ScriptaidHDAC inhibitor,novel and cell-permeable CAS# 287383-59-9 |
- Tubastatin A
Catalog No.:BCC2158
CAS No.:1252003-15-8
- Panobinostat (LBH589)
Catalog No.:BCC3601
CAS No.:404950-80-7
- PCI-24781 (CRA-024781)
Catalog No.:BCC2155
CAS No.:783355-60-2
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
- KD 5170
Catalog No.:BCC2420
CAS No.:940943-37-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 287383-59-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5186 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H18N2O4 | M.Wt | 326.35 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Scriptide | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (306.42 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
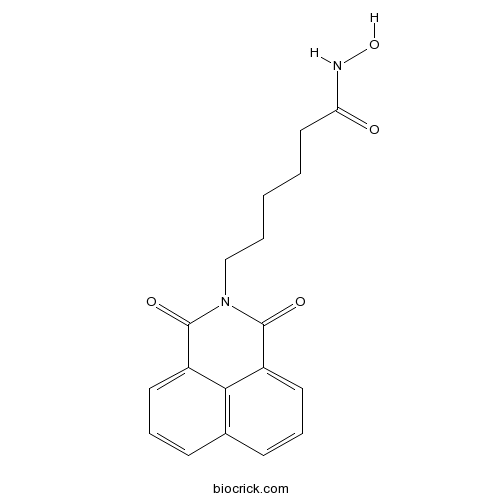
| Chemical Name | 6-(1,3-dioxobenzo[de]isoquinolin-2-yl)-N-hydroxyhexanamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C3C(=C1)C(=O)N(C(=O)C3=CC=C2)CCCCCC(=O)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JTDYUFSDZATMKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H18N2O4/c21-15(19-24)10-2-1-3-11-20-17(22)13-8-4-6-12-7-5-9-14(16(12)13)18(20)23/h4-9,24H,1-3,10-11H2,(H,19,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Produces > 100-fold increase in histone acetylation and displays relatively low toxicity. |

Scriptaid Dilution Calculator

Scriptaid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0642 mL | 15.321 mL | 30.6419 mL | 61.2839 mL | 76.6049 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6128 mL | 3.0642 mL | 6.1284 mL | 12.2568 mL | 15.321 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3064 mL | 1.5321 mL | 3.0642 mL | 6.1284 mL | 7.6605 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0613 mL | 0.3064 mL | 0.6128 mL | 1.2257 mL | 1.5321 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1532 mL | 0.3064 mL | 0.6128 mL | 0.766 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
Scriotaid, a HDAC inhibitor, exhibited greater efficacy to ehance in vitro developmental competence in ovine SCNT embryos, where increased acetylation at acH4K12 and acH3K9 was observed at different stages.
Abstract
The treatment of Scriptaid significantly improved the developmental competence and cryosurvival of cloned yak embryos, whose donor nucleus was from yak fibroblasts pretreated with Scriptaid plus Zebularine.
Abstract
Scriptaid, a HDAC inhibitor, exerted long-lasting protection of motor and cognitive functions against CCI-induce injury through increasing surviving neurons and their activities in the CA3 region of the hippocampus and the pericontusional cortex, where the mechanism of protective effects includes Scriptaid-modulated AKT signaling pathway.
Abstract
Although Scriptaid, a HDAC inhibitor, enhances blastocyst formation and cloning efficiency of reconstructed embryos undergone SCNT, the combination of Scriptaid and MG132 failed to show improved activities.
Abstract
Scriptaid, a HDAC inhibitor, induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines through promoting expression of α-ER and sensitized tamoxifen hormone-resistant breast cancer cell lines to the treatment of tamoxifen.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Scriptaid, identified by a high-throughput transcriptional screening, is a novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) with specific potency towards class I HDACs (50% inhibition concentration IC50 values of 0.6 μM for HDAC1 and HDAC3 and 1 μM for HDAC8). Scriptaid shares a similar chemical structure with several others hydroxamic acid-containing HDAC inhibitors (such as TSA and nullscript), which consists of a hydroxamic acid group, an aliphatic chain and an aromatic cap at the other end. Scriptaid has the potential to be used for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), one of the most challenging solid cancers to treat, for its ability to induce apoptosis in glioblastoma cells.
Reference
Sharma V, Koul N, Joseph C, Dixit D, Ghosh S, Sen E. HDAC inhibitor, scriptaid, induces glioma cell apoptosis through JNK activation and inhibits telomerase activity. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(8):2151-2161.
Hu E, Dul E, Sung CM, Chen Z, Kirkpatrick R, Zhang GF, Johanson K, Liu R, Lago A, Hofmann G, Macarron R, de los Frailes M, Perez P, Krawiec J, Winkler J, Jaye M. Identification of novel isoform-selective inhibitors within class I histone deacetylases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;307(2):720-728.
Su GH, Sohn TA, Ryu B, Kern SE. A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor identified by high-throughput transcriptional screening of a compound library. Cancer Res. 2000; 60(12):3137-3142.
- Oxcarbazepine
Catalog No.:BCC5077
CAS No.:28721-07-5
- MA 2029
Catalog No.:BCC7983
CAS No.:287206-61-5
- PD 180970
Catalog No.:BCC3894
CAS No.:287204-45-9
- NCX 4040
Catalog No.:BCC7944
CAS No.:287118-97-2
- Ezatiostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4259
CAS No.:286942-97-0
- Fesoterodine Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4584
CAS No.:286930-03-8
- 6'-Amino-3',4'-(methylenedioxy)acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8760
CAS No.:28657-75-2
- Epoxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN5382
CAS No.:28649-60-7
- Euphorbiasteroid
Catalog No.:BCN2781
CAS No.:28649-59-4
- Multicaulisin
Catalog No.:BCN7840
CAS No.:286461-76-5
- L-838,417
Catalog No.:BCC7617
CAS No.:286456-42-6
- Meloscandonine
Catalog No.:BCN5186
CAS No.:28645-27-4
- 3CAI
Catalog No.:BCC5402
CAS No.:28755-03-5
- Apigenin 5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN5185
CAS No.:28757-27-9
- Rosuvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC4139
CAS No.:287714-41-4
- 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno [3,2,c]pyridine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8664
CAS No.:28783-41-7
- Nordihydrocapsaicin
Catalog No.:BCN2387
CAS No.:28789-35-7
- H-Cys(Acm)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2903
CAS No.:28798-28-9
- Peptone, bacteriological
Catalog No.:BCC1210
CAS No.:288-88-0
- Tetrazole
Catalog No.:BCC2847
CAS No.:288-94-8
- Heraclenin
Catalog No.:BCN5187
CAS No.:2880-49-1
- 4,7-Bis(5-bromo-2-thienyl)-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8668
CAS No.:288071-87-4
- Fraxinellone
Catalog No.:BCN1272
CAS No.:28808-62-0
- Cixiophiopogon A
Catalog No.:BCN2778
CAS No.:288143-27-1
Scriptaid Upregulates Expression of Development-Related Genes, Inhibits Apoptosis, and Improves the Development of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer Mini-Pig Embryos.[Pubmed:28055234]
Cell Reprogram. 2017 Feb;19(1):19-26.
The present study was undertaken to investigate the mechanisms by which Scriptaid treatment improves the developmental competence of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) mini-pig embryos in vitro. We found that treatment with 500 nmol/L Scriptaid for 15 hours significantly improved the development of mini-pig SCNT embryos. Compared with the control group, the blastocyst rate was higher (18.3% vs. 10.7%; p < 0.05). The acetylation level on H3K14 of the Scriptaid-treated group was higher compared with the control group in SCNT embryos at two-cell, four-cell, and blastocyst stages (p < 0.05). After Scriptaid treatment, histone deacetylase gene HDAC5 expression level was significantly decreased in four-cell embryos and blastocysts, while the expression levels of the embryos' development-related genes AKT, Oct4, and apoptosis inhibited gene PGC-1alpha were significantly increased in blastocysts (p < 0.05). The number of apoptotic cells per blastocyst in the Scriptaid-treated group was lower compared with the control group (p < 0.05). These results indicate that Scriptaid repressed HDCA5 gene expression, increased the acetylation level of H3K14, upregulated the expression of AKT, Oct4, and PGC-1alpha genes, improved embryos' development, and reduced apoptosis, which favors development of the SCNT mini-pig embryos to blastocysts.
Effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor 'Scriptaid' on the developmental competence of mouse embryos generated through round spermatid injection.[Pubmed:27864358]
Hum Reprod. 2017 Jan;32(1):76-87.
STUDY QUESTION: Can the histone deacetylase inhibitor Scriptaid improve the efficiency of the development of round spermatid injection (ROSI)-fertilized embryos in a mouse model? SUMMARY ANSWER: Treatment of ROSI mouse zygotes with Scriptaid increased the expression levels of several development-related genes at the blastocyst stage, resulting in more efficient in vitro development of the blastocyst and an increased birth rate of ROSI-derived embryos. WHAT IS KNOWN ALREADY: The full-term development of embryos derived through ROSI is significantly lower than that following ICSI in humans and other species. STUDY DESIGN, SIZE, DURATION: Oocytes, spermatozoa and round spermatids were collected from BDF1 (C57BL/6 x DBA/2) mice. For in vitro development experiments, mouse ROSI-derived zygotes were treated with Scriptaid at different concentrations (0, 125, 250, 500 and 1000 nM) and for different exposure times (0, 6, 10, 16 or 24 h). Next, blastocysts of the optimal Scriptaid-treated group and the non-treated ROSI group were separately transferred into surrogate ICR mice to compare in vivo development with the ICSI group (control). Each experiment was repeated at least three times. PARTICIPANTS/MATERIALS, SETTING, METHODS: Metaphase II (MII) oocytes, spermatozoa and round spermatids were obtained from sexually mature BDF1 female or male mice. The developmental potential of embryos among the three groups (the ICSI, ROSI and optimal Scriptaid-treated ROSI groups) was assessed based on the rates of obtaining zygotes, two-cell stage embryos, four-cell stage embryos, blastocysts and full-term offspring. In addition, the expression levels of development-related genes (Oct4, Nanog, Klf4 and Sox2) were analysed using real-time PCR, and the methylation states of imprinted genes (H19 and Snrpn) in these three groups were detected using methylation-specific PCR (MS-PCR) sequencing following bisulfite treatment. MAIN RESULTS AND THE ROLE OF CHANCE: The in vitro experiments revealed that treating ROSI-derived zygotes with 250 nM Scriptaid for 10 h significantly improved the blastocyst formation rate (59%) compared with the non-treated group (38%) and further increased the birth rates of ROSI-derived embryos from 21% to 40% in vivo. Moreover, in ROSI-derived embryos, the expression of the Oct4, Nanog and Sox2 genes at the blastocyst stage was decreased, but the optimal Scriptaid treatment restored expression to a level similar to their ICSI counterparts. In addition, Scriptaid treatment moderately repaired the abnormal DNA methylation pattern in the imprinting control regions (ICRs) of H19 and Snrpn. LARGE SCALE DATA: N/A LIMITATIONS, REASONS FOR CAUTION: Because of the ethics regarding the use of human gametes for ROSI studies, the mouse model was used as an approach to explore the effects of Scriptaid on the developmental potential of ROSI-derived embryos. However, to determine whether these findings can be applied to humans, further investigation will be required. WIDER IMPLICATIONS OF THE FINDINGS: Scriptaid treatment provides a new means of improving the efficiency and safety of clinical human ROSI. STUDY FUNDING/COMPETING INTERESTS: The study was financially supported through grants from the National Key Research Program of China (No. 2016YFC1304800); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos: 81170756, 81571486); the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Nos: 15140901700, 15ZR1424900) and the Programme for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning. There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Scriptaid overcomes hypoxia-induced cisplatin resistance in both wild-type and mutant p53 lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:27708247]
Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):71841-71855.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), comprising 85% of lung cancer cases, has been associated with resistance to chemo/radiotherapy. The hypoxic tumor micro-environment, where insufficient vasculature results in poor drug penetrance and sub-optimal chemotherapy in the tumor interiors contributes heavily to this resistance. Additionally, epigenetic changes in tumorigenic cells also change their response to different forms of therapy. In our study, we have investigated the effectiveness of a combination of cisplatin with Scriptaid [a pan-Histone Deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi)] in a model that mimics the tumor microenvironment of hypoxia and sub-lethal chemotherapy. Scriptaid synergistically increases the efficacy of cisplatin in normoxia as well as hypoxia, accompanied with reduced metastasis and enhanced DNA damage. Addition of Scriptaid also overcomes the cisplatin resistance exhibited in lung cancer cells with stabilized hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF1)-alpha (mutant) and mutant p53. Molecular studies showed that the combination treatment increased apoptotic cell death in both normoxia and hypoxia with a dual role of p38MAPK. Together, our results suggest that the combination of low dose cisplatin and Scriptaid is cytotoxic to NSCLC lines, can overcome hypoxia induced resistance and mutant p53- induced instability often associated with this cancer, and has the potential to be an effective therapeutic modality.
Scriptaid enhances skeletal muscle insulin action and cardiac function in obese mice.[Pubmed:28155245]
Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Jul;19(7):936-943.
AIM: To determine the effect of Scriptaid, a compound that can replicate aspects of the exercise adaptive response through disruption of the class IIa histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressor complex, on muscle insulin action in obesity. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Diet-induced obese mice were administered Scriptaid (1 mg/kg) via daily intraperitoneal injection for 4 weeks. Whole-body and skeletal muscle metabolic phenotyping of mice was performed, in addition to echocardiography, to assess cardiac morphology and function. RESULTS: Scriptaid treatment had no effect on body weight or composition, but did increase energy expenditure, supported by increased lipid oxidation, while food intake was also increased. Scriptaid enhanced the expression of oxidative genes and proteins, increased fatty acid oxidation and reduced triglycerides and diacylglycerides in skeletal muscle. Furthermore, ex vivo insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by skeletal muscle was enhanced. Surprisingly, heart weight was reduced in Scriptaid-treated mice and was associated with enhanced expression of genes involved in oxidative metabolism in the heart. Scriptaid also improved indices of both diastolic and systolic cardiac function. CONCLUSION: These data show that pharmacological targeting of the class IIa HDAC corepressor complex with Scriptaid could be used to enhance muscle insulin action and cardiac function in obesity.
A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor identified by high-throughput transcriptional screening of a compound library.[Pubmed:10866300]
Cancer Res. 2000 Jun 15;60(12):3137-42.
Libraries of compounds are increasingly becoming commercially available for the use of individual academic laboratories. A high-throughput system based on a stably integrated transcriptional reporter was used to screen a library of random compounds to identify agents that conferred robust augmentation of a signal transduction pathway. A novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, termed Scriptaid, conferred the greatest effect, a 12- to 18-fold augmentation. This facilitation of transcriptional events was generally applicable to exogenous gene constructs, including viral and cellular promoters, different cell lines and reporter genes, and stably integrated and transiently introduced sequences. Scriptaid did not interfere with a further induction provided by stimulation of the cognate signal transduction pathway (transforming growth factor beta/Smad4), which implied the functional independence of ligand-stimulated transcriptional activation and histone acetylation states in this system. Additional insights into this and other signal transduction systems are likely to be afforded through the application of compound screening technologies.


