CP 31398 dihydrochloridep53 stabilizer CAS# 1217195-61-3 |
- WR 1065
Catalog No.:BCC2417
CAS No.:14653-77-1
- PRIMA-1MET
Catalog No.:BCC2414
CAS No.:5291-32-7
- PRIMA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2413
CAS No.:5608-24-2
- Pifithrin-μ
Catalog No.:BCC2412
CAS No.:64984-31-2
- NSC 319726
Catalog No.:BCC2242
CAS No.:71555-25-4
- JNJ-26854165 (Serdemetan)
Catalog No.:BCC2240
CAS No.:881202-45-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1217195-61-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9826309 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H22F3N5O | M.Wt | 477.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
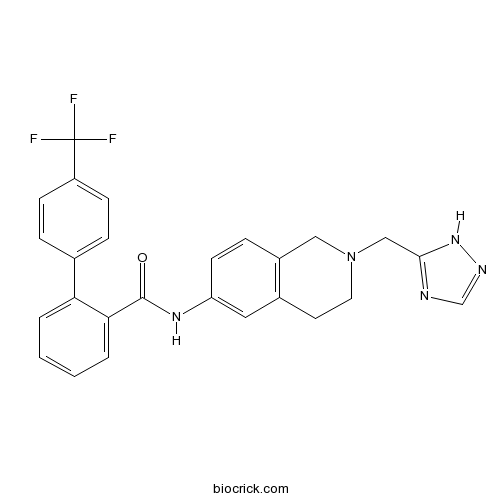
| Chemical Name | N-[2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-ylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-6-yl]-2-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CC2=C1C=C(C=C2)NC(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(F)(F)F)CC5=NC=NN5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WNDIAFXQKOHFLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H22F3N5O/c27-26(28,29)20-8-5-17(6-9-20)22-3-1-2-4-23(22)25(35)32-21-10-7-19-14-34(12-11-18(19)13-21)15-24-30-16-31-33-24/h1-10,13,16H,11-12,14-15H2,(H,32,35)(H,30,31,33) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | p53 stabilizing agent. Stabilizes the active conformation of p53 and promotes p53 activity in cancer cell lines with mutant or wild-type p53. Inhibits growth of small human tumor xenografts in vivo. |

CP 31398 dihydrochloride Dilution Calculator

CP 31398 dihydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0942 mL | 10.4712 mL | 20.9424 mL | 41.8848 mL | 52.356 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4188 mL | 2.0942 mL | 4.1885 mL | 8.377 mL | 10.4712 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2094 mL | 1.0471 mL | 2.0942 mL | 4.1885 mL | 5.2356 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0419 mL | 0.2094 mL | 0.4188 mL | 0.8377 mL | 1.0471 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0209 mL | 0.1047 mL | 0.2094 mL | 0.4188 mL | 0.5236 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CP 31398 dihydrochloride is a potent activator of p53 with maximum tolerated dose of 400 ppm [2].
Tumor protein p53 (p53) is a crucial protein in multicellular organisms and plays an important role in preventing cancer formation. Many studies have shown that activated p53 regulates the expression of p21 which binds to the G1-S/CDK complexes (molecules important for the G1/S transition in the cell cycle) and inhibits their activity [1].
CP 31398 dihydrochloride is a potent p53 stabilization and is regarded as a promising agent which combines with chemotherapy drugs for cancer treatment. When tested with a panel of 9 human cancer cell lines, CP 31398 dihydrochloride treatment resulted in cell apoptosis in mutant or wild-type p53 expressed cell lines (SW480, SKBr3, PA1, U20S, HCT116, and Saos-2) and enhanced chemotherapeutic drugs effect on cell killing while had no effect on cell lines not expressed p53 [1]. In four human HNSCC cell lines (JHU-O29, UMSCC-22A and Fadu), administration of CP 31398 dihydrochloride for 96 h inhibited the cell growth by accumulating p53 expression [2].
In colon adenocarcinomas F344 rast model, combination low dose of CP 31398 dihydrochloride with celecoxib markedly suppressed colon adenocarcinoma incidence (78%) and multiplicity (90%) by enhancing the expression of p53 which indicated that a combination of low dose CP-31398 dihydrochloride and celecoxib could be a promising therapy for colon cancer in clinic [3].
References:
[1]. Takimoto, R., et al., The mutant p53-conformation modifying drug, CP-31398, can induce apoptosis of human cancer cells and can stabilize wild-type p53 protein. Cancer Biol Ther, 2002. 1(1): p. 47-55.
[2]. Roh, J.L., et al., p53-Reactivating small molecules induce apoptosis and enhance chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol, 2011. 47(1): p. 8-15.
[3]. Rao, C.V., et al., Inhibition of azoxymethane-induced colorectal cancer by CP-31398, a TP53 modulator, alone or in combination with low doses of celecoxib in male F344 rats. Cancer Res, 2009. 69(20): p. 8175-82.
- 6-O-p-Methoxycinnamoylcatalpol
Catalog No.:BCN6109
CAS No.:121710-02-9
- GYKI 47261 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7566
CAS No.:1217049-32-5
- BU 239 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5668
CAS No.:1217041-98-9
- PTC209 HBr
Catalog No.:BCC5640
CAS No.:1217022-63-3
- Moluccanin diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6108
CAS No.:121700-27-4
- Moluccanin
Catalog No.:BCN6107
CAS No.:121700-26-3
- Sarafotoxin S6c
Catalog No.:BCC5721
CAS No.:121695-87-2
- CGP 20712 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6893
CAS No.:1216905-73-5
- ZK 93426 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7229
CAS No.:1216792-30-1
- GSK 4112
Catalog No.:BCC7741
CAS No.:1216744-19-2
- BYK 191023 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7506
CAS No.:1216722-25-6
- SCH 79797 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7125
CAS No.:1216720-69-2
- A 350619 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5939
CAS No.:1217201-17-6
- VD2-D3
Catalog No.:BCC2034
CAS No.:1217448-46-8
- Ro 26-4550 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC5813
CAS No.:1217448-66-2
- Isoderrone
Catalog No.:BCN3698
CAS No.:121747-89-5
- Isochandalone
Catalog No.:BCN4767
CAS No.:121747-90-8
- (+)-UH 232 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6790
CAS No.:1217473-50-1
- NAS-181
Catalog No.:BCC7056
CAS No.:1217474-40-2
- threo-1-C-Syringylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN6110
CAS No.:121748-11-6
- BYL-719
Catalog No.:BCC3707
CAS No.:1217486-61-7
- SB 205607 dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC5687
CAS No.:1217628-73-3
- SB 258719 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5937
CAS No.:1217674-10-6
- RS 16566 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6890
CAS No.:1217788-97-0
A compound CP-31398 suppresses excitotoxicity-induced neurodegeneration.[Pubmed:23988450]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Oct 25;440(3):359-63.
Neurodegeneration causes dysfunction and degeneration of neurons and is triggered by various factors including genetic defects, free radicals, injury, and glutamate excitotoxicity. Among those, glutamate excitotoxicity is implicated in chronic disorders including AD and ALS, and in acute insults in the CNS including traumatic brain injury. Neurological disorders show hallmark morphological abnormalities such as axon degeneration and cell body death. The molecular mechanisms underlying excitotoxicity-induced neurodegeneration are complex and deciphering a molecular mechanism from one angle is beneficial to understand the process, however, still difficult to develop strategies to suppress excitotoxicity-induced degeneration due to existence of other mechanisms. Thus, directly identifying compounds that can modulate excitotoxicity-induced neurodegeneration and subsequently clarifiying the molecular mechanism is a valid approach to develop effective strategies to suppress neurodegeneration. We searched for compounds that can suppress excitotoxicity-induced neurodegeneration and found that CP-31398, a known compound that can rescue the structure and function of the tumor suppressor protein p53 mutant form and stabilize the active conformation of the p53 wild-type form, suppresses excitotoxicity-induced axon degeneration and cell body death. Moreover, CP-31398 suppresses mitochondrial dysfunction which has a strong correlation with excitotoxicity. Thus, our findings identify a compound that can serve as a novel modulator of neurodegeneration induced by glutamate excitotoxicity.
Subchronic oral toxicity and metabolite profiling of the p53 stabilizing agent, CP-31398, in rats and dogs.[Pubmed:21864638]
Toxicology. 2011 Nov 18;289(2-3):141-50.
CP-31398 (N'-[2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethenyl]-4-quinazolinyl]-N,N-dimethyl-1,3-propanediami ne dihydrochloride) is a styrylquinazoline that stabilizes the DNA binding conformation of p53, thereby maintaining the activity of p53 as a transcription factor and tumor suppressor. In consideration of the potential use of p53 stabilizers for cancer prevention and therapy, 28-day studies (with recovery) were performed to characterize the toxicity of CP-31398 in rats and dogs. In the rat study, groups of 15 CD rats/sex received daily gavage exposure to CP-31398 at 0, 40, 80, or 160mg/kg/day (0, 240, 480, or 960mg/m(2)/day). In the dog study, groups of five beagle dogs received daily gavage exposure to CP-31398 at 0, 10, 20, or 40mg/kg/day (0, 200, 400, or 800mg/m(2)/day). The high dose of CP-31398 induced mortality in both species: seven male rats and four female rats died as a result of hepatic infarcts, and two female dogs died as a result of hepatic necrosis without evidence of thrombosis. No deaths were seen in the mid- or low-dose groups in either species. In dogs, sporadic emesis was seen in the high dose and mid dose groups, and reductions in body weight gain were observed in all drug-exposed groups. CP-31398 induced mild anemia in both species; clinical pathology data also demonstrated hepatic toxicity, renal toxicity, inflammatory reactions, and coagulopathies in rats in the high dose and mid dose groups. Treatment-related microscopic changes in high dose and mid dose rats were identified in the liver, kidney, heart, bone marrow, lung, adrenals, spleen, thymus, skeletal muscle, and ovary; microscopic changes in the liver, heart, lung, and adrenals persisted through the recovery period. In dogs, microscopic changes were identified in the central nervous system, lung, and liver; changes in all tissues remained at the end of the recovery period. The liver is the primary site of limiting toxicity for CP-31398 in rats, and is also a key site of toxicity in dogs. The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) for subchronic oral administration of CP-31398 is 80mg/kg/day (480mg/m(2)/day) in rats and 20mg/kg/day (400mg/m(2)/day) in dogs. Although only modest and apparently reversible toxicities (microscopic changes in rats; reductions in body weight gain and alterations in red cell parameters in dogs) were seen in the low dose groups, no observed adverse effect levels (NOAELs) for CP-31398 could not be established for either species. The toxicity of CP-31398 suggests that this agent may not be suitable for use in cancer prevention. However, should in vivo antitumor efficacy be achievable at doses that do not induce limiting toxicity, CP-31398 may have utility as a cancer therapeutic. Modification of the primary sites of CP-31398 metabolism (N-demethylation of the alkyl side chain; hydroxylation and O-demethylation of the styryl benzene group) may result in the development of CP-31398 analogs with comparable pharmacologic activity and reduced toxicity.
CP-31398 restores DNA-binding activity to mutant p53 in vitro but does not affect p53 homologs p63 and p73.[Pubmed:15308639]
J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 29;279(44):45887-96.
The p53 protein plays a major role in the maintenance of genome stability in mammalian cells. Mutations of p53 occur in over 50% of all cancers and are indicative of highly aggressive cancers that are hard to treat. Recently, there has been a high degree of interest in therapeutic approaches to restore growth suppression functions to mutant p53. Several compounds have been reported to restore wild type function to mutant p53. One such compound, CP-31398, has been shown effective in vivo, but questions have arisen to whether it actually affects p53. Here we show that mutant p53, isolated from cells treated with CP-31398, is capable of binding to p53 response elements in vitro. We also show the compound restores DNA-binding activity to mutant p53 in cells as determined by a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. In addition, using purified p53 core domain from two different hotspot mutants (R273H and R249S), we show that CP-31398 can restore DNA-binding activity in a dose-dependent manner. Using a quantitative DNA binding assay, we also show that CP-31398 increases significantly the amount of mutant p53 that binds to cognate DNA (B(max)) and its affinity (K(d)) for DNA. The compound, however, does not affect the affinity (K(d) value) of wild type p53 for DNA and only increases B(max) slightly. In a similar assay PRIMA1 does not have any effect on p53 core DNA-binding activity. We also show that CP-31398 had no effect on the DNA-binding activity of p53 homologs p63 and p73.
CP-31398, a novel p53-stabilizing agent, induces p53-dependent and p53-independent glioma cell death.[Pubmed:14614447]
Oncogene. 2003 Nov 13;22(51):8233-45.
CP-31398 is a prototype small molecule that stabilizes the active conformation of p53 and promotes p53 activity in cancer cell lines with mutant or wild-type p53. Here, we report that CP-31398 induces p53 reporter gene activity and p21 expression in all of 11 glioma cell lines harboring wild-type or mutant p53, but not in p53-null LN-308 cells. Upon prolonged exposure to CP-31398, all glioma cell lines undergo caspase-independent and bcl-x(L)-insensitive cell death with EC(50) concentrations of 10-36 microM. By comparing p53 wild-type U87MG and p53-null LN-308 cells expressing the temperature-sensitive p53(V135A) mutant, we delineate two pathways of CP-31398-induced cell death: an early, p53-dependent pathway that requires (new p53) protein synthesis and a late, p53-independent pathway characterized by aurintricarboxylic acid -sensitive calcium release and epiphenomenal free radical formation. Post-transcriptional repression of p53 synthesis by an intracellularly transcribed short interfering RNA confirmed the presence of these two pathways of cell death. These observations point out some of the liabilities of CP-31398 as a prototype p53-based therapeutic and define a rationale for further refinement of small molecules that specifically target the p53 pathway, but lack the p53-independent effects.
Pharmacological rescue of mutant p53 conformation and function.[Pubmed:10617466]
Science. 1999 Dec 24;286(5449):2507-10.
Compounds that stabilize the DNA binding domain of p53 in the active conformation were identified. These small synthetic molecules not only promoted the stability of wild-type p53 but also allowed mutant p53 to maintain an active conformation. A prototype compound caused the accumulation of conformationally active p53 in cells with mutant p53, enabling it to activate transcription and to slow tumor growth in mice. With further work aimed at improving potency, this class of compounds may be developed into anticancer drugs of broad utility.


