EuphorbiasteroidCAS# 28649-59-4 |
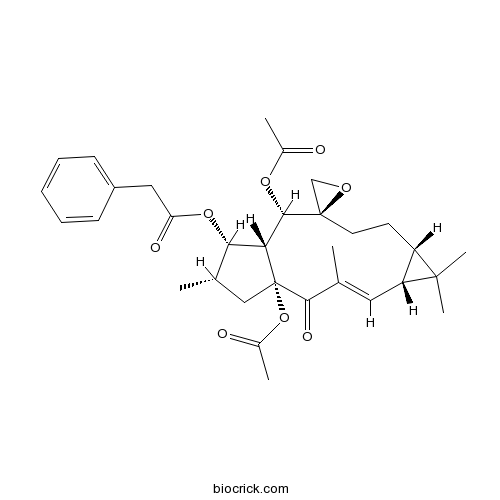
- Euphorbia factor L1
Catalog No.:BCN0415
CAS No.:76376-43-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 28649-59-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15940183 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C32H40O8 | M.Wt | 552.66 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Euphorbia factor L1;76376-43-7 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1'R,2R,3'E,5'R,7'S,11'S,12'R,13'S,14'S)-1',11'-diacetyloxy-3',6',6',14'-tetramethyl-2'-oxospiro[oxirane-2,10'-tricyclo[10.3.0.05,7]pentadec-3-ene]-13'-yl] 2-phenylacetate | ||
| SMILES | CC1CC2(C(C1OC(=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(C4(CCC5C(C5(C)C)C=C(C2=O)C)CO4)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SDGDWRYYHQOQOJ-XXMLZKCSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H40O8/c1-18-14-24-23(30(24,5)6)12-13-31(17-37-31)29(38-20(3)33)26-27(39-25(35)15-22-10-8-7-9-11-22)19(2)16-32(26,28(18)36)40-21(4)34/h7-11,14,19,23-24,26-27,29H,12-13,15-17H2,1-6H3/b18-14+/t19-,23-,24+,26+,27-,29-,31+,32+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Euphorbiasteroid has anti-obesity activities, it inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells through activation of the AMPK pathway. Euphorbiasteroid could be a transport substrate for P-gp that can effectively inhibit P-gp-mediated drug transport and reverse resistance to anticancer drugs in MES-SA/Dx5 cells; it induces HL-60 cells to apoptosis via promoting Bcl-2/Bax apoptotic signaling pathway in a dose-dependent manner.Euphorbia factor L1 inhibits osteoclastogenesis and induces osteoclast apoptosis, it can enhance the ATP hydrolysis activity of ABCB1 stimulated by verapamil. Euphorbia factor L1 inhibits the efflux of ABCB1 in KBv200 and MCF-7/adr cells, does not downregulate their expression either in mRNA or protein level. |
| Targets | AMPK | P-gp | Bcl-2/Bax | ATPase | ERK | Akt |
| In vitro | Apoptosis sensitization by Euphorbia factor L1 in ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistant K562/ADR cells.[Pubmed: 24135937]Molecules. 2013 Oct 16;18(10):12793-808.
Euphorbiasteroid, a component of Euphorbia lathyris L., inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed: 25914364]Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Jun;33(4):220-5.The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of Euphorbiasteroid, a component of Euphorbia lathyris L., on adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes and its underlying mechanisms. Euphorbiasteroid reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multi-drug resistance in human sarcoma cell line MES-SA/Dx5.[Pubmed: 19960428 ]Phytother Res. 2010 Jul;24(7):1042-6.
|
| Kinase Assay | Euphorbia factor L1 reverses ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance involving interaction with ABCB1 independent of ABCB1 downregualtion.[Pubmed: 21308736 ]J Cell Biochem. 2011 Apr;112(4):1076-83.Euphorbia factor L1 (EFL1) belongs to diterpenoids of genus Euphorbia. |
| Cell Research | Mechanism of euphorbiasteroid inducing apoptosis of HL-60 cells[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention & Treatment, 2014 , 21 (23) :1865-1870.To investigate the effect of Euphorbiasteroid on inducing the apoptosis of HL-60 cells and identify the role of Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathway in this process. |

Euphorbiasteroid Dilution Calculator

Euphorbiasteroid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8094 mL | 9.0472 mL | 18.0943 mL | 36.1886 mL | 45.2358 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3619 mL | 1.8094 mL | 3.6189 mL | 7.2377 mL | 9.0472 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1809 mL | 0.9047 mL | 1.8094 mL | 3.6189 mL | 4.5236 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0362 mL | 0.1809 mL | 0.3619 mL | 0.7238 mL | 0.9047 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0181 mL | 0.0905 mL | 0.1809 mL | 0.3619 mL | 0.4524 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Multicaulisin
Catalog No.:BCN7840
CAS No.:286461-76-5
- L-838,417
Catalog No.:BCC7617
CAS No.:286456-42-6
- Meloscandonine
Catalog No.:BCN5186
CAS No.:28645-27-4
- Nigericin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7915
CAS No.:28643-80-3
- KRN 633
Catalog No.:BCC2544
CAS No.:286370-15-8
- S 14506 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7174
CAS No.:286369-38-8
- Erythristemine
Catalog No.:BCN5184
CAS No.:28619-41-2
- 8-Prenylkaempferol
Catalog No.:BCN3311
CAS No.:28610-31-3
- Isoanhydroicaritin
Catalog No.:BCN3879
CAS No.:28610-30-2
- Orientin
Catalog No.:BCN4984
CAS No.:28608-75-5
- CCG-1423
Catalog No.:BCC5581
CAS No.:285986-88-1
- BIRB 796 (Doramapimod)
Catalog No.:BCC2535
CAS No.:285983-48-4
- Epoxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN5382
CAS No.:28649-60-7
- 6'-Amino-3',4'-(methylenedioxy)acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8760
CAS No.:28657-75-2
- Fesoterodine Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4584
CAS No.:286930-03-8
- Ezatiostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4259
CAS No.:286942-97-0
- NCX 4040
Catalog No.:BCC7944
CAS No.:287118-97-2
- PD 180970
Catalog No.:BCC3894
CAS No.:287204-45-9
- MA 2029
Catalog No.:BCC7983
CAS No.:287206-61-5
- Oxcarbazepine
Catalog No.:BCC5077
CAS No.:28721-07-5
- Scriptaid
Catalog No.:BCC2163
CAS No.:287383-59-9
- 3CAI
Catalog No.:BCC5402
CAS No.:28755-03-5
- Apigenin 5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN5185
CAS No.:28757-27-9
- Rosuvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC4139
CAS No.:287714-41-4
Euphorbia factor L1 reverses ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance involving interaction with ABCB1 independent of ABCB1 downregualtion.[Pubmed:21308736]
J Cell Biochem. 2011 Apr;112(4):1076-83.
Euphorbia factor L1 (EFL1) belongs to diterpenoids of genus Euphorbia. In this article, its reversal activity against ABCB1-mediated MDR in KBv200 and MCF-7/adr cells was reported. However, EFL1 did not alter the sensitivity of KB and MCF-7 cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Meanwhile, EFL1 significantly increased accumulation of doxorubicin and rhodamine 123 in KBv200 and MCF-7/adr cells, showing no significant influence on that of KB and MCF-7 cells. Furthermore, EFL1 could enhance the ATP hydrolysis activity of ABCB1 stimulated by verapamil. At the same time, EFL1 inhibited the efflux of ABCB1 in KBv200 and MCF-7/adr cells. In addition, EFL1 did not downregulate expression of ABCB1 in KBv200 and MCF-7/adr cells either in mRNA or protein level.
Apoptosis sensitization by Euphorbia factor L1 in ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistant K562/ADR cells.[Pubmed:24135937]
Molecules. 2013 Oct 16;18(10):12793-808.
In this article, reversal activities of Euphorbia factor L1 (EFL1) against ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance (MDR) and apoptosis sensitization in K562/ADR cells are reported. EFL1 decreased the IC50 values of anticancer agents in K562/ADR cells over-expressing ABCB1. However, EFL1 did not affect the IC50 values of anticancer agents in sensitive K562 cells. Additionally, EFL1 increased the intracellular accumulation of rhodamine 123 and doxorubicin in K562/ADR cells without affecting their accumulation in K562 cells. Furthermore, EFL1 sensitized the apoptosis triggered by vincristine in K562/ADR cells via mitochondrial pathway, as confirmed by Annexin V-FITC/PI detection and western blot. At the same time, EFL1 did not influence the apoptosis induced by vincristine in K562 cells. Western blot results showed that EFL1 did not affect the phosphorylation level of AKT and ERK in K562 and K562/ADR cells. Finally, EFL1 did not down-regulate protein expression of ABCB1.
Euphorbiasteroid reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multi-drug resistance in human sarcoma cell line MES-SA/Dx5.[Pubmed:19960428]
Phytother Res. 2010 Jul;24(7):1042-6.
In this study, we evaluated whether Euphorbiasteroid isolated from Euphorbia lathyris has the potential to reverse P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated multi-drug resistance (MDR) by using the drug-sensitive human sarcoma cell line MES-SA and its MDR counterpart MES-SA/Dx5. Interestingly, even at low concentrations of Euphorbiasteroid (1-3 microM), it efficiently restored the toxicities of anticancer drugs including vinblastine, taxol and doxorubicin in MES-SA/Dx5 cells. Additionally, the computational Bayesian model for predicting potential P-gp substrates or inhibitors revealed that Euphorbiasteroid showed 97% probability for substrate likeness having similar molecular features with 50 P-gp substrates. Consistent with this result, the substrate likeness of Euphorbiasteroid was also experimentally confirmed by P-gp ATPase activity assay. In conclusion, our finding suggested that Euphorbiasteroid could be a transport substrate for P-gp that can effectively inhibit P-gp-mediated drug transport and reverse resistance to anticancer drugs in MES-SA/Dx5 cells.
Euphorbiasteroid, a component of Euphorbia lathyris L., inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed:25914364]
Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Jun;33(4):220-5.
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of Euphorbiasteroid, a component of Euphorbia lathyris L., on adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes and its underlying mechanisms. Euphorbiasteroid decreased differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells via reduction of intracellular triglyceride (TG) accumulation at concentrations of 25 and 50 muM. In addition, Euphorbiasteroid altered the key regulator proteins of adipogenesis in the early stage of adipocyte differentiation by increasing the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Subsequently, levels of adipogenic proteins, including fatty acid synthase, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha, were decreased by Euphorbiasteroid treatment at the late stage of adipocyte differentiation. The anti-adipogenic effect of Euphorbiasteroid may be derived from inhibition of early stage of adipocyte differentiation. Taken together, Euphorbiasteroid inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells through activation of the AMPK pathway. Therefore, Euphorbiasteroid and its source plant, E. lathyris L., could possibly be one of the fascinating anti-obesity agent.


