NSC 3852HDAC inhibitor CAS# 3565-26-2 |
- Tenovin-1
Catalog No.:BCC2239
CAS No.:380315-80-0
- PRIMA-1MET
Catalog No.:BCC2414
CAS No.:5291-32-7
- PRIMA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2413
CAS No.:5608-24-2
- Pifithrin-α (PFTα)
Catalog No.:BCC2241
CAS No.:63208-82-2
- MIRA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2409
CAS No.:72835-26-8
- JNJ-26854165 (Serdemetan)
Catalog No.:BCC2240
CAS No.:881202-45-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3565-26-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 19103 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H6N2O2 | M.Wt | 174.16 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 10 mM in ethanol | ||
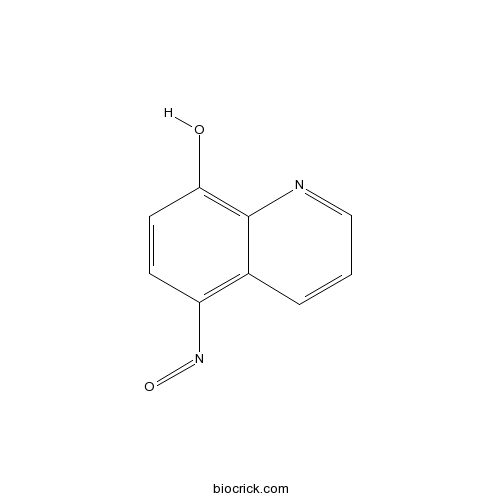
| Chemical Name | 5-nitrosoquinolin-8-ol | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=CC(=C2N=C1)O)N=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RZWRYPGAUIOOMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H6N2O2/c12-8-4-3-7(11-13)6-2-1-5-10-9(6)8/h1-5,12H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Histone deacetylase inhibitor. Causes cell differentiation and antiproliferative activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro and displays antitumor activity in vivo. |

NSC 3852 Dilution Calculator

NSC 3852 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.7418 mL | 28.7092 mL | 57.4185 mL | 114.8369 mL | 143.5462 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1484 mL | 5.7418 mL | 11.4837 mL | 22.9674 mL | 28.7092 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5742 mL | 2.8709 mL | 5.7418 mL | 11.4837 mL | 14.3546 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1148 mL | 0.5742 mL | 1.1484 mL | 2.2967 mL | 2.8709 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0574 mL | 0.2871 mL | 0.5742 mL | 1.1484 mL | 1.4355 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
NSC 3852 is a potent inhibitor of histone deacetylase [1].
Histone deacetylases (HADC) are a series of enzymes that remove acetyl groups from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone and make the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly, which prevent transcription.
In MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, NSC 3852 induced the formation of the DMPO-OH adduct, which was catalyzed by superoxide dismutase. The result suggested that NSC 3852 induced generation of superoxide and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which produced DNA damage and induced apoptosis. Also, NSC 3852 resulted in cells accumulation in G0, hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma protein(Rb) and reduced E2F1 and Myc protein [1]. In HS68 cell, NSC 3852 inhibited Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite propagation with EC50 value of 78.6 nM. Also, in human red blood cells, NSC 3852 inhibited Plasmodium falciparum growth with EC50 value of 1.3 μM. NSC 3852 inhibited Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite propagation by involving redox reactions [2].
References:
[1]. Martirosyan A, Leonard S, Shi X, et al. Actions of a histone deacetylase inhibitor NSC3852 (5-nitroso-8-quinolinol) link reactive oxygen species to cell differentiation and apoptosis in MCF-7 human mammary tumor cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2006, 317(2): 546-552.
[2]. Strobl JS, Seibert CW, Li Y, et al. Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium falciparum infections in vitro by NSC3852, a redox active antiproliferative and tumor cell differentiation agent. J Parasitol, 2009, 95(1): 215-223.
- Benzbromarone
Catalog No.:BCC4634
CAS No.:3562-84-3
- Mesuaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN5298
CAS No.:3561-81-7
- CP 20961
Catalog No.:BCC6063
CAS No.:35607-20-6
- N-Desethyl Sunitinib
Catalog No.:BCC1792
CAS No.:356068-97-8
- Toceranib
Catalog No.:BCC2005
CAS No.:356068-94-5
- Darapladib
Catalog No.:BCC1515
CAS No.:356057-34-6
- Fluocinonide
Catalog No.:BCC4953
CAS No.:356-12-7
- Betmidin
Catalog No.:BCN8253
CAS No.:35589-22-1
- tert-Butyl rosuvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC9163
CAS No.:355806-00-7
- N,N-dimethyl-2-Quinoxalinamine
Catalog No.:BCC9066
CAS No.:35552-76-2
- Buflomedil HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4760
CAS No.:35543-24-9
- YM-155 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2066
CAS No.:355406-09-6
- SB-505124 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1930
CAS No.:356559-13-2
- SB525334
Catalog No.:BCC2531
CAS No.:356559-20-1
- Fmoc-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3034
CAS No.:35661-39-3
- Fmoc-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3535
CAS No.:35661-40-6
- Fmoc-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3509
CAS No.:35661-60-0
- Deoxylapachol
Catalog No.:BCN5299
CAS No.:3568-90-9
- Dihydrobaicalein
Catalog No.:BCN3887
CAS No.:35683-17-1
- Questinol
Catalog No.:BCN7443
CAS No.:35688-09-6
- Valerenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7546
CAS No.:3569-10-6
- Naloxone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4612
CAS No.:357-08-4
- Brucine
Catalog No.:BCN2390
CAS No.:357-57-3
- Galantamine
Catalog No.:BCN2868
CAS No.:357-70-0
Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium falciparum infections in vitro by NSC3852, a redox active antiproliferative and tumor cell differentiation agent.[Pubmed:18837587]
J Parasitol. 2009 Feb;95(1):215-23.
We searched the National Cancer Institute (NCI) compound library for structures related to the antitumor quinoline NSC3852 (5-nitroso-8-quinolinol) and used a computer algorithm to predict the antiprotozoan activity for each of 13 structures. Half of these compounds inhibited Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite propagation in human fibroblasts at < or =1 microM. The active compounds comprise a series of low-molecular-weight quinolines bearing nitrogen substituents in the ring-5 position. NSC3852 (EC(50) 80 nM) and NSC74949 (EC(50) 646 nM) were the most potent. NSC3852 also inhibited Plasmodium falciparum growth in human red blood cells (EC(50) 1.3 microM). To investigate the mechanism for NSC3852's anti-T. gondii activity, we used chemiluminescence assays to detect reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation in freshly isolated tachyzoites and in infected host cells; the absence of ROS generation by NSC3852 in these assays indicated NSC3852 does not redox cycle in T. gondii. Inhibitors of enzyme sources of free radicals such as superoxide anion, nitric oxide (NO), and their reaction product peroxynitrite did not interfere with the anti-T. gondii activity of NSC3852. However, inhibition of T. gondii tachyzoite propagation by NSC3852 involved redox reactions because tachyzoites were protected from NSC3852 by inclusion of the cell permeant superoxide dismutase mimetic, MnTMPyP, or N-acetylcysteine in the culture medium. We conclude that the Prediction of Activity Spectra for Substances (PASS) computer program is useful in finding new compounds that inhibit T. gondii tachyzoites in vitro and that NSC3852 is a potent T. gondii inhibitor that acts by indirect generation of oxidative stress in T. gondii.
Actions of a histone deacetylase inhibitor NSC3852 (5-nitroso-8-quinolinol) link reactive oxygen species to cell differentiation and apoptosis in MCF-7 human mammary tumor cells.[Pubmed:16497787]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 May;317(2):546-52.
NSC3852 (5-nitroso-8-quinolinol) has cell differentiation and antiproliferative activity in human breast cancer cells in tissue culture and antitumor activity in mice bearing P388 and L1210 leukemic cells. We investigated the mechanism of NSC3852 action in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells using electron spin resonance (ESR). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) were detected in MCF-7 cell suspensions incubated with NSC3852 using the spin trap 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide (DMPO). Formation of the DMPO-OH adduct was quenched by the addition of superoxide dismutase but not by catalase, and we concluded that superoxide was generated in the NSC3852-treated cells. The flavoprotein inhibitor diphenylene iodonium suppressed ROS production, providing evidence for the involvement of a flavin-dependent enzyme system in the ROS response to NSC3852. A biologically significant oxidative response to NSC3852 occurred in MCF-7 cells. An early marker of oxidative stress was a decrease in the [glutathione]/[glutathione disulfide] ratio 1 h after NSC3852 addition. Oxidative DNA damage, marked by the presence of 8-oxoguanine, and DNA-strand breakage occurred in cells exposed to NSC3852 for 24 h. Apoptosis peaked 48 h after exposure to NSC3852. Pretreatment with the glutathione precursor N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) prevented DNA-strand breakage and apoptosis. Pretreatment with NAC also reversed NSC3852 decreases in E2F1, Myc, and phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein, indicative of redox-sensitive pathway(s) in MCF-7 cells during G(1) phase of the cell cycle. We conclude that ROS formation is involved in the apoptotic and cell differentiation responses to NSC3852 in MCF-7 cells.
Differentiation-inducing quinolines as experimental breast cancer agents in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell model.[Pubmed:15450938]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Nov 1;68(9):1729-38.
The purpose of this work is to develop agents for cancer differentiation therapy. We showed that five antiproliferative quinoline compounds in the National Cancer Institute database stimulated cell differentiation at growth inhibitory concentrations (3-14 microM) in MCF-7 human breast tumor cells in vitro. The differentiation-inducing quinolines caused lipid droplet accumulation, a phenotypic marker of differentiation, loss of Ki67 antigen expression, a cell cycle marker indicative of exit into G0, and reduced protein levels of the G1--S transcription factor, E2F1. The antimalarial quinolines, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine and quinidine had similar effects in MCF-7 cells, but were 3-10 times less potent than the NSC compounds. NSC3852 and NSC86371 inhibited histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity in vitro and caused DNA damage and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells, consistent with their differentiation and antiproliferative activities. However, the HDAC assay results showed that for other compounds, direct HDAC enzyme inhibition was not required for differentiation activity. E2F1 protein was suppressed by all differentiation quinolines, but not by non-differentiating analogs, quinoline and primaquine. At equivalent antiproliferative concentrations, NSC69603 caused the greatest decrease in E2F1 protein (90%) followed by antimalarials quinidine and hydroxychloroquine. NSC69603 did not cause DNA damage. The other NSC compounds caused DNA damage and apoptosis and reduced E2F1 levels. The physicochemical properties of NSC3852, NSC69603, NSC86371, and NSC305819 predicted they are drug candidates suitable for development as experimental breast tumor cell differentiation agents. We conclude DNA damage and reductions in E2F1 protein are mechanistically important to the differentiation and antiproliferative activities of these quinoline drug candidates.


