PRIMA-1METRestore mutant p53 activity, induce BAX and PUMA CAS# 5291-32-7 |
- CP 31398 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2406
CAS No.:1217195-61-3
- Tenovin-1
Catalog No.:BCC2239
CAS No.:380315-80-0
- PRIMA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2413
CAS No.:5608-24-2
- Pifithrin-α (PFTα)
Catalog No.:BCC2241
CAS No.:63208-82-2
- NSC 319726
Catalog No.:BCC2242
CAS No.:71555-25-4
- PhiKan 083
Catalog No.:BCC2411
CAS No.:880813-36-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 5291-32-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 52918385 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H17NO3 | M.Wt | 199.25 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | APR-246 | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 50 mg/mL (250.94 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
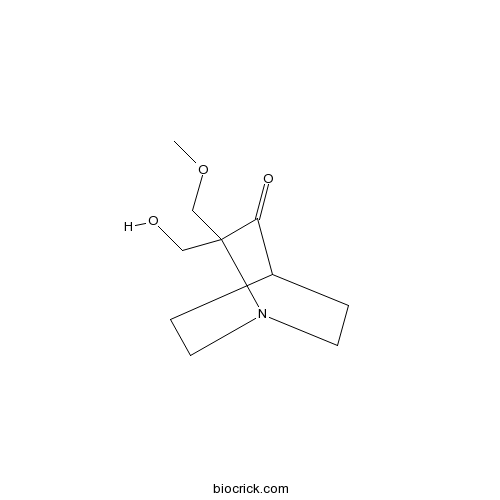
| Chemical Name | 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(methoxymethyl)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-one | ||
| SMILES | COCC1(C(=O)C2CCN1CC2)CO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BGBNULCRKBVAKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H17NO3/c1-14-7-10(6-12)9(13)8-2-4-11(10)5-3-8/h8,12H,2-7H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Methylated derivative of PRIMA-1. Restores mutant activity p53 activity. Acts synergistically with chemotherapeutic agents to inhibit tumor cell proliferation. |

PRIMA-1MET Dilution Calculator

PRIMA-1MET Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0188 mL | 25.0941 mL | 50.1882 mL | 100.3764 mL | 125.4705 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0038 mL | 5.0188 mL | 10.0376 mL | 20.0753 mL | 25.0941 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5019 mL | 2.5094 mL | 5.0188 mL | 10.0376 mL | 12.5471 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1004 mL | 0.5019 mL | 1.0038 mL | 2.0075 mL | 2.5094 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0502 mL | 0.2509 mL | 0.5019 mL | 1.0038 mL | 1.2547 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PRIMA-1MET selectively restores the activity of mutant p53 in tumor cells.[1]
The p53 is encoded in humans by the TP53 gene. The molecular mass of p53 is 53 KD. The p53 has the function of regulating the cell cycle, thus, it functions as preventing cancer, a tumor suppressor. The p53 plays an important role in apoptosis, inhibition of angiogenesis and genomic stability by activating DNA repair proteins, arresting cell growth though holding the cell cycle and initiating apoptosis. p53 becomes activated in response to DNA damage, osmotic shock, oxidative stress or other myriad stressors. Activated p53 activates the expression of several genes by binding DNA including p21. p21 binds to the G1-S/CDK complexes which is an important molecules for the G1/S transition, then causes cell cycle arrest. The increasing amount of p53 may be a solution for prevention of tumors spreading or treatment of them. About half of human tumours have mutant p53 then lose the control for cell apotosis.[2]
PRIMA-1MET is a methylated derivative of PRIMA-1. PRIMA-1 suppressed the growth of Saos-2-His-273 osteosarcoma cell but did not affect the cell lines which express wild type P53. PRIMA-1 directly binds to mutant p53 according to gel shift assay.[2] PRIMA-1MET induced nucleolar translocation of Hsp70, PML, CBP and p53 in MCF 7 cells.[3] PRIMA -1MET reactivate the mutant p53, then results in enhanced expression of genes which are involved in apoptosis and cell-cycle regulation[4]. In the H1299-His175 cells, treatment with 50μM PRIMA-1MET leaded to significant caspase-2 activation , then induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.[1]
PRIMA-1 MET at 25μM reduced the IC50 of cisplatin in H1299 cells by inducing mutant P53-dependent apotosis.[5]
In SCID mice with H1299-His175 tumor xenografts, the combination of PRIMA-1MET at 100mg/Kg and cisplatin significantly inhibited tumor grown compared to cisplatin only. [5]
References:
[1]. Shen J, Vakifahmetoglu H, Stridh H, Zhivotovsky B, Wiman KG: PRIMA-1MET induces mitochondrial apoptosis through activation of caspase-2. Oncogene 2008, 27(51):6571-6580.
[2]. Bykov VJ, Selivanova G, Wiman KG: Small molecules that reactivate mutant p53. Eur J Cancer 2003, 39(13):1828-1834.
[3]. Stuber G, Flaberg E, Petranyi G, Otvos R, Rokaeus N, Kashuba E, Wiman KG, Klein G, Szekely L: PRIMA-1MET induces nucleolar translocation of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA-5 protein. Mol Cancer 2009, 8:23.
[4]. Lambert JM, Moshfegh A, Hainaut P, Wiman KG, Bykov VJ: Mutant p53 reactivation by PRIMA-1MET induces multiple signaling pathways converging on apoptosis. Oncogene 2010, 29(9):1329-1338.
[5]. Bykov VJ, Zache N, Stridh H, Westman J, Bergman J, Selivanova G, Wiman KG: PRIMA-1(MET) synergizes with cisplatin to induce tumor cell apoptosis. Oncogene 2005, 24(21):3484-3491.
- Motilin (human, porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5894
CAS No.:52906-92-0
- 6,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8287
CAS No.:529-84-0
- Euxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN5694
CAS No.:529-61-3
- Genistin
Catalog No.:BCN2396
CAS No.:529-59-9
- Prunin
Catalog No.:BCN5693
CAS No.:529-55-5
- Scutellarein
Catalog No.:BCN5380
CAS No.:529-53-3
- Azaleatin
Catalog No.:BCN8207
CAS No.:529-51-1
- Gentisein
Catalog No.:BCN3356
CAS No.:529-49-7
- Myricetin
Catalog No.:BCN5692
CAS No.:529-44-2
- Ombuin
Catalog No.:BCN5691
CAS No.:529-40-8
- Chamazulene
Catalog No.:BCC8145
CAS No.:529-05-5
- 20-Hydroxyecdysone
Catalog No.:BCN5688
CAS No.:5289-74-7
- Dammaradienyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5689
CAS No.:52914-31-5
- Neosophoramine
Catalog No.:BCN5690
CAS No.:52932-74-8
- Nanaomycin A
Catalog No.:BCC3611
CAS No.:52934-83-5
- N-(2,6-Diphenylmethyl)-1-piperazine acetylamine
Catalog No.:BCC9052
CAS No.:5294-61-1
- Genz-644282
Catalog No.:BCC1592
CAS No.:529488-28-6
- Ajugol
Catalog No.:BCN2883
CAS No.:52949-83-4
- Acetylisocupressic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5695
CAS No.:52992-82-2
- Prednisone
Catalog No.:BCC4957
CAS No.:53-03-2
- Estrone
Catalog No.:BCN2201
CAS No.:53-16-7
- Mitotane (Lsodren)
Catalog No.:BCC3815
CAS No.:53-19-0
- Cocaine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5943
CAS No.:53-21-4
- Methylprednisolone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9043
CAS No.:53-36-1
PRIMA-1Met suppresses colorectal cancer independent of p53 by targeting MEK.[Pubmed:27806324]
Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):83017-83030.
PRIMA-1MET is the methylated PRIMA-1 (p53 reactivation and induction of massive apoptosis) and could restore tumor suppressor function of mutant p53 and induce p53 dependent apoptosis in cancer cells harboring mutant p53. However, p53 independent activity of PRIMA-1MET remains elusive. Here we reported that PRIMA-1MET attenuated colorectal cancer cell growth irrespective of p53 status. Kinase profiling revealed that mitogen-activated or extracellular signal-related protein kinase (MEK) might be a potential target of PRIMA-1MET. Pull-down binding and ATP competitive assay showed that PRIMA-1MET directly bound MEK in vitro and in cells. Furthermore, the direct binding sites of PRIMA-1MET were explored by using a computational docking model. Treatment of colorectal cancer cells with PRIMA-1MET inhibited p53-independent phosphorylation of MEK, which in turn impaired anchorage-independent cell growth in vitro. Moreover, PRIMA-1MET suppressed colorectal cancer growth in xenograft mouse model by inhibiting MEK1 activity.Taken together, our findings demonstrate a novel p53-independent activity of PRIMA-1MET to inhibit MEK and suppress colorectal cancer growth.
Sensitivity to PRIMA-1MET is associated with decreased MGMT in human glioblastoma cells and glioblastoma stem cells irrespective of p53 status.[Pubmed:27533246]
Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):60245-60269.
Alterations of the TP53 tumor suppressor gene occur in ~30% of primary glioblastoma (GBM) with a high frequency of missense mutations associated with the acquisition of oncogenic "gain-of-function" (GOF) mutant (mut)p53 activities. PRIMA-1MET/APR-246, emerged as a promising compound to rescue wild-type (wt)p53 function in different cancer types. Previous studies suggested the role of wtp53 in the negative regulation of the DNA repair protein O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), a major determinant in resistance to therapy in GBM treatment. The potential role of MGMT in expression of p53 and the efficacy of PRIMA-1MET with respect to TP53 status and expression of MGMT in GBM remain unknown. We investigated response to PRIMA-1MET of wtp53/MGMT-negative (U87MG, A172), mutp53/MGMT-positive U138, LN-18, T98/Empty vector (T98/EV) and its isogenic MGMT/shRNA gene knockdown counterpart (T98/shRNA). We show that MGMT silencing decreased expression of mutp53/GOF in T98/shRNA. PRIMA-1MET further cleared T98/shRNA cells of mutp53, decreased proliferation and clonogenic potential, abrogated the G2 checkpoint control, increased susceptibility to apoptotic cell death, expression of GADD45A and sustained expression of phosphorylated Erk1/2. PRIMA-1MET increased expression of p21 protein in U87MG and A172 and promoted senescence in U87MG cell line. Importantly, PRIMA-1MET decreased relative cell numbers, disrupted the structure of neurospheres of patient-derived GBM stem cells (GSCs) and enabled activation of wtp53 with decreased expression of MGMT in MGMT-positive GSCs or decreased expression of mutp53. Our findings highlight the cell-context dependent effects of PRIMA-1MET irrespective of p53 status and suggest the role of MGMT as a potential molecular target of PRIMA-1MET in MGMT-positive GSCs.
PRIMA-1(MET) induces mitochondrial apoptosis through activation of caspase-2.[Pubmed:28192401]
Oncogene. 2017 Jun 22;36(25):3650.
This corrects the article DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.210.
PRIMA-1MET induces nucleolar translocation of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA-5 protein.[Pubmed:19323829]
Mol Cancer. 2009 Mar 26;8:23.
The low molecular weight compound, PRIMA-1MET restores the transcriptional transactivation function of certain p53 mutants in tumor cells. We have previously shown that PRIMA-1MET induces nucleolar translocation of p53, PML, CBP and Hsp70. The Epstein-Barr virus encoded, latency associated antigen EBNA-5 (also known as EBNA-LP) is required for the efficient transformation of human B lymphocytes by EBV. EBNA-5 associates with p53-hMDM2-p14ARF complexes. EBNA-5 is a nuclear protein that translocates to the nucleolus upon heat shock or inhibition of proteasomes along with p53, hMDM2, Hsp70, PML and proteasome subunits. Here we show that PRIMA-1MET induces the nucleolar translocation of EBNA-5 in EBV transformed B lymphoblasts and in transfected tumor cells. The PRIMA-1MET induced translocation of EBNA-5 is not dependent on the presence of mutant p53. It also occurs in p53 null cells or in cells that express wild type p53. Both the native and the EGFP or DSRed conjugated EBNA-5 respond to PRIMA-1MET treatment in the same way. Image analysis of DSRed-EBNA-5 expressing cells, using confocal fluorescence time-lapse microscopy showed that the nucleolar translocation requires several hours to complete. FRAP (fluorescence recovery after photobleaching) and FLIP (fluorescence loss in photobleaching) measurements on live cells showed that the nucleolar translocation was accompanied by the formation of EBNA-5 aggregates. The process is reversible since the aggregates are dissolved upon removal of PRIMA-1MET. Our results suggest that mutant p53 is not the sole target of PRIMA-1MET. We propose that PRIMA-1MET may reversibly inhibit cellular chaperons that prevent the aggregation of misfolded proteins, and that EBNA-5 may serve as a surrogate drug target for elucidating the precise molecular action of PRIMA-1MET.
PRIMA-1MET induces mitochondrial apoptosis through activation of caspase-2.[Pubmed:18663359]
Oncogene. 2008 Nov 20;27(51):6571-80.
p53 mutations occur frequently in human tumors. The low-molecular-weight compound PRIMA-1(MET) reactivates mutant p53, induces apoptosis in human tumor cells and inhibits tumor xenograft growth in vivo. Here, we show that PRIMA-1(MET) induces mutant p53-dependent mitochondria-mediated apoptosis through activation of caspase-2 with subsequent cytochrome c release and further activation of downstream caspase-9 and caspase-3. Inhibition of caspase-2 by a selective inhibitor and/or siRNA prevents cytochrome c release on PRIMA-1(MET) treatment and causes a significant reduction in PRIMA-1(MET)-induced cell death. Our findings highlight a chain of cellular events triggered by PRIMA-1(MET) that lead to apoptotic cell death. This should facilitate further development and optimization of efficient PRIMA-1(MET)-based anticancer drugs.
PRIMA-1(MET) synergizes with cisplatin to induce tumor cell apoptosis.[Pubmed:15735745]
Oncogene. 2005 May 12;24(21):3484-91.
Mutant p53-carrying tumors are often more resistant to chemotherapeutical drugs. We demonstrate here that the mutant p53-reactivating compound PRIMA-1(MET) acts synergistically with several chemotherapeutic drugs to inhibit tumor cell growth. Combined treatment with cisplatin and PRIMA-1(MET) resulted in a synergistic induction of tumor cell apoptosis and inhibition of human tumor xenograft growth in vivo in SCID mice. The induction of mutant p53 levels by chemotherapeutic drugs is likely to increase the sensitivity of tumor cells to PRIMA-1(MET). Thus, the combination of PRIMA-1(MET) with currently used chemotherapeutic drugs may represent a novel and more efficient therapeutic strategy for treatment of mutant p53-carrying tumors.


