Tiotropium BromideMAChR M antagonist CAS# 136310-93-5 |
- A-867744
Catalog No.:BCC1324
CAS No.:1000279-69-5
- Rocuronium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC1068
CAS No.:119302-91-9
- Rivastigmine
Catalog No.:BCC1900
CAS No.:123441-03-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 136310-93-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5487426 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H22BrNO4S2 | M.Wt | 472.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ba 679 BR | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (63.50 mM) H2O : 25 mg/mL (52.92 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
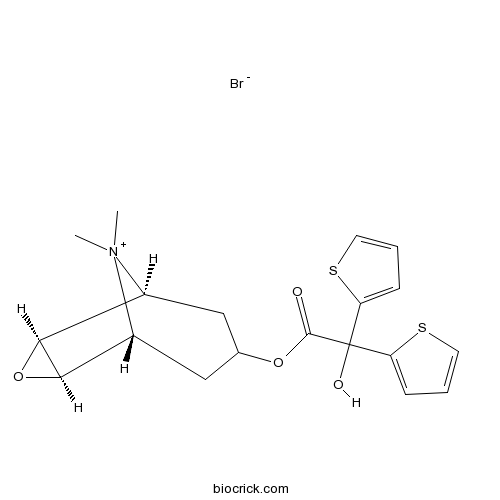
| SMILES | C[N+]1(C2CC(CC1C3C2O3)OC(=O)C(C4=CC=CS4)(C5=CC=CS5)O)C.[Br-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DQHNAVOVODVIMG-RGECMCKFSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H22NO4S2.BrH/c1-20(2)12-9-11(10-13(20)17-16(12)24-17)23-18(21)19(22,14-5-3-7-25-14)15-6-4-8-26-15;/h3-8,11-13,16-17,22H,9-10H2,1-2H3;1H/q+1;/p-1/t11?,12-,13+,16-,17+; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent muscarinic receptor antagonist. Inhibits electrical field stimulation-induced contraction of guinea pig trachea in vitro (IC50 = 0.17 nM). Induces smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation. |

Tiotropium Bromide Dilution Calculator

Tiotropium Bromide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1168 mL | 10.5838 mL | 21.1676 mL | 42.3352 mL | 52.919 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4234 mL | 2.1168 mL | 4.2335 mL | 8.467 mL | 10.5838 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2117 mL | 1.0584 mL | 2.1168 mL | 4.2335 mL | 5.2919 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0423 mL | 0.2117 mL | 0.4234 mL | 0.8467 mL | 1.0584 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0212 mL | 0.1058 mL | 0.2117 mL | 0.4234 mL | 0.5292 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Tiotropium Bromide is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR M) antagonist that blocks the binding of the acetylcholine ligand and subsequent opening of the ligand-gated ion channel. This stops signaling between neurons and leads to muscle relaxation. Tiotropium Bromide is a long-acting, 24 hour, anticholinergic bronchodilator used in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tiotropium Bromide improves symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated by chronic heart failure.
- Methyl 3-amino-2-[[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]amino]benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC9037
CAS No.:136304-78-4
- Ethyl 2-(((2'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8965
CAS No.:136285-67-1
- Ethyl2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8978
CAS No.:136285-65-9
- Boc-ß-HoArg(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3227
CAS No.:136271-81-3
- TAT 14
Catalog No.:BCC6295
CAS No.:1362661-34-4
- GNE-617
Catalog No.:BCC4280
CAS No.:1362154-70-8
- Absinthiin
Catalog No.:BCN2314
CAS No.:1362-42-1
- KW 3902
Catalog No.:BCC6124
CAS No.:136199-02-5
- 3,4'-Dihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxypropiophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1579
CAS No.:136196-47-9
- Go 6976
Catalog No.:BCC3703
CAS No.:136194-77-9
- PALDA
Catalog No.:BCC7287
CAS No.:136181-87-8
- Neosarranicine
Catalog No.:BCN2024
CAS No.:136173-27-8
- Isophysalin A
Catalog No.:BCN7916
CAS No.:1363398-67-7
- SR 27897
Catalog No.:BCC7277
CAS No.:136381-85-6
- Duloxetine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3773
CAS No.:136434-34-9
- YH239-EE
Catalog No.:BCC5454
CAS No.:1364488-67-4
- Trilostane
Catalog No.:BCC2302
CAS No.:13647-35-3
- Abacavir
Catalog No.:BCC1325
CAS No.:136470-78-5
- 11β-Hydroxy-2'-methyl-5'βH-pregna-1,4-dieno[17,16-d]oxazole-3,20-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8435
CAS No.:13649-88-2
- Rink Amide Resin
Catalog No.:BCC2570
CAS No.:13653-84-4
- BQ-123
Catalog No.:BCC6963
CAS No.:136553-81-6
- Fmoc-D-Trp-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3560
CAS No.:136554-94-4
- Anemarsaponin E
Catalog No.:BCN6290
CAS No.:136565-73-6
- Curdione
Catalog No.:BCN5936
CAS No.:13657-68-6
Impact of Long-Term Tiotropium Bromide Therapy on Annual Lung Function Decline in Adult Patients with Cystic Fibrosis.[Pubmed:27351829]
PLoS One. 2016 Jun 28;11(6):e0158193.
BACKGROUND: Chronic lung disease is the leading cause of death in patients with Cystic Fibrosis (CF) and is often treated with bronchodilators. It is not known whether long-term Tiotropium Bromide treatment may have a positive impact on lung function. METHODS: This retrospective cohort study estimated annual lung function decline utilizing longitudinal data for forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1). RESULTS: A total of 160 adult patients with CF were analyzed. The subjects treated for 24 months with Tiotropium Bromide had a significantly slower decline of mean annual change of FEV1 (treated: -0.3+/-4.0%; control: -2.3+/-5.0%; p = 0.0130). In patients with FEV1 >/=70% predicted, long-term Tiotropium Bromide treatment was associated with greater improvements in annual lung function decline (FEV1 >/=70% predicted: treated: +0.5+/-4.7%; control: -4.0+/-6.3%; p = 0.0132; FEV1 50-69% predicted: treated: -0.5+/-4.4%; control: -0.8+/-3.8%; p = 0.7142; FEV1 Tiotropium Bromide treatment may be associated with reduced annual decline of FEV1 in patients with CF, particularly in adults with a mild degree of severity.
Erratum: Triple therapy with salmeterol/fluticasone propionate 50/250 plus tiotropium bromide improve lung function versus individual treatments in moderate-to-severe Japanese COPD patients: a randomized controlled trial - Evaluation of Airway sGaw after treatment with tripLE [Corrigendum].[Pubmed:27274224]
Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 May 17;11:1031-1033.
[This corrects the article on p. 2393 in vol. 10, PMID: 26604737.].
Pharmacokinetic Bioequivalence of Two Inhaled Tiotropium Bromide Formulations in Healthy Volunteers.[Pubmed:27470430]
Clin Drug Investig. 2016 Sep;36(9):753-762.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE: A novel Tiotropium Bromide monodose capsule dry powder inhaler (DPI) formulation and device have been developed. The formulation was based on a spray-dried matrix that enhances the aerosolizaton properties, allowing a less active tiotropium metered dose (13 microg/capsule) while maintaining the same delivered dose (10 microg/actuation). This study describes the pharmacokinetic bioequivalence to the reference product. METHODS: This randomized, two-stage, crossover, semi-replicate (three-way) study was performed in healthy volunteers. In each study period, subjects received a single dose of two capsules (20 mug delivered dose) of the study medication, separated by a 14-day washout period: tiotropium 10 mug delivered dose (Laboratorios Liconsa, Spain) and Spiriva HandiHaler((R)) (Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co KG, Germany). Blood samples were obtained up to 48 h post-dose to evaluate the comparative bioavailability. Tiotropium was measured in plasma by means of dual stage liquid-liquid extraction followed by the two-dimensional ultra-high performance liquid chromatography sensitive sub-pg/mL bioanalytical method. The main pharmacokinetic parameters were maximum plasma concentration (C max), area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) from time zero hours to the last observed concentration at time t (AUC t ), and AUC from time zero hours to 30 min (AUC0.5). Bioequivalence was accepted if the 90.20 % confidence interval (CI) for the ratio test/reference of the primary pharmacokinetic parameters lay within the acceptance range of 80-125 %. Safety assessment was a secondary endpoint. RESULTS: A total of 30 subjects were randomized and bioequivalence was demonstrated for all primary pharmacokinetic parameters: C max (CI 87.26-106.60 %), AUC t (CI 101.33-111.64 %), and AUC0.5 (CI 97.95-113.49 %). Both study treatments were well tolerated (four non-serious adverse events [AEs] were reported in four subjects: one AE before any product administration, two AEs after test product administration; and one AE after reference product administration). CONCLUSIONS: Both products containing tiotropium 10 microg delivered-dose DPI were bioequivalent and showed good tolerability and a similar safety profile.
Bronchoprotection by olodaterol is synergistically enhanced by tiotropium in a guinea pig model of allergic asthma.[Pubmed:24307202]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Feb;348(2):303-10.
The novel once-daily beta(2)-agonist bronchodilator drug olodaterol has recently been shown to be effective in patients with allergic asthma for >24 hours. An increased cholinergic tone common to these patients may decrease the effectiveness of beta(2)-agonists. This could provide a rationale for combination therapy with olodaterol and the long-acting anticholinergic tiotropium to aim for a once-daily treatment regimen. In guinea pigs, we evaluated the protective effects of olodaterol, alone and in combination with tiotropium, on airway responsiveness to histamine, which is partially mediated by a cholinergic reflex mechanism. In addition, using a guinea pig model of acute allergic asthma, we examined the cooperative effects of these bronchodilators on allergen-induced early (EAR) and late (LAR) asthmatic reactions, airway hyper-responsiveness (AHR) to histamine, and airway inflammation. It was demonstrated that the protective effect of olodaterol against histamine-induced bronchoconstriction was synergistically enhanced and prolonged in the presence of tiotropium. In addition, tiotropium synergistically augmented both the reversal of and the protection against the allergen-induced AHR after the EAR by olodaterol. Olodaterol and tiotropium were highly effective in inhibiting the magnitude of the allergen-induced EAR and LAR, and both reactions were fully inhibited by the combination of these drugs. It is remarkable that these effects were not associated with an effect on inflammatory cell infiltration in the airways. In conclusion, the results indicate that combination therapy with olodaterol and tiotropium may be highly effective in the treatment of allergen-induced asthmatic reactions and AHR.
Comparative characterization of lung muscarinic receptor binding after intratracheal administration of tiotropium, ipratropium, and glycopyrrolate.[Pubmed:21358117]
J Pharmacol Sci. 2011;115(3):374-82. Epub 2011 Feb 24.
The aim of the current study was to characterize comparatively the binding of muscarinic receptor in the lung of rats intratracheally administered anticholinergic agents (tiotropium, ipratropium, glycopyrrolate) used clinically to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Binding parameters of [N-methyl-(3)H]scopolamine methyl chloride ([(3)H]NMS) were determined in tissues (lung, bladder, submaxillary gland) of rats intratracheally administered tiotropium, ipratropium, and glycopyrrolate. The in vitro binding affinity of tiotropium for the receptors was 10-11-fold higher than those of ipratropium and glycopyrrolate. Intratracheal administration of tiotropium (0.6-6.4 nmol/kg) caused sustained (lasting at least 24 h) increase in the apparent dissociation constant (K(d)) for [(3)H]NMS binding in rat lung compared with the control value. Concomitantly, there was a long-lasting decrease in the maximal number of binding sites (B(max)) for [(3)H]NMS. Similary, ipratropium and glycopyrrolate at 7.3 and 7.5 nmol/kg, respectively, brought about a significant increase in K(d) for [(3)H]NMS binding. The effect by ipratropium was observed at 2 h but not 12 h, and that by glycopyrrolate lasted for 24 h. Both agents had little influence on the muscarinic receptors in the bladder and submaxillary gland. The present study provides the first evidence that tiotropium, ipratropium, and glycopyrrolate administered intratracheally in rats selectively bound muscarinic receptors of the lung, and tiotropium and glycopyrrolate had a much longer-lasting effect than ipratropium.
Effect of Ba 679 BR, a novel long-acting anticholinergic agent, on cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig and human airways.[Pubmed:7952627]
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Dec;150(6 Pt 1):1640-5.
We investigated the effect of Ba 679 BR, a novel long-acting antimuscarinic agent, on cholinergic neural responses in guinea pig and human airways. Ba 679 BR, atropine, and ipratropium bromide inhibited electrical field stimulation (EFS)-induced contraction with IC50 values of 0.17, 0.74, and 0.58 nM, respectively, in guinea pig trachea. Ba 679 BR had a slower onset and longer duration of action than atropine or ipratropium bromide (the times required to attain 50% of the maximum response were 34.8, 3.8, and 7.6 min, respectively, and the times required for 50% recovery of the response were 540, 31.6, and 81.2 min, respectively). Ba 679 BR, as well as atropine and ipratropium bromide, facilitated evoked [3H]acetylcholine release (an inhibitory effect on prejunctional muscarinic M2 receptors). The facilitation of acetylcholine release by Ba 679 BR was lost 2 h after washout, however, when there was still complete blockade of cholinergic contractile responses evoked by EFS (an effect on airway smooth muscle M3 receptors), confirming binding studies that suggest that Ba 679 BR shows "kinetic receptor subtype selectivity" for M3 over M2 receptors. The high potency, slow onset, and long duration of action of Ba 679 BR were also observed in human bronchi, suggesting that Ba 679 BR may be a useful drug to provide convenient therapy for patients with obstructive airway disease.


