Nanaomycin ADNMT3B inhibitor CAS# 52934-83-5 |
- SGI-1027
Catalog No.:BCC4588
CAS No.:1020149-73-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 52934-83-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442757 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H14O6 | M.Wt | 302.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >15.1mg/mL in DMSO | ||
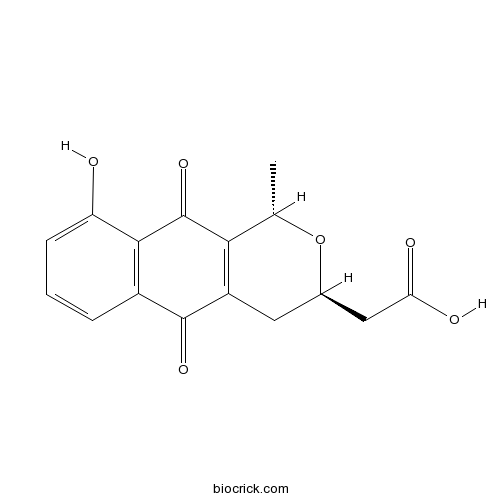
| Chemical Name | 2-[(1S,3R)-9-hydroxy-1-methyl-5,10-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[g]isochromen-3-yl]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1C2=C(CC(O1)CC(=O)O)C(=O)C3=C(C2=O)C(=CC=C3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZCJHPTKRISJQTN-JGVFFNPUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14O6/c1-7-13-10(5-8(22-7)6-12(18)19)15(20)9-3-2-4-11(17)14(9)16(13)21/h2-4,7-8,17H,5-6H2,1H3,(H,18,19)/t7-,8+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nanaomycin A is a selective inhibitor of DNMT3B. | |||||
| Targets | DNMT3B | |||||
| IC50 | 500 nM | |||||
| Cell experiment[1]: | |
| Cell lines | A549, HL60, HeLa and HCT116 cells |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | Ranging from 10 nM to 10 μM for 72 h |
| Applications | Nanaomycin A, initially identified by a virtual screening for inhibitors against DNMT1, as a compound inducing antiproliferative effects in three different tumor cell lines originating from different tissues. Nanaomycin A treatment reduced the global methylation levels in all three cell lines and reactivated transcription of the RASSF1A tumor suppressor gene. In biochemical assays, nanaomycin A revealed selectivity toward DNMT3B. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | Guinea pigs |
| Application | The therapeutic effect of nanaomycin A and siccanin against experimental cutaneous Trichophyton mentagrophytes infection in guinea pigs was investigated. Topically applied formulation of nanaomycin A was very effective in improving the condition of lesions and in preventing fungal growth in the infected tissues. Nanaomycin A and siccanin were comparable in activity in experiments. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Kuck D1, Caulfield T, Lyko F et al. Nanaomycin A selectively inhibits DNMT3B and reactivates silenced tumor suppressor genes in human cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Nov;9(11):3015-23. 2. Kitaura K, Araki Y, Marumo H. The therapeutic effect of nanaomycin A against experimental Trichophyton mentagrophytes infection in guinea pigs. Kitaura K, Araki Y, Marumo H. | |

Nanaomycin A Dilution Calculator

Nanaomycin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3082 mL | 16.541 mL | 33.0819 mL | 66.1638 mL | 82.7048 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6616 mL | 3.3082 mL | 6.6164 mL | 13.2328 mL | 16.541 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3308 mL | 1.6541 mL | 3.3082 mL | 6.6164 mL | 8.2705 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3308 mL | 0.6616 mL | 1.3233 mL | 1.6541 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1654 mL | 0.3308 mL | 0.6616 mL | 0.827 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Nanaomycin A is a selective inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) with IC50 value of 500 nM [1].
In the biochemical in vitro methylation assay, Nanaomycin A showed selective inhibition of DNMT3B but not DNMT1 although it was docked to the catalytic domain of human DNMT1 in a multi-step docking approach. Nanaomycin A showed cell viability inhibition in HCT116, A549 and HL60 cells with IC50 values of 400 nM, 4100 nM and 800 nM, respectively. It decreased the genomic methylation level of these cells significantly. Besides that, Nanaomycin A treatment resulted in demethylation of the RASSF1A promoter in A549 cells. The demethylation caused by Nanaomycin A reactivated the transcription and expression of a silenced tumor suppressor gene [1].
References:
[1] Kuck D, Caulfield T, Lyko F, et al. Nanaomycin A selectively inhibits DNMT3B and reactivates silenced tumor suppressor genes in human cancer cells. Molecular cancer therapeutics, 2010, 9(11): 3015-3023.
- Neosophoramine
Catalog No.:BCN5690
CAS No.:52932-74-8
- Dammaradienyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5689
CAS No.:52914-31-5
- PRIMA-1MET
Catalog No.:BCC2414
CAS No.:5291-32-7
- Motilin (human, porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5894
CAS No.:52906-92-0
- 6,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8287
CAS No.:529-84-0
- Euxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN5694
CAS No.:529-61-3
- Genistin
Catalog No.:BCN2396
CAS No.:529-59-9
- Prunin
Catalog No.:BCN5693
CAS No.:529-55-5
- Scutellarein
Catalog No.:BCN5380
CAS No.:529-53-3
- Azaleatin
Catalog No.:BCN8207
CAS No.:529-51-1
- Gentisein
Catalog No.:BCN3356
CAS No.:529-49-7
- Myricetin
Catalog No.:BCN5692
CAS No.:529-44-2
- N-(2,6-Diphenylmethyl)-1-piperazine acetylamine
Catalog No.:BCC9052
CAS No.:5294-61-1
- Genz-644282
Catalog No.:BCC1592
CAS No.:529488-28-6
- Ajugol
Catalog No.:BCN2883
CAS No.:52949-83-4
- Acetylisocupressic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5695
CAS No.:52992-82-2
- Prednisone
Catalog No.:BCC4957
CAS No.:53-03-2
- Estrone
Catalog No.:BCN2201
CAS No.:53-16-7
- Mitotane (Lsodren)
Catalog No.:BCC3815
CAS No.:53-19-0
- Cocaine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5943
CAS No.:53-21-4
- Methylprednisolone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9043
CAS No.:53-36-1
- Oxandrolone
Catalog No.:BCC5242
CAS No.:53-39-4
- Dehydroepiandrosterone
Catalog No.:BCN2202
CAS No.:53-43-0
- Indomethacin
Catalog No.:BCC3794
CAS No.:53-86-1
Molecular dynamics simulations of human DNA methyltransferase 3B with selective inhibitor nanaomycin A.[Pubmed:21839172]
J Struct Biol. 2011 Nov;176(2):185-91.
DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) are involved in epigenetic regulation of the genome and are promising targets for therapeutic intervention in cancer and other diseases. Until now, very limited information is available concerning the molecular dynamics of DNMTs. The natural product Nanaomycin A is the first selective inhibitor of DNMT3B that induce genomic demethylation. Herein we report long (>100ns) molecular dynamics simulations for human DNMT3B bound to Nanaomycin A with and without the presence of the cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM). We concluded that SAM favors the binding of Nanaomycin A to DNMT3B. Key interactions of Nanaomycin A with DNMT3B involve long lasting interactions with Arg731, Arg733, Arg832, and the catalytic Cys651. Results further support the previous hypothesis that Nanaomycin A has key interactions with amino acid residues involved in the mechanism of methylation. This work represents one of the first molecular dynamics studies of DNMT3B. Results of this work shed light on the structure and binding recognition process of a key epigenetic enzyme with a small molecule inhibitor.
Nanaomycin A selectively inhibits DNMT3B and reactivates silenced tumor suppressor genes in human cancer cells.[Pubmed:20833755]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Nov;9(11):3015-23.
Enzymes involved in the epigenetic regulation of the genome represent promising starting points for therapeutic intervention by small molecules, and DNA methyltransferases (DNMT) are emerging targets for the development of a new class of cancer therapeutics. In this work, we present Nanaomycin A, initially identified by a virtual screening for inhibitors against DNMT1, as a compound inducing antiproliferative effects in three different tumor cell lines originating from different tissues. Nanaomycin A treatment reduced the global methylation levels in all three cell lines and reactivated transcription of the RASSF1A tumor suppressor gene. In biochemical assays, Nanaomycin A revealed selectivity toward DNMT3B. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first DNMT3B-selective inhibitor identified to induce genomic demethylation. Our study thus establishes the possibility of selectively inhibiting individual DNMT enzymes.
New compounds, nanaomycin F and G, discovered by physicochemical screening from a culture broth of Streptomyces rosa subsp. notoensis OS-3966.[Pubmed:26100318]
J Biosci Bioeng. 2015 Nov;120(5):596-600.
Two new compounds, nanaomycin F and G, were isolated by physicochemical screening method from cultured broth of Streptomyces rosa subsp. notoensis OS-3966, which is known to produce Nanaomycin A, B, C, D, and E. Nanaomycin F is a new Nanaomycin Analog, a 4a-hydroxyl analog of nanaomycin B. Nanaomycin G has a unique skeleton with 1-indanone infused with a tetrahydropyran ring. Nanaomycin A possesses broad antimicrobial activity but nanaomycin F and G demonstrated no bioactivity against all bacteria and fungi tested in this study. In addition, in both nanaomycin F and G, the production of superoxide radicals was majorly decreased in comparison to Nanaomycin A. It was considered that the antimicrobial properties were lost as a result of the decrease in production of the superoxide radicals.
Nanaomycin H: A new nanaomycin analog.[Pubmed:28202308]
J Biosci Bioeng. 2017 Jun;123(6):765-770.
Physicochemical screening identified a new Nanaomycin Analog, nanaomycin H, which was isolated from a culture broth of Streptomyces rosa subsp. notoensis OS-3966. This microorganism is already known to produce seven nanaomycin compounds, (Nanaomycin A to G). Structural elucidation of nanaomycin H showed it to be a pyranonaphthoquinone with a mycothiol moiety. A N-acetylcysteine S-conjugate of nanaomycin H, without alpha-glucosamine linked to myo-inositol moiety, mercapturic acid derivative, was also detected in the same culture broth. Mercapturic acid derivatives of secondary metabolites are known to be produced for xenobiotic metabolism outside microbial cells. Mycothiol acts as a detoxifier to help prevent cell damage from factors such as oxidative stress. The production of O2(-) generated by reduction of Nanaomycin A is correlated with antibacterial activity. Mycothiol-containing nanaomycin H proved to be markedly decreased in O2(-) and did not express any notable antimicrobial activity. It is suggested that nanaomycin H is produced in the detoxification process.


