchanged Li-, Na-, K-, and Mg-ZK-5 zeolites were correlated to the molecular structures determined by Rietveld refinements of synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction patterns. Li-, K-, and Na-ZK-5 all exhibited high isosteric heats of adsorption (Qst ) at low CO2 coverage, with Na-ZK-5 having the highest Qst (ca. 49 kJ mol(-1) ). Mg(2+) was located at the center of the zeolite hexagonal prism with the cation inaccessible to CO2 , leading to a much lower Qst (ca. 30 kJ mol(-1) ) and lower overall uptake capacity. Multiple CO2 adsorption sites were identified at a given CO2 loading amount for all four cation-exchanged ZK-5 adsorbents. Site A at the flat eight-membered ring windows and site B/B* in the gamma-cages were the primary adsorption sites in Li- and Na-ZK-5 zeolites. Relatively strong dual-cation adsorption sites contributed significantly to an enhanced electrostatic interaction for CO2 in all ZK-5 samples. This interaction gives rise to a migration of Li(+) and Mg(2+) cations from their original locations at the center of the hexagonal prisms toward the alpha-cages, in which they interact more strongly with the adsorbed CO2 .
K+ exchanged zeolite ZK-4 as a highly selective sorbent for CO2.[Pubmed:25072512]
Langmuir. 2014 Aug 19;30(32):9682-90.
Adsorbents with high capacity and selectivity for adsorption of CO2 are currently being investigated for applications in adsorption-driven separation of CO2 from flue gas. An adsorbent with a particularly high CO2-over-N2 selectivity and high capacity was tested here. Zeolite ZK-4 (Si:Al approximately 1.3:1), which had the same structure as zeolite A (LTA), showed a high CO2 capacity of 4.85 mmol/g (273 K, 101 kPa) in its Na(+) form. When approximately 26 at. % of the extraframework cations were exchanged for K(+) (NaK-ZK-4), the material still adsorbed a large amount of CO2 (4.35 mmol/g, 273 K, 101 kPa), but the N2 uptake became negligible (<0.03 mmol/g, 273 K, 101 kPa). The majority of the CO2 was physisorbed on zeolite ZK-4 as quantified by consecutive volumetric adsorption measurements. The rate of physisorption of CO2 was fast, even for the highly selective sample. The molecular details of the sorption of CO2 were revealed as well. Computer modeling (Monte Carlo, molecular dynamics simulations, and quantum chemical calculations) allowed us to partly predict the behavior of fully K(+) exchanged zeolite K-ZK-4 upon adsorption of CO2 and N2 for Si:Al ratios up to 4:1. Zeolite K-ZK-4 with Si:Al ratios below 2.5:1 restricted the diffusion of CO2 and N2 across the cages. These simulations could not probe the delicate details of the molecular sieving of CO2 over N2. Still, this study indicates that zeolites NaK-ZK-4 and K-ZK-4 could be appealing adsorbents with high CO2 uptake ( approximately 4 mmol/g, 101 kPa, 273 K) and a kinetically enhanced CO2-over-N2 selectivity.
A phase II trial of PTK787/ZK 222584 in recurrent or progressive radiation and surgery refractory meningiomas.[Pubmed:24449400]
J Neurooncol. 2014 Mar;117(1):93-101.
When surgery and radiation are no longer treatment options, salvage systemic therapy has been used for recurrent meningiomas with little compelling evidence to suggest effectiveness. Patients with surgery and radiation refractory recurrent meningiomas were treated with the oral multifunctional tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK787) at a dose of 500 mg twice a day. Each treatment cycle was 4 weeks with MRI done every 8 weeks. Twenty-five patients (14 men; 11 women) with a median age of 59 years and KPS of 80 were treated. Meningioma WHO Grade was I in 2 patients, II in 14 patients and III in 8 patients; 1 patient had a hemangiopericytoma. All patients had prior surgery, external beam radiation therapy or radiosurgery and 11 patients prior systemic chemotherapy. Median number of cycles of PTK 787 administered was 4 (range <1-22). Best response in the 22 evaluable patients was stable disease in 15 (68.2 %). Predominant PTK787 related toxicities included fatigue (60 %), hypertension (24 %) and elevated transaminases (24 %). Grade II patients had a progression free survival (PFS)-6 of 64.3 %, a median PFS of 6.5 months and an overall survival (OS) of 26.0 months; grade III patients had a PFS-6 of 37.5 %, median PFS of 3.6 months and OS 23 months. PTK787 was modestly toxic at the dose of 500 mg administered twice per day. Activity as determined by PFS-6 suggests that targeting PDGF/VEGF pathway warrants further investigation.
Development of an efficient electroporation method for iturin A-producing Bacillus subtilis ZK.[Pubmed:25837631]
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Apr 1;16(4):7334-51.
In order to efficiently introduce DNA into B. subtilis ZK, which produces iturin A at a high level, we optimized seven electroporation conditions and explored an efficient electroporation method. Using the optimal conditions, the electroporation efficiency was improved to 1.03 x 10(70 transformants/mug of DNA, an approximately 10,000-fold increase in electroporation efficiency. This efficiency is the highest electroporation efficiency for B. subtilis and enables the construction of a directed evolution library or the knockout of a gene in B. subtilis ZK for molecular genetics studies. In the optimization process, the combined effects of three types of wall-weakening agents were evaluated using a response surface methodology (RSM) design, which led to a two orders of magnitude increase in electroporation efficiency. To the best of our limited knowledge, this study provides the first demonstration of using an RSM design for optimization of the electroporation conditions for B. subtilis. To validate the electroporation efficiency, a case study was performed and a gene (rapC) was inactivated in B. subtilis ZK using a suicide plasmid pMUTIN4. Moreover, we found that the rapC mutants exhibited a marked decrease in iturin A production, suggesting that the rapC gene was closely related to the iturin A production.
Synthesis and biological evaluation of stilbene-based pure estrogen antagonists.[Pubmed:15324884]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 20;14(18):4659-63.
Replacement of one of the ethyl substituents in diethylstilbestrol by side chains with functional groups converted this potent estrogen into pure antiestrogens with the potential for the treatment of breast cancer. These agents completely suppressed estrogen receptor-mediated gene activation and inhibited the growth of estrogen-sensitive MCF-7 breast cancer cells in submicromolar concentrations. The most potent derivative displayed similar activity as fulvestrant (ICI 182,780) in vitro and in the mouse uterine weight test. Obviously, the stilbene structure can act as a substitute for estradiol in the development of pure estrogen antagonists.
The anti-estrogen hydroxytamoxifen is a potent antagonist in a novel yeast system.[Pubmed:10614829]
Biol Chem. 1999 Nov;380(11):1341-5.
The budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been used extensively as a biological 'test tube' to study the regulation of the human estrogen receptor (ER) alpha. However, anti-estrogens, which are of great importance as therapeutic agents and research tools, fail to antagonize the activation by estrogen in yeast. Here, we have surveyed the antagonistic potential of five different anti-estrogens of diverse chemical nature. While they all act as agonists for wild-type ERalpha, we have established a novel yeast assay system for anti-estrogens, in which at least the commonly used anti-estrogen hydroxytamoxifen is a potent antagonist.


