Go 6976PKCα/PKCβ1 inhibitor CAS# 136194-77-9 |
- Ro 31-8220
Catalog No.:BCC4295
CAS No.:125314-64-9
- Go 6983
Catalog No.:BCC3705
CAS No.:133053-19-7
- Sotrastaurin (AEB071)
Catalog No.:BCC3857
CAS No.:425637-18-9
- Dequalinium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4998
CAS No.:522-51-0
- Staurosporine
Catalog No.:BCC3612
CAS No.:62996-74-1
- K-252c
Catalog No.:BCC3706
CAS No.:85753-43-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 136194-77-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3501 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H18N4O | M.Wt | 378.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
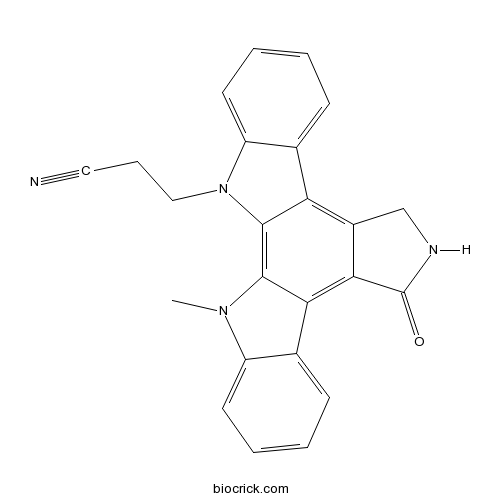
| SMILES | CN1C2=CC=CC=C2C3=C4C(=C5C6=CC=CC=C6N(C5=C31)CCC#N)CNC4=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VWVYILCFSYNJHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H18N4O/c1-27-17-9-4-2-7-14(17)20-21-16(13-26-24(21)29)19-15-8-3-5-10-18(15)28(12-6-11-25)23(19)22(20)27/h2-5,7-10H,6,12-13H2,1H3,(H,26,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor (IC50 = 7.9 nM). Discriminates between Ca2+-dependent and -independent isoforms of PKC in vitro; selectively inhibits PKCα and PKCβ1 (IC50 values are 2.3 and 6.2 nM respectively). Does not inhibit the activity of PKCδ, -ε, or -ζ (IC50 > 3μM). Also inhibits TrkA, TrkB, JAK2 and JAK3 tyrosine kinases (IC50 values are 5, 30, 130 and 370 nM respectively), PKCμ (PKD1) and the mitotic spindle checkpoint. |

Go 6976 Dilution Calculator

Go 6976 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6425 mL | 13.2125 mL | 26.425 mL | 52.8499 mL | 66.0624 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5285 mL | 2.6425 mL | 5.285 mL | 10.57 mL | 13.2125 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2642 mL | 1.3212 mL | 2.6425 mL | 5.285 mL | 6.6062 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0528 mL | 0.2642 mL | 0.5285 mL | 1.057 mL | 1.3212 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0264 mL | 0.1321 mL | 0.2642 mL | 0.5285 mL | 0.6606 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Go 6976 is a selective inhibitor of PKC with IC50 value of 20 nM [1] [2].
Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of protein kinase enzymes and plays an important role in controlling the function of other proteins by the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins [1-3].
Go 6976 is a potent PKC inhibitor and has a more potent activity with the reported PKC inhibitor H-7. When tested with nRT cells, Go 6976 showed a marked decrease the baseline T-current amplitude nearly 40% at the dose of 10 μM by inhibiting Ca2+-dependent PKC pathway [3]. In T cell lines ACH-2 and U1 infected with HIV-1, Go 6976 treatment effectively blocked viral transcription induced by Bryostain 1 or tumor necrosis factor α which lead to the inhibition of intracellular viral protein synthesis and viral shedding and also blocked IL-6 mediated posttranscriptional inducetion of viral protein [2].
It is also reported that Go 6976 is a potent inhibitor to EGFR and FLT3with IC50 value ranges from 0.033 nM to 3.3 μM and 0.7 nM, respectively [4] [5].
References:
[1]. Gschwendt, M., et al., Inhibition of protein kinase C mu by various inhibitors. Differentiation from protein kinase c isoenzymes. FEBS Lett, 1996. 392(2): p. 77-80.
[2]. Qatsha, K.A., et al., Go 6976, a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C, is a potent antagonist of human immunodeficiency virus 1 induction from latent/low-level-producing reservoir cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1993. 90(10): p. 4674-8.
[3]. Joksovic, P.M., et al., Mechanisms of inhibition of T-type calcium current in the reticular thalamic neurons by 1-octanol: implication of the protein kinase C pathway. Mol Pharmacol, 2010. 77(1): p. 87-94.
[4]. Taube, E., et al., A novel treatment strategy for EGFR mutant NSCLC with T790M-mediated acquired resistance. Int J Cancer, 2012. 131(4): p. 970-9.
[5]. Yoshida, A., et al., Go6976, a FLT3 kinase inhibitor, exerts potent cytotoxic activity against acute leukemia via inhibition of survivin and MCL-1. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014. 90(1): p. 16-24.
- PALDA
Catalog No.:BCC7287
CAS No.:136181-87-8
- Neosarranicine
Catalog No.:BCN2024
CAS No.:136173-27-8
- Neosarracine
Catalog No.:BCN2026
CAS No.:136173-26-7
- Sarranicine
Catalog No.:BCN2025
CAS No.:136173-25-6
- 6-O-Caffeoylarbutin
Catalog No.:BCN6192
CAS No.:136172-60-6
- Lobetyol
Catalog No.:BCN3321
CAS No.:136171-87-4
- INNO-206
Catalog No.:BCC1651
CAS No.:1361644-26-9
- E3330
Catalog No.:BCC6421
CAS No.:136164-66-4
- (S)-(+)-Dimethindene maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7061
CAS No.:136152-65-3
- Minocycline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4679
CAS No.:13614-98-7
- 3,7-Di-O-methylducheside A
Catalog No.:BCN6191
CAS No.:136133-08-9
- Przewalskinic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN2925
CAS No.:136112-75-9
- 3,4'-Dihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxypropiophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1579
CAS No.:136196-47-9
- KW 3902
Catalog No.:BCC6124
CAS No.:136199-02-5
- Absinthiin
Catalog No.:BCN2314
CAS No.:1362-42-1
- GNE-617
Catalog No.:BCC4280
CAS No.:1362154-70-8
- TAT 14
Catalog No.:BCC6295
CAS No.:1362661-34-4
- Boc-ß-HoArg(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3227
CAS No.:136271-81-3
- Ethyl2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8978
CAS No.:136285-65-9
- Ethyl 2-(((2'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8965
CAS No.:136285-67-1
- Methyl 3-amino-2-[[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]amino]benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC9037
CAS No.:136304-78-4
- Tiotropium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2000
CAS No.:136310-93-5
- Isophysalin A
Catalog No.:BCN7916
CAS No.:1363398-67-7
- SR 27897
Catalog No.:BCC7277
CAS No.:136381-85-6
Possible involvement of atypical protein kinase C (PKC) in glucose-sensitive expression of the human insulin gene: DNA-binding activity and transcriptional activity of pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene-1 (PDX-1) are enhanced via calphostin C-sensitive but phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and Go 6976-insensitive pathway.[Pubmed:10426567]
Endocr J. 1999 Feb;46(1):43-58.
Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene-1 (PDX-1) is a transcription factor which regulates the insulin gene expression. In this study, we tried to elucidate the role of PDX-1 in the glucose-induced transcriptional activation of the human insulin gene promoter in MIN6 cells. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) assay demonstrated that both DNA-binding activity and transcriptional activity of PDX-1 were increased with 20 mmol/l glucose more than with 2 mmol/l glucose. The DNA-binding activity of PDX-1 induced by high glucose was blocked by phosphatase treatment, suggesting the involvement of PDX-1 phosphorylation in this event. In an in vitro phosphorylation study, PDX-1 was phosphorylated by protein kinase C (PKC), but not by cAMP dependent protein kinase (PKA) or mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Furthermore, increased PDX-1 function induced by high glucose was blocked by calphostin C, an inhibitor of all PKC isoforms, but unaffected by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), an activator of classical and novel PKC, or Go 6976, an inhibitor of classical and novel PKC, which suggested that the PKC family which activated PDX-1 in MIN6 cells was atypical PKC. Western blot and immunocytochemical studies with anti-PKC zeta antibody confirmed the presence of PKC zeta, one of the isoforms of atypical PKC, in MIN6 cells. Furthermore, PKC zeta activity was significantly increased by glucose stimulation. These results suggest that high glucose increased DNA-binding activity of PDX-1 by activating atypical PKC including PKC zeta, resulting in transcriptional activation of the human insulin gene promoter.
Go 6976 is a potent inhibitor of neurotrophin-receptor intrinsic tyrosine kinase.[Pubmed:10037462]
J Neurochem. 1999 Mar;72(3):919-24.
We report here that addition of the protein kinase C inhibitor Go 6976 blocked neurotrophin-induced signaling and autophosphorylation of neurotrophin-specific tyrosine kinase (Trk) receptors, either Trk B in cortical neurons or Trk A in GT1-1-trk9 cells. The effect of Go 6976 on Trk autophosphorylation was not inhibited by 100 microM orthovanadate, suggesting that the block was not due to the activation of tyrosine phosphatases. Moreover, addition of 10-100 nM concentrations of Go 6976 inhibited either Trk B or Trk A intrinsic kinase activity in cell-free assays. Go 6976 also blocked the ability of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to promote cortical neuronal survival and the ability of nerve growth factor to promote PC12 cell survival and differentiation. These results suggest that Go 6976, besides its known inhibitory effects on lipid- and calcium-dependent isoforms of protein kinase C, can also inhibit neurotrophin signaling by directly inhibiting the intrinsic Trk.
Go-6976 reverses hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance independently of cPKC inhibition in adipocytes.[Pubmed:25330241]
PLoS One. 2014 Oct 15;9(10):e108963.
Chronic hyperglycemia induces insulin resistance by mechanisms that are incompletely understood. One model of hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance involves chronic preincubation of adipocytes in the presence of high glucose and low insulin concentrations. We have previously shown that the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) plays a partial role in the development of insulin resistance in this model. Here, we demonstrate that treatment with Go-6976, a widely used "specific" inhibitor of cPKCs, alleviates hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance. However, the effects of mTOR inhibitor, rapamycin and Go-6976 were not additive and only rapamycin restored impaired insulin-stimulated AKT activation. Although, PKCalpha, (but not -beta) was abundantly expressed in these adipocytes, our studies indicate cPKCs do not play a major role in causing insulin-resistance in this model. There was no evidence of changes in the expression or phosphorylation of PKCalpha, and PKCalpha knock-down did not prevent the reduction of insulin-stimulated glucose transport. This was also consistent with lack of IRS-1 phosphorylation on Ser-24 in hyperglycemia-induced insulin-resistant adipocytes. Treatment with Go-6976 did inhibit a component of the mTORC1 pathway, as evidenced by decreased phosphorylation of S6 ribosomal protein. Raptor knock-down enhanced the effect of insulin on glucose transport in insulin resistant adipocytes. Go-6976 had the same effect in control cells, but was ineffective in cells with Raptor knock-down. Taken together these findings suggest that Go-6976 exerts its effect in alleviating hyperglycemia-induced insulin-resistance independently of cPKC inhibition and may target components of the mTORC1 signaling pathway.


