CCG-1423RhoA inhibitor CAS# 285986-88-1 |
- JNK-IN-7
Catalog No.:BCC1672
CAS No.:1408064-71-0
- JNK-IN-8
Catalog No.:BCC1673
CAS No.:1410880-22-6
- CC-401 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1458
CAS No.:1438391-30-0
- AS 602801
Catalog No.:BCC1369
CAS No.:848344-36-5
- DB07268
Catalog No.:BCC1519
CAS No.:929007-72-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 285986-88-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2726015 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H13ClF6N2O3 | M.Wt | 454.75 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 26 mg/mL (57.17 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
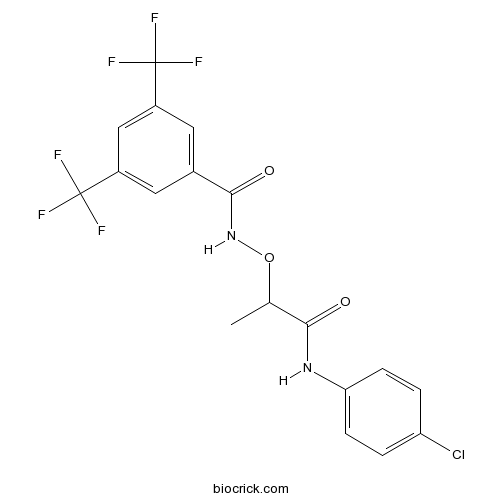
| Chemical Name | N-[1-(4-chloroanilino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl)ONC(=O)C2=CC(=CC(=C2)C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DSMXVSGJIDFLKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H13ClF6N2O3/c1-9(15(28)26-14-4-2-13(19)3-5-14)30-27-16(29)10-6-11(17(20,21)22)8-12(7-10)18(23,24)25/h2-9H,1H3,(H,26,28)(H,27,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Rho/SRF pathway inhibitor; stimulates apoptosis of a melanoma cell line overexpressing RhoC (A375M2). Suppresses Rho-dependent invasion of PC-3 prostate cancer cells in vitro and inhibits lysophosphatidic acid-induced DNA synthesis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. When used in combination with Retinoic acid,LY 294002 and Pyridone 6, it induces intermediate mesoderm differentiation from ESCs. |

CCG-1423 Dilution Calculator

CCG-1423 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.199 mL | 10.9951 mL | 21.9901 mL | 43.9802 mL | 54.9753 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4398 mL | 2.199 mL | 4.398 mL | 8.796 mL | 10.9951 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2199 mL | 1.0995 mL | 2.199 mL | 4.398 mL | 5.4975 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.044 mL | 0.2199 mL | 0.4398 mL | 0.8796 mL | 1.0995 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.022 mL | 0.11 mL | 0.2199 mL | 0.4398 mL | 0.5498 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CCG-1423 is a small-molecule inhibitor of RhoA transcriptional signaling. The interaction between MRTF-A and importin a/b1 was inhibited by CCG-1423, but monomeric G-actin binding to MRTF-A was not inhibited [4].
Multiple members of the Rho family of small GTPases play important roles in these cellular processes and in some human tumors (e.g., colon, esophageal, lung, pancreatic, and inflammatory breast cancers), up-regulation of RhoA or RhoC is associated with a poor clinical outcome (2, 3).
CCG-1423 has nanomolar to low micromolar potency as well as selectivity toward Rho-overexpressing and invasive cancer cell lines for inhibition of DNA synthesis, cell growth, and/or invasion. Caspase-3 activation in the highly metastatic RhoC-overexpressing A375M2 melanoma cell line was enhanced by CCG-1423 whereas a smaller increase was seen with the parental A375 cell line, whereas just the opposite pattern was seen with daunorubicin [2].
References:
[1]. Minami T, Kuwahara K, Nakagawa Y et al. Reciprocal expression of MRTF-A and myocardin is crucial for pathological vascular remodelling in mice. EMBO J. 2012 Nov 28;31(23):4428-40. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.296. Epub 2012 Oct 26.
[2]. Hayashi K, Watanabe B, Nakagawa Y et al. RPEL proteins are the molecular targets for CCG-1423, an inhibitor of Rho signaling. PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e89016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089016. eCollection 2014.
- BIRB 796 (Doramapimod)
Catalog No.:BCC2535
CAS No.:285983-48-4
- 22-Dehydroclerosteryl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5183
CAS No.:28594-00-5
- Docosyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN5182
CAS No.:28593-92-2
- Eicosanyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN7209
CAS No.:28593-90-0
- Persicogenin
Catalog No.:BCN7744
CAS No.:28590-40-1
- 7-Geranyloxy-6-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN5181
CAS No.:28587-43-1
- 4-Benzoyloxy-2-azetidinone
Catalog No.:BCC8696
CAS No.:28562-58-5
- Theaflavin-3'-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN5421
CAS No.:28543-07-9
- BML-190
Catalog No.:BCC4410
CAS No.:2854-32-2
- 1-Amino-2-methylpropan-2-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1773
CAS No.:2854-16-2
- Anadoline N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2029
CAS No.:28513-29-3
- Malvidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3032
CAS No.:28500-04-1
- Orientin
Catalog No.:BCN4984
CAS No.:28608-75-5
- Isoanhydroicaritin
Catalog No.:BCN3879
CAS No.:28610-30-2
- 8-Prenylkaempferol
Catalog No.:BCN3311
CAS No.:28610-31-3
- Erythristemine
Catalog No.:BCN5184
CAS No.:28619-41-2
- S 14506 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7174
CAS No.:286369-38-8
- KRN 633
Catalog No.:BCC2544
CAS No.:286370-15-8
- Nigericin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7915
CAS No.:28643-80-3
- Meloscandonine
Catalog No.:BCN5186
CAS No.:28645-27-4
- L-838,417
Catalog No.:BCC7617
CAS No.:286456-42-6
- Multicaulisin
Catalog No.:BCN7840
CAS No.:286461-76-5
- Euphorbiasteroid
Catalog No.:BCN2781
CAS No.:28649-59-4
- Epoxylathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN5382
CAS No.:28649-60-7
RPEL proteins are the molecular targets for CCG-1423, an inhibitor of Rho signaling.[Pubmed:24558465]
PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e89016.
Epithelial-msenchymal transition (EMT) is closely associated with cancer and tissue fibrosis. The nuclear accumulation of myocardin-related transcription factor A (MRTF-A/MAL/MKL1) plays a vital role in EMT. In various cells treated with CCG-1423, a novel inhibitor of Rho signaling, the nuclear accumulation of MRTF-A is inhibited. However, the molecular target of this inhibitor has not yet been identified. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of this effect of CCG-1423. The interaction between MRTF-A and importin alpha/beta1 was inhibited by CCG-1423, but monomeric G-actin binding to MRTF-A was not inhibited. We coupled Sepharose with CCG-1423 (CCG-1423 Sepharose) to investigate this mechanism. A pull-down assay using CCG-1423 Sepharose revealed the direct binding of CCG-1423 to MRTF-A. Furthermore, we found that the N-terminal basic domain (NB) of MRTF-A, which acts as a functional nuclear localization signal (NLS) of MRTF-A, was the binding site for CCG-1423. G-actin did not bind to CCG-1423 Sepharose, but the interaction between MRTF-A and CCG-1423 Sepharose was reduced in the presence of G-actin. We attribute this result to the high binding affinity of MRTF-A for G-actin and the proximity of NB to G-actin-binding sites (RPEL motifs). Therefore, when MRTF-A forms a complex with G-actin, the binding of CCG-1423 to NB is expected to be blocked. NF-E2 related factor 2, which contains three distinct basic amino acid-rich NLSs, did not bind to CCG-1423 Sepharose, but other RPEL-containing proteins such as MRTF-B, myocardin, and Phactr1 bound to CCG-1423 Sepharose. These results suggest that the specific binding of CCG-1423 to the NLSs of RPEL-containing proteins. Our proposal to explain the inhibitory action of CCG-1423 is as follows: When the G-actin pool is depleted, CCG-1423 binds specifically to the NLS of MRTF-A/B and prevents the interaction between MRTF-A/B and importin alpha/beta1, resulting in inhibition of the nuclear import of MRTF-A/B.
Design, synthesis and prostate cancer cell-based studies of analogs of the Rho/MKL1 transcriptional pathway inhibitor, CCG-1423.[Pubmed:19963382]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):665-72.
We recently identified bis(amide) CCG-1423 (1) as a novel inhibitor of RhoA/C-mediated gene transcription that is capable of inhibiting invasion of PC-3 prostate cancer cells in a Matrigel model of metastasis. An initial structure-activity relationship study focusing on bioisosteric replacement of the amides and conformational restriction identified two compounds, 4g and 8, with improved selectivity for inhibition of RhoA/C-mediated gene transcription and attenuated cytotoxicity relative to 1. Both compounds were also capable of inhibiting cell invasion with equal efficacy to 1 but with less attendant cytotoxicity.
Stereospecific Inhibitory Effects of CCG-1423 on the Cellular Events Mediated by Myocardin-Related Transcription Factor A.[Pubmed:26295164]
PLoS One. 2015 Aug 21;10(8):e0136242.
CCG-1423 suppresses several pathological processes including cancer cell migration, tissue fibrosis, and the development of atherosclerotic lesions. These suppressions are caused by inhibition of myocardin-related transcription factor A (MRTF-A), which is a critical factor for epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). CCG-1423 can therefore be a potent inhibitor for EMT. CCG-1423 and related compounds, CCG-100602 and CCG-203971 possess similar biological activities. Although these compounds are comprised of two stereoisomers, the differences in their biological activities remain to be assessed. To address this issue, we stereoselectively synthesized optically pure isomers of these compounds and validated their biological activities. The S-isomer of CCG-1423 rather than the R-isomer exhibited modestly but significantly higher inhibitory effects on the cellular events triggered by MRTF-A activation including serum response factor-mediated gene expression and cell migration of fibroblasts and B16F10 melanoma cells. Accordingly, the S-isomer of CCG-1423 more potently blocked the serum-induced nuclear import of MRTF-A than the R-isomer. No such difference was observed in cells treated with each of two stereoisomers of CCG-100602 or CCG-203971. We previously reported that the N-terminal basic domain (NB), which functions as a nuclear localization signal of MRTF-A, is a binding site for CCG-1423. Consistent with the biological activities of two stereoisomers of CCG-1423, docking simulation demonstrated that the S-isomer of CCG-1423 was more likely to bind to NB than the R-isomer. This is a first report demonstrating the stereospecific biological activities of CCG-1423.
Design and synthesis of tag-free photoprobes for the identification of the molecular target for CCG-1423, a novel inhibitor of the Rho/MKL1/SRF signaling pathway.[Pubmed:23766813]
Beilstein J Org Chem. 2013 May 21;9:966-73.
CCG-1423 and related analogues represent a new class of inhibitors of Rho/MKL1/SRF-mediated gene transcription, a pathway that has been implicated in both cancer and fibrosis. The molecular target for these compounds is unknown. To facilitate its identification, a series of tag-free photoaffinity probes was designed and synthesized, each one containing a photoactivatable group and an acetylenic end group for subsequent attachment to a fluorescent tag using click chemistry. All were confirmed to maintain biological activity in a cell-based assay for inhibition of SRE-Luc expression. The functional activity of the most potent probe 24 was further confirmed in an assay for PC-3 cell migration. Photolysis of 24 in intact PC-3 cells followed by cell lysis, click ligation of a fluorescent dye, and gel electrophoresis revealed specific labeling of a single 24 kDa band that could be blocked with an active competitor. Future work will focus on identifying the labeled protein(s).
CCG-1423: a small-molecule inhibitor of RhoA transcriptional signaling.[Pubmed:17699722]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Aug;6(8):2249-60.
Lysophosphatidic acid receptors stimulate a Galpha(12/13)/RhoA-dependent gene transcription program involving the serum response factor (SRF) and its coactivator and oncogene, megakaryoblastic leukemia 1 (MKL1). Inhibitors of this pathway could serve as useful biological probes and potential cancer therapeutic agents. Through a transcription-based high-throughput serum response element-luciferase screening assay, we identified two small-molecule inhibitors of this pathway. Mechanistic studies on the more potent CCG-1423 show that it acts downstream of Rho because it blocks SRE.L-driven transcription stimulated by Galpha(12)Q231L, Galpha(13)Q226L, RhoA-G14V, and RhoC-G14V. The ability of CCG-1423 to block transcription activated by MKL1, but not that induced by SRF-VP16 or GAL4-VP16, suggests a mechanism targeting MKL/SRF-dependent transcriptional activation that does not involve alterations in DNA binding. Consistent with its role as a Rho/SRF pathway inhibitor, CCG-1423 displays activity in several in vitro cancer cell functional assays. CCG-1423 potently (<1 mumol/L) inhibits lysophosphatidic acid-induced DNA synthesis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells, and whereas it inhibits the growth of RhoC-overexpressing melanoma lines (A375M2 and SK-Mel-147) at nanomolar concentrations, it is less active on related lines (A375 and SK-Mel-28) that express lower levels of Rho. Similarly, CCG-1423 selectively stimulates apoptosis of the metastasis-prone, RhoC-overexpressing melanoma cell line (A375M2) compared with the parental cell line (A375). CCG-1423 inhibited Rho-dependent invasion by PC-3 prostate cancer cells, whereas it did not affect the Galpha(i)-dependent invasion by the SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cell line. Thus, based on its profile, CCG-1423 is a promising lead compound for the development of novel pharmacologic tools to disrupt transcriptional responses of the Rho pathway in cancer.


