Fesoterodine FumarateCAS# 286930-03-8 |
- Erastin
Catalog No.:BCC4497
CAS No.:571203-78-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 286930-03-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9849808 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H41NO7 | M.Wt | 527.65 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Toviaz | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
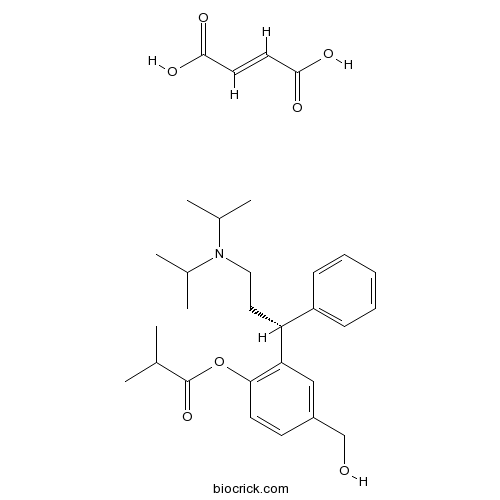
| Chemical Name | (E)-but-2-enedioic acid;[2-[(1R)-3-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(=O)OC1=C(C=C(C=C1)CO)C(CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C)C2=CC=CC=C2.C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MWHXMIASLKXGBU-RNCYCKTQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H37NO3.C4H4O4/c1-18(2)26(29)30-25-13-12-21(17-28)16-24(25)23(22-10-8-7-9-11-22)14-15-27(19(3)4)20(5)6;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h7-13,16,18-20,23,28H,14-15,17H2,1-6H3;1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b;2-1+/t23-;/m1./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fesoterodine Fumarate is an antimuscarinic agent and is rapidly de-esterified to its active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine that is a muscarinic receptor antagonist.
IC50 value:
Target: mAChR
Fesoterodine has the advantage of allowing more flexible dosage than other muscarinic antagonists. Its tolerability and side effects are similar to other muscarinic antagonists and as a new drug seems unlikely to make great changes in practices of treatment for overactive bladder. References: | |||||

Fesoterodine Fumarate Dilution Calculator

Fesoterodine Fumarate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8952 mL | 9.476 mL | 18.952 mL | 37.9039 mL | 47.3799 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.379 mL | 1.8952 mL | 3.7904 mL | 7.5808 mL | 9.476 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1895 mL | 0.9476 mL | 1.8952 mL | 3.7904 mL | 4.738 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0379 mL | 0.1895 mL | 0.379 mL | 0.7581 mL | 0.9476 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.019 mL | 0.0948 mL | 0.1895 mL | 0.379 mL | 0.4738 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fesoterodine (Toviaz) is an antimuscarinic drug to treat overactive bladder syndrome (OAB).
- 6'-Amino-3',4'-(methylenedioxy)acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8760
CAS No.:28657-75-2
- Epoxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN5382
CAS No.:28649-60-7
- Euphorbiasteroid
Catalog No.:BCN2781
CAS No.:28649-59-4
- Multicaulisin
Catalog No.:BCN7840
CAS No.:286461-76-5
- L-838,417
Catalog No.:BCC7617
CAS No.:286456-42-6
- Meloscandonine
Catalog No.:BCN5186
CAS No.:28645-27-4
- Nigericin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7915
CAS No.:28643-80-3
- KRN 633
Catalog No.:BCC2544
CAS No.:286370-15-8
- S 14506 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7174
CAS No.:286369-38-8
- Erythristemine
Catalog No.:BCN5184
CAS No.:28619-41-2
- 8-Prenylkaempferol
Catalog No.:BCN3311
CAS No.:28610-31-3
- Isoanhydroicaritin
Catalog No.:BCN3879
CAS No.:28610-30-2
- Ezatiostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4259
CAS No.:286942-97-0
- NCX 4040
Catalog No.:BCC7944
CAS No.:287118-97-2
- PD 180970
Catalog No.:BCC3894
CAS No.:287204-45-9
- MA 2029
Catalog No.:BCC7983
CAS No.:287206-61-5
- Oxcarbazepine
Catalog No.:BCC5077
CAS No.:28721-07-5
- Scriptaid
Catalog No.:BCC2163
CAS No.:287383-59-9
- 3CAI
Catalog No.:BCC5402
CAS No.:28755-03-5
- Apigenin 5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN5185
CAS No.:28757-27-9
- Rosuvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC4139
CAS No.:287714-41-4
- 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno [3,2,c]pyridine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8664
CAS No.:28783-41-7
- Nordihydrocapsaicin
Catalog No.:BCN2387
CAS No.:28789-35-7
- H-Cys(Acm)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2903
CAS No.:28798-28-9
The short-term and long-term adverse ocular effects of fesoterodine fumarate.[Pubmed:26340514]
Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016 Sep;35(3):181-4.
AIM: To evaluate the short-term and long-term effects of Fesoterodine Fumarate treatment which is used for overactive bladder (OAB) on pupil diameter (PD), intraocular pressure (IOP) and accommodation amplitude (AA). METHOD: Ophthalmic examination was performed before and after receiving medication (on the 30th and 90th day) on 120 eyes of 120 women whom were planned to begin anticholinergic treatment (Fesoterodine Fumarate, 4 mg/day, peroral) for OAB, prospectively. The changes in PD, IOP and AA were analyzed statistically. RESULTS: The mean age of 120 women was 52.06 +/- 9.39 years (30-70 years). The mean PD, IOP and AA values were 4.12 +/- 0.61 mm (3.00-5.70 mm), 15.58 +/- 1.74 mmHg (11-20 mmHg) 2.28 +/- 1.26 Diopter (D) (0.50-5.50 D) at baseline; 4.68 +/- 0.65 mm (3.20-5.80 mm), 16.11 +/- 1.72 mmHg (11-20 mmHg), 1.68 +/- 1.04 D (0.25-4.50 D) at 30th day; and 4.28 +/- 0.58 mm (3.10-5.70 mm), 16.09 +/- 1.96 mmHg (11-19 mmHg), 2.18 +/- 1.19 D (0.50-5.00 D) at 90th day, respectively. Although increases in PD values and decreases in AA values were statistically significant (p < 0.001 for each), the changes in IOP values were not as such (p = 0.642). Visual complaint was not observed in any patient. DISCUSSION: The newest anticholinergic medication in women with OAB increased the PD and decreased the AA statistically significantly. Clinically, it seems to be well-tolerated by the patient.
The short-term and long-term adverse ocular effects of fesoterodine fumarate.[Pubmed:26264533]
Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2015 Aug 12:1-4.
AIM: To evaluate the short-term and long-term effects of Fesoterodine Fumarate treatment which is used for overactive bladder (OAB) on pupil diameter (PD), intraocular pressure (IOP) and accommodation amplitude (AA). METHOD: Ophthalmic examination was performed before and after receiving medication (on the 30th and 90th day) on 120 eyes of 120 women whom were planned to begin anticholinergic treatment (Fesoterodine Fumarate, 4 mg/day, peroral) for OAB, prospectively. The changes in PD, IOP and AA were analyzed statistically. RESULTS: The mean age of 120 women was 52.06 +/- 9.39 years (30-70 years). The mean PD, IOP and AA values were 4.12 +/- 0.61 mm (3.00-5.70 mm), 15.58 +/- 1.74 mmHg (11-20 mmHg) 2.28 +/- 1.26 Diopter (D) (0.50-5.50 D) at baseline; 4.68 +/- 0.65 mm (3.20-5.80 mm), 16.11 +/- 1.72 mmHg (11-20 mmHg), 1.68 +/- 1.04 D (0.25-4.50 D) at 30th day; and 4.28 +/- 0.58 mm (3.10-5.70 mm), 16.09 +/- 1.96 mmHg (11-19 mmHg), 2.18 +/- 1.19 D (0.50-5.00 D) at 90th day, respectively. Although increases in PD values and decreases in AA values were statistically significant (p < 0.001 for each), the changes in IOP values were not as such (p = 0.642). Visual complaint was not observed in any patient. DISCUSSION: The newest anticholinergic medication in women with OAB increased the PD and decreased the AA statistically significantly. Clinically, it seems to be well-tolerated by the patient.
Early Fesoterodine Fumarate Administration Prevents Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in a Spinal Cord Transected Rat Model.[Pubmed:28060912]
PLoS One. 2017 Jan 6;12(1):e0169694.
BACKGROUND: In spinal cord injury, onset of detrusor overactivity (DO) is detrimental for quality of life (incontinence) and renal risk. Prevention has only been achieved with complex sophisticated electrical neuromodulation techniques. PURPOSE: To assess the efficacy of early Fesoterodine Fumarate (FF) administration in preventing bladder overactivity in a spinal cord transected (SCT) rat model. METHODS: 33 Sprague-Dawley rats were allocated to 6 groups-Group 1: 3 normal controls; Group 2: 6 SCT controls; Group 3: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.18 mg/kg/d; Group 4: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.12 mg/kg/d; Group 5: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.18 mg/kg/d + 72-h wash-out period; Group 6: 6 SCT rats + FF 0.12 mg/kg/d + 72-h wash-out period. SCT was performed at T10. FF was continuously administered. Cystometry was undertaken 6 weeks after SCT in awake rats recording intermicturition pressure (IMP), baseline pressure, threshold pressure (Pthres) and maximum pressure (Pmax). Normal controls and SCT controls were initially compared using the Mann-Whitney U tests in order to confirm the SCT effect on cystometric parameters. The comparisons in cystometric and metabolic cage parameters between SCT controls and treated rats were done using post-hoc Dunn's tests for Kruskal-Wallis analysis. Statistical testing was conducted at the two-tailed alpha-level of 0.05. RESULTS: Pressure parameters were significantly higher in SCT control group compared to normal controls. Six weeks after SCT, IMP was significantly lower in low dose treated group than in SCT controls. Pmax was significantly lower in 3 treated groups compared to SCT controls. Pthres was significantly lower in full time treated groups than in SCT controls. CONCLUSION: Early administration of FF modulates bladder overactivity in a SCT rat model. Whereas short-term prevention has been demonstrated, the long-term should be further analyzed. Clinical application of these results should confirm this finding through randomized research protocols.
Safety and efficacy of fesoterodine fumarate in patients with overactive bladder: results of a post-marketing surveillance study in Korea.[Pubmed:27046653]
Curr Med Res Opin. 2016 Aug;32(8):1361-6.
OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Fesoterodine Fumarate (fesoterodine; Toviaz ) in Korean patients with overactive bladder (OAB) in routine clinical practice. METHODS: This was an open-label, non-interventional, prospective, post-marketing surveillance study submitted to the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. A total of 3109 patients aged >/=18 years with OAB symptoms were prescribed flexible doses of fesoterodine at the investigator's discretion. Safety was assessed based upon the reporting of adverse events (AEs). Efficacy was evaluated on the basis of patient self-assessment using a bladder diary as well as on the basis of investigator assessment in terms of overall clinical efficacy. RESULTS: A final analysis was performed on 3107 (99.9%) and 2978 (95.8%) patients for safety and efficacy analysis, respectively. The mean treatment duration of fesoterodine was 83.2 days. The incidence of AEs was 8.5% (265/3107). Common AEs that accounted for more than 1.0% of the total AE incidence included dry mouth (5.4%, 168/3107), constipation (1.5%, 48/3107) and micturition disorder (1.1%, 35/3107). Mean episodes of urinary frequency, urgency, and urgency urinary incontinence (UUI) per 24 hours decreased by 4.0, 2.4, and 0.8, respectively (all p < 0.001). At the final follow-up visit, the investigators found improvement in clinical efficacy for the majority of patients (90.1%, 2684/2978). Limitations of this study include the observational study design and the relatively short treatment duration. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that fesoterodine is a well tolerated and effective treatment for Korean patients with OAB in routine clinical practice.


