AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)HDAC inhibitor,novel and potent CAS# 935881-37-1 |
- CUDC-101
Catalog No.:BCC2149
CAS No.:1012054-59-9
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- NSC 3852
Catalog No.:BCC2423
CAS No.:3565-26-2
- LAQ824 (NVP-LAQ824,Dacinostat)
Catalog No.:BCC2160
CAS No.:404951-53-7
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
- KD 5170
Catalog No.:BCC2420
CAS No.:940943-37-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 935881-37-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6918848 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H20N2O3 | M.Wt | 312.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 63 mg/mL (201.69 mM) in DMSO | ||
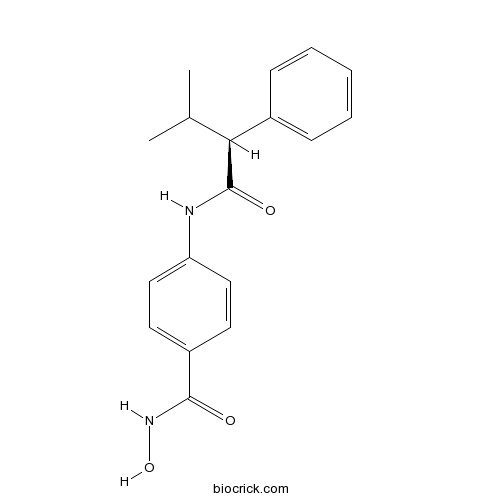
| Chemical Name | N-hydroxy-4-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-phenylbutanoyl]amino]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)C(=O)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LAMIXXKAWNLXOC-INIZCTEOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H20N2O3/c1-12(2)16(13-6-4-3-5-7-13)18(22)19-15-10-8-14(9-11-15)17(21)20-23/h3-12,16,23H,1-2H3,(H,19,22)(H,20,21)/t16-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AR-42 is an inhibitor of HDAC with IC50 of 30 nM. | |||||
| Targets | HDAC | |||||
| IC50 | 30 nM | |||||

AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42) Dilution Calculator

AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2014 mL | 16.0072 mL | 32.0143 mL | 64.0287 mL | 80.0359 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6403 mL | 3.2014 mL | 6.4029 mL | 12.8057 mL | 16.0072 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3201 mL | 1.6007 mL | 3.2014 mL | 6.4029 mL | 8.0036 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.064 mL | 0.3201 mL | 0.6403 mL | 1.2806 mL | 1.6007 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.032 mL | 0.1601 mL | 0.3201 mL | 0.6403 mL | 0.8004 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
The treatment of AR-42 and CRT/E7 DNA vaccine resulted in longer survival, decreased tumor growth and enhanced E7-specific immune response in HPV-16 E7-expressing murine TC-1 tumor-bearing mice compared to AR-42 or CRT/E7 DNA vaccine alone, which indicates AR-42 is capable of enhancing the potency of the CRT/E7 DNA vaccine by improving tumor-specific immune responses and antitumor effects. Moreover, AR-42 increased the surface expression of MHC class I molecules in TC-1 cells and its susceptibility to the cytotoxicity of E7-specific T cells.
Abstract
AR-42 is a potent HDACI in AML that increases miR-29b levels and induces down-regulation of known miR-29n targets. The AR-42-and-then-decitabine regime exhibited stronger anti-leukemic activity in vitro and in vivo than the decitabine-and-then AR-42 regime and each mono-therapy.
Abstract
Although it inhibited cell proliferation in both Ben-Men-1 and meningeal cells through increasing the expression of p16(INK4A), P21(CIP1/WAF1) and p27(KIP1), AR-42 induced cell arrest at G(2)-M and significantly reduced cyclin B expression in Ben-Men-1 cells whereas induced cell arrest at G(1) and reduced expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclins D1, E and A in meningeal cells. Additionally, AR-42 decreased the expression of Aurora A, Aurora B and Bcl(XL),increased Bim expression and caused regression of Ben-Men-1-LucB tumors.
Abstract
AR-42 exhibited cytotoxicity against MM cells at a mean LC(50) of 0.18 ± 0.06 μmol/l, which induced apoptosis with cleavage of caspases 8,9 and 3 and affected gp130/STAT-3 pathway through down-regulation of expression of gp130 and STAT3-regulated targets and inhibition of STAT3 activation.
Abstract
AR-42, a novel DAC inhibitor, was evaluated for its efficacy to treat B-cell malignancies.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AR-42 (also known as OSU-HDAC42), a derivative of hydroxamate-tethered phenylbutyrate, is a novel and potent inhibitor of histone deacetylase (HDAC) that potently inhibits the activity of HDAC with 50% inhibition concentration IC50 value of 16 nM and induces histone H3 acetylation, α-tubulin acetylation and p21 up-regulation, which have been considered as the hallmark indicators of HDAC inhibition. AR-42 has been found to modulate several apoptosis inhibitors as well as cell survival regulator, including Akt, Bcl-xL, Bax, Ku70 and surviving, and exert potent antitumor activity against multiple tumor types, such as human prostate and hepatic cancers, at least partially through PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition.
Reference
Matthew L. Bush†, Janet Oblinger†, Victoria Brendel, Griffin Santarelli, Jie Huang, Elena M. Akhmametyeva, Sarah S. Burns, Justin Wheeler, Jeremy Davis, Charles W. Yates, Abhik R. Chaudhury, Samuel Kulp, Ching-Shih Chen, Long-Sheng Chang, D. Bradley Welling, and Abraham Jacob. AR42, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, as a potential therapy for vestibular schwannomas and meningiomas. Neuro-Oncology 13(9):983–999, 2011
Aaron M. Sargeant, Robert C. Rengel, Samuel K. Kulp, et al. OSU-HDAC42, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Blocks Prostate Tumor Progression in the Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of the Mouse Prostate Model Cancer Res 2008;68:3999-4009.
Qiang Lu, Da-Sheng Wang, Chang-Shi Chen, Yuan-Dong Hu, and Ching-Shih Chen. Structure-Based Optimization of Phenylbutyrate-Derived Histone Deacetylase
Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5530-5535
- BIX 01294
Catalog No.:BCC1131
CAS No.:935693-62-2
- AZD1480
Catalog No.:BCC2191
CAS No.:935666-88-9
- MDL 72527
Catalog No.:BCC6060
CAS No.:93565-01-6
- Euphorbia factor L7a
Catalog No.:BCN3784
CAS No.:93550-94-8
- TH-237A
Catalog No.:BCC5378
CAS No.:935467-97-3
- (4->2)-Abeo-16-hydroxycleroda-2,13-dien-15,16-olide-3-al
Catalog No.:BCN7498
CAS No.:935293-70-2
- 2-Iodomelatonin
Catalog No.:BCC6772
CAS No.:93515-00-5
- Glimepiride
Catalog No.:BCC2109
CAS No.:93479-97-1
- Karavilagenin D
Catalog No.:BCN4480
CAS No.:934739-29-4
- Cobimetinib (racemate)
Catalog No.:BCC1492
CAS No.:934662-91-6
- Cobimetinib (R-enantiomer)
Catalog No.:BCC1493
CAS No.:934660-94-3
- Cobimetinib
Catalog No.:BCC1491
CAS No.:934660-93-2
- Oprozomib (ONX-0912)
Catalog No.:BCC1146
CAS No.:935888-69-0
- 5-(6-Hydroxybenzofuran-2-yl)-2-(3-methylbut-1-enyl)benzene-1,3-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1304
CAS No.:936006-11-0
- Daphnenone
Catalog No.:BCN3229
CAS No.:936006-13-2
- cAMPS-Sp, triethylammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC8081
CAS No.:93602-66-5
- TG101209
Catalog No.:BCC2198
CAS No.:936091-14-4
- TG101348 (SAR302503)
Catalog No.:BCC2190
CAS No.:936091-26-8
- ACET
Catalog No.:BCC7462
CAS No.:936095-50-0
- Ajuganipponin A
Catalog No.:BCN3660
CAS No.:936323-13-6
- PCI-32765 Racemate
Catalog No.:BCC5124
CAS No.:936563-87-0
- PCI-32765 (Ibrutinib)
Catalog No.:BCC1266
CAS No.:936563-96-1
- LCZ696
Catalog No.:BCC5505
CAS No.:936623-90-4
- VX-809
Catalog No.:BCC3712
CAS No.:936727-05-8
The Effect of a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor (AR-42) on Canine Prostate Cancer Growth and Metastasis.[Pubmed:28181686]
Prostate. 2017 May;77(7):776-793.
BACKGROUND: Canine prostate cancer (PCa) is an excellent preclinical model for human PCa. AR-42 is a histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) developed at The Ohio State University that inhibits the proliferation of several cancers, including multiple myeloma, lung, and hepatocellular cancer. In this study, we investigated whether AR-42 would prevent or decrease. The growth and metastasis of a canine PCa (Ace-1 cells) to bone in vitro and in vivo. METHODS: Proliferation, cell viability, invasion, and metastasis of a canine prostate cancer cell line (Ace-1) were measured following treatment with AR-42. Expression of anoikis resistance, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and stem cell-related markers were also evaluated. To assess the efficacy of AR-42 on prevention of PCa metastasis to bone, Ace-1 cells were injected in the left cardiac ventricle of nude mice, mice were treated with AR-42, and the incidence and growth of bone metastasis were measured. Bioluminescence was performed to monitor the bone metastases in nude mice. RESULTS: AR-42 inhibited the in vitro proliferation of Ace-1 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. The IC50 concentration of AR-42 for Ace-1 cells was 0.42 muM after 24 hr of treatment. AR-42 induced apoptosis, decreased cell migration, and increased the stem cell properties of Ace-1 cells in vitro. AR-42 downregulated E-cadherin, N-cadherin, TWIST, MYOF, anoikis resistance, and osteomimicry genes, while it upregulated SNAIL, PTEN, FAK, and ZEB1 gene expression in Ace-1 cells. Importantly, AR-42 decreased the bioluminescence and incidence of bone metastasis in nude mice. In addition, AR-42 induced apoptosis and altered the tumor cell morphology to an irregular cell phenotype with condensed chromatin in the bone metastases. CONCLUSION: AR-42 decreased PCa growth and bone metastasis, induced apoptosis, and downregulated osteomimicry genes in PCa cells in the bone microenvironment. Prostate 77:776-793, 2017. (c) 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Suppression of Tumor Growth and Muscle Wasting in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer by the Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor AR-42.[Pubmed:27889645]
Neoplasia. 2016 Dec;18(12):765-774.
PURPOSE: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the third leading cause of cancer death in the United States. This study was aimed at evaluating the efficacy of AR-42 (formerly OSU-HDAC42), a novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor currently in clinical trials, in suppressing tumor growth and/or cancer-induced muscle wasting in murine models of PDAC. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: The in vitro antiproliferative activity of AR-42 was evaluated in six human pancreatic cancer cell lines (AsPC-1, COLO-357, PANC-1, MiaPaCa-2, BxPC-3, SW1990). AsPC-1 subcutaneous xenograft and transgenic KP(fl/fl)C (LSL-Kras(G12D);Trp53(flox/flox);Pdx-1-Cre) mouse models of pancreatic cancer were used to evaluate the in vivo efficacy of AR-42 in suppressing tumor growth and/or muscle wasting. RESULTS: Growth suppression in AR-42-treated cells was observed in all six human pancreatic cancer cell lines with dose-dependent modulation of proliferation and apoptotic markers, which was associated with the hallmark features of HDAC inhibition, including p21 upregulation and histone H3 hyperacetylation. Oral administration of AR-42 at 50 mg/kg every other day resulted in suppression of tumor burden in the AsPC-1 xenograft and KP(fl/fl)C models by 78% and 55%, respectively, at the end of treatment. Tumor suppression was associated with HDAC inhibition, increased apoptosis, and inhibition of proliferation. Additionally, AR-42 as a single agent preserved muscle size and increased grip strength in KP(fl/fl)C mice. Finally, the combination of AR-42 and gemcitabine in transgenic mice demonstrated a significant increase in survival than either agent alone. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that AR-42 represents a therapeutically promising strategy for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Association of downregulated HDAC 2 with the impaired mitochondrial function and cytokine secretion in the monocytes/macrophages from gestational diabetes mellitus patients.[Pubmed:26936353]
Cell Biol Int. 2016 Jun;40(6):642-51.
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and cardiovascular diseases in later life, yet with underlying mechanisms unclear. The present study was to explore the association of upregulated histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC 2) with the impaired mitochondrial function and the cytokine secretion in the monocytes/macrophages from GDM patients. In this study, we examined the mitochondrial function, proinflamatory cytokine secretion and the HDAC 2 level in the serum or in the monocytes/macrophages from GDM patients, investigated the influence by HDAC 2 inhibitor, AR-42 (N-hydroxy-4-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-phenylbutanoyl]amino]benzamide), on the mitochondrial function and cytokine secretion in the isolated GDM monocytes/macrophages. Results demonstrated an increased mitochondria size, mitochondrial superoxide and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and an undermined mitochondria membrane potential (MMP) in the GDM monocytes/macrophages. And the serum levels of interleukin (IL)-1beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and IL-6 were also markedly higher in the GDM pregnancies, while the expression and activity of HDAC 2 was downregulated. Moreover, AR-42-mediated HDAC 2 inhibition in vitro contributed to the impaired mitochondrial function and the proinflamatory cytokine secretion. In conclusion, this study suggests an association of the impaired mitochondrial function and the promoted proinflamatory cytokine secretion with the reduced HDAC 2 activity in GDM. These findings may present HDAC 2 as a target for GDM treatment.
Preclinical Pharmacokinetics Study of R- and S-Enantiomers of the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, AR-42 (NSC 731438), in Rodents.[Pubmed:26943915]
AAPS J. 2016 May;18(3):737-45.
AR-42, a new orally bioavailable, potent, hydroxamate-tethered phenylbutyrate class I/IIB histone deacetylase inhibitor currently is under evaluation in phase 1 and 2 clinical trials and has demonstrated activity in both hematologic and solid tumor malignancies. This report focuses on the preclinical characterization of the pharmacokinetics of AR-42 in mice and rats. A high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay has been developed and applied to the pharmacokinetic study of the more active stereoisomer, S-AR-42, when administered via intravenous and oral routes in rodents, including plasma, bone marrow, and spleen pharmacokinetics (PK) in CD2F1 mice and plasma PK in F344 rats. Oral bioavailability was estimated to be 26 and 100% in mice and rats, respectively. R-AR-42 was also evaluated intravenously in rats and was shown to display different pharmacokinetics with a much shorter terminal half-life compared to that of S-AR-42. Renal clearance was a minor elimination pathway for parental S-AR-42. Oral administration of S-AR-42 to tumor-bearing mice demonstrated high uptake and exposure of the parent drug in the lymphoid tissues, spleen, and bone marrow. This is the first report of the pharmacokinetics of this novel agent, which is now in early phase clinical trials.
Non-epigenetic function of HDAC8 in regulating breast cancer stem cells by maintaining Notch1 protein stability.[Pubmed:26625202]
Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1796-807.
Here, we report a novel non-epigenetic function of histone deacetylase (HDAC) 8 in activating cancer stem cell (CSC)-like properties in breast cancer cells by enhancing the stability of Notch1 protein. The pan-HDAC inhibitors AR-42 and SAHA, and the class I HDAC inhibitor depsipeptide, suppressed mammosphere formation and other CSC markers by reducing Notch1 expression in MDA-MB-231 and SUM-159 cells. Interrogation of individual class I isoforms (HDAC1-3 and 8) using si/shRNA-mediated knockdown, ectopic expression and/or pharmacological inhibition revealed HDAC8 to be the primary mediator of this drug effect. This suppression of Notch1 in response to HDAC8 inhibition was abrogated by the proteasome inhibitor MG132 and siRNA-induced silencing of Fbwx7, indicating Notch1 suppression occurred through proteasomal degradation. However, co-immunoprecipitation analysis indicated that HDAC8 did not form complexes with Notch1 and HDAC inhibition had no effect on Notch1 acetylation. In a xenograft tumor model, the tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells was decreased by HDAC8 knockdown. These findings suggest the therapeutic potential of HDAC8 inhibition to suppress Notch1 signaling in breast cancer.


