Duloxetine HClPotent 5-HT and NA reuptake inhibitor; also blocks dopamine reuptake CAS# 136434-34-9 |
- Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
Catalog No.:BCC2156
CAS No.:1069-66-5
- Scriptaid
Catalog No.:BCC2163
CAS No.:287383-59-9
- Panobinostat (LBH589)
Catalog No.:BCC3601
CAS No.:404950-80-7
- Belinostat (PXD101)
Catalog No.:BCC2153
CAS No.:414864-00-9
- Trichostatin A (TSA)
Catalog No.:BCC3605
CAS No.:58880-19-6
- ITF2357 (Givinostat)
Catalog No.:BCC2150
CAS No.:732302-99-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 136434-34-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 60834 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H20ClNOS | M.Wt | 333.88 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (S)-Duloxetine hydrochloride; LY-248686 hydrochloride | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (299.51 mM) H2O : 5 mg/mL (14.98 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
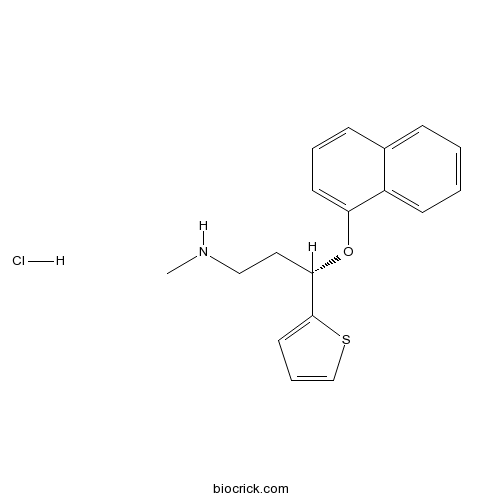
| Chemical Name | (+)-(S)-N-Methyl-3-(1-naphthyloxy)- | ||
| SMILES | [Cl-].CNCC[C@H](Oc1cccc2ccccc12)c3sccc3.[H+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BFFSMCNJSOPUAY-LMOVPXPDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H19NOS.ClH/c1-19-12-11-17(18-10-5-13-21-18)20-16-9-4-7-14-6-2-3-8-15(14)16;/h2-10,13,17,19H,11-12H2,1H3;1H/t17-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | High affinity, competitive 5-HT and noradrenaline (NA) re-uptake inhibitor (Ki values are 8.5 and 45 nM for 5-HT and NA reuptake respectively in cortical synaptosomes; IC50 values are 28 and 46 nM for 5-HT and NA reuptake respectively in rat hippocampal slices). Also blocks dopamine reuptake (Ki = 300 nM in striatal synaptosomes). Exhibits antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. Orally bioavailable. |

Duloxetine HCl Dilution Calculator

Duloxetine HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9951 mL | 14.9754 mL | 29.9509 mL | 59.9018 mL | 74.8772 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.599 mL | 2.9951 mL | 5.9902 mL | 11.9804 mL | 14.9754 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2995 mL | 1.4975 mL | 2.9951 mL | 5.9902 mL | 7.4877 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0599 mL | 0.2995 mL | 0.599 mL | 1.198 mL | 1.4975 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.03 mL | 0.1498 mL | 0.2995 mL | 0.599 mL | 0.7488 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Duloxetine HCl is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor .
- SR 27897
Catalog No.:BCC7277
CAS No.:136381-85-6
- Isophysalin A
Catalog No.:BCN7916
CAS No.:1363398-67-7
- Tiotropium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2000
CAS No.:136310-93-5
- Methyl 3-amino-2-[[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]amino]benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC9037
CAS No.:136304-78-4
- Ethyl 2-(((2'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8965
CAS No.:136285-67-1
- Ethyl2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8978
CAS No.:136285-65-9
- Boc-ß-HoArg(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3227
CAS No.:136271-81-3
- TAT 14
Catalog No.:BCC6295
CAS No.:1362661-34-4
- GNE-617
Catalog No.:BCC4280
CAS No.:1362154-70-8
- Absinthiin
Catalog No.:BCN2314
CAS No.:1362-42-1
- KW 3902
Catalog No.:BCC6124
CAS No.:136199-02-5
- 3,4'-Dihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxypropiophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1579
CAS No.:136196-47-9
- YH239-EE
Catalog No.:BCC5454
CAS No.:1364488-67-4
- Trilostane
Catalog No.:BCC2302
CAS No.:13647-35-3
- Abacavir
Catalog No.:BCC1325
CAS No.:136470-78-5
- 11β-Hydroxy-2'-methyl-5'βH-pregna-1,4-dieno[17,16-d]oxazole-3,20-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8435
CAS No.:13649-88-2
- Rink Amide Resin
Catalog No.:BCC2570
CAS No.:13653-84-4
- BQ-123
Catalog No.:BCC6963
CAS No.:136553-81-6
- Fmoc-D-Trp-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3560
CAS No.:136554-94-4
- Anemarsaponin E
Catalog No.:BCN6290
CAS No.:136565-73-6
- Curdione
Catalog No.:BCN5936
CAS No.:13657-68-6
- Irinotecan HCl Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5091
CAS No.:136572-09-3
- Spermine NONOate
Catalog No.:BCC6950
CAS No.:136587-13-8
- Fmoc-Tyr(3-NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3280
CAS No.:136590-09-5
Duloxetine HCl lipid nanoparticles: preparation, characterization, and dosage form design.[Pubmed:22167415]
AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012 Mar;13(1):125-33.
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) of duloxetine hydrochloride (DLX) were prepared to circumvent the problems of DLX, which include acid labile nature, high first-pass metabolism, and high-dosing frequency. The DLX-SLNs were prepared by using two different techniques, viz. solvent diffusion method and ultrasound dispersion method, and evaluated for particle size, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency, physical characteristics, and chemical stability. Best results were obtained when SLNs were prepared by ultrasound dispersion method using glyceryl mono stearate as solid lipid and DLX in ratio of 1:20 and mixture of polysorbate 80 and poloxamer 188 as surfactant in concentration of 3%. The mean particle size of formulation and entrapment efficiency was 91.7 nm and 87%, respectively, and had excellent stability in acidic medium. Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction data showed complete amorphization of DLX in lipid. In vitro drug release from SLNs was observed for 48 h and was in accordance with Higuchi kinetics. In vivo antidepressant activity was evaluated in mice by forced swim test. DLX-SLNs showed significant enhancement in antidepressant activity at 24 h when administered orally in comparison to drug solution. These results confirm the potential of SLNs in enhancing chemical stability and improving the efficacy of DLX via oral route. The SLN dispersion was converted into solid granules by adsorbing on colloidal silicon dioxide and characterized for particle size after redispersion, morphology, and flow properties. Results indicated that nanoparticles were successfully adsorbed on the carrier and released SLNs when dispersed in water.
Characterization of impurities formed by interaction of duloxetine HCl with enteric polymers hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate.[Pubmed:9452973]
J Pharm Sci. 1998 Jan;87(1):81-5.
Duloxetine hydrochloride ((S)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-2-thiophenepropanamine hydrochloride) has been found to react with polymer degradation products or residual free acids present in the enteric polymers hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP) in dosage formulations to form succinamide and phthalamide impurities, respectively. The rate of formation of the impurities is accelerated by heat and humidity. The structures were deduced using molecular weights obtained from LC-MS experiments and confirmed by comparison of UV spectra, HPLC retention times, and electrospray mass spectra to independently synthesized material. It is proposed that polymer-bound succinic and phthalic substituents can be cleaved from the polymer, resulting in the formation of either the free acids or the anhydrides. It is postulated that the reaction is enabled by migration of either (1) the free acid or anhydride or (2) the parent drug through the formulation. The formation of these impurities was minimized by increasing the thickness of the physical barrier separating the enteric coating from the drug.
Is HCl duloxetine effective in the management of urinary stress incontinence after radical prostatectomy?[Pubmed:16825808]
Urol Int. 2006;77(1):9-12.
INTRODUCTION: Up to 70% of patients who undergo radical prostatectomy complain about urine leakage, but persistent stress incontinence 1 year after surgery affects <5% of them. HCl duloxetine is a dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that relieves the symptoms of stress urinary incontinence. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of HCl duloxetine in the management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy and its impact in urodynamic parameters such as maximal urethral closure pressure (MUCP), abdominal leak point pressure (ALPP) and retrograde leak point pressure (RLPP). MATERIAL AND METHODS: The study included 18 men with stress urinary incontinence 12 months after radical prostatectomy. All underwent a pad test to quantify the degree of urine loss and a urodynamic evaluation before and after a three month treatment with HCl duloxetine. The intrinsic sphincter was evaluated by ALPP and RLPP and the striated sphincter by MUCP. RESULTS: At the pretreatment evaluation the mean ALPP was 52.1 cm H(2)O, the mean MUCP was 52.5 cm H(2)O and the mean RLPP was 43.1 cm H(2)O. After 3 months of HCl duloxetine treatment the mean ALPP was 59.1 cm H(2)O, the mean MUCP was 67.3 cm H(2)O and the mean RLPP was 45.1 cm H(2)O. There was a statistically significant correlation among RLPP, MUCP and ALPP before treatment. After HCl duloxetine treatment there was significant correlation between RLPP and ALPP. CONCLUSION: The use of HCl duloxetine results in mild increase of MUCP and in significant reduction of urine loss. Its action on the extrinsic sphincter does not provide a complete treatment option for postprostatectomy incontinence.
A validated stability indicating rapid LC method for duloxetine HCl.[Pubmed:19216224]
Pharmazie. 2009 Jan;64(1):10-3.
The present paper describes the development of a reversed phase liquid chromatographic (RPLC) analytical method for Duloxetine HCl in the presence of its impurities and degradation products generated from forced decomposition studies. The drug substance was subjected to stress conditions of hydrolysis, oxidation, photolysis and thermal degradation. The degradation of Duloxetine HCl was observed under acid hydrolysis. The drug was found to be stable in other stress conditions studied. Successful separation of the drug from the synthetic impurities and degradation products formed under stress conditions was achieved on a Zorabax XDB C18, 50 mm x 4.6 mm, 5.0 micron column using a mixture of aqueous 0.1% trifluroacetic acid, methanol, tetrahydrofuran (60:20:20, v/v/v) as mobile phase. The HPLC method developed was validated with respect to linearity, accuracy, precisions, specificity and ruggedness. To our knowledge, a rapid stability indicating LC method for Duloxetine HCl has not been published elsewhere.
Blockade of the serotonin and norepinephrine uptake processes by duloxetine: in vitro and in vivo studies in the rat brain.[Pubmed:8613930]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Apr;277(1):278-86.
In in vitro uptake experiments, duloxetine inhibited [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and [3H]norepinephrine (NE) uptake in hippocampus slices of control rats with IC50 values of 28 and 46 nM, respectively. The uptake of both[3H]5-HT and [3H]NE was equipotently inhibited in hippocampus slices prepared from rats treated for 2 days with different doses of duloxetine (5, 10, 15 and 20 mg/kg/day s.c.). In in vivo electrophysiological experiments in the hippocampus, the effects of duloxetine on the suppression of CA3 pyramidal neuronal firing activity by microiontophoretically applied 5-HT and NE were examined with two modes of administration. Five successive i.v. injections (2 mg/kg each) significantly and dose-dependently prolonged the recovery time of the firing activity of hippocampus CA3 pyramidal neurons from the 5-HT applications. A 2-day treatment (10, 15 and 20 mg/kg/day s.c.) also increased the recovery time in a dose-dependent manner. Whereas the recovery time from NE applications was unaffected by low doses of duloxetine (2 mg/kg i.v.; 10 mg/kg/day for 2 days), it was prolonged significantly by higher doses (8 and 1 0 mg/kg iv.; 20 mg/kg/day for 2 days). Acute i.v. injections of duloxetine suppressed the spontaneous firing activity of dorsal raphe 5-HT and locus ceruleus NE neurons with ED50 values of 99 and 475 microgram/kg, respectively. Taken together, the present results confirmed that duloxetine is a dual 5-HT/NE uptake inhibitor. Furthermore, the results obtained in in vivo experiments indicate that duloxetine has a preferential inhibitory effect on the 5-HT transporter.
LY227942, an inhibitor of serotonin and norepinephrine uptake: biochemical pharmacology of a potential antidepressant drug.[Pubmed:2850421]
Life Sci. 1988;43(24):2049-57.
LY227942, (+/-)-N-methyl-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-3-(2-thiophene)propanamine ethanedioate, is a new, competitive inhibitor of monoamine uptake in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain. LY227942 inhibits uptake of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT) and norepinephrine (NE) in cortical synaptosomes and uptake of dopamine (DA) in striatal synaptosomes with inhibitor constants (Ki values) of 8.5, 45 and 300 nM, respectively. Upon administration in vivo, LY227942 lowers 5HT and NE uptake in hypothalamus homogenates to half their respective control activities (ED50) at 0.74 and 1.2 mg/kg s.c., 7 and 12 mg/kg i.p., and 12 and 22 mg/kg p.o., but LY227942 at doses up to 30 mg/kg p.o. does not change DA uptake in striatal homogenates. Lowering of 5HT and NE uptake is demonstrated after 15 min and 6 hr, but has dissipated by 16 hr after oral administration. According to radioligand binding determinations, LY227942 possesses only weak affinity for muscarinic receptors, histamine-1 receptors, adrenergic receptors, dopamine receptors and serotonin receptors. These findings suggest that LY227942 has the pharmacological profile of an antidepressant drug and is useful to study the pharmacological responses of concerted enhancement of serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmission.


