(+)-UH 232 maleateD2 autoreceptor antagonist. Also D3 partial agonist CAS# 1217473-50-1 |
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996)
Catalog No.:BCC1014
CAS No.:96249-43-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1217473-50-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46830250 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H33NO5 | M.Wt | 391.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water | ||
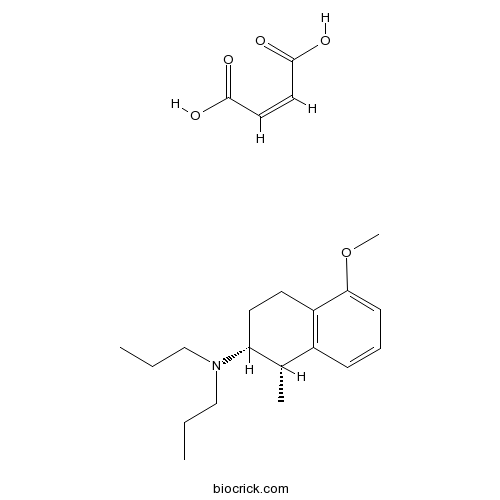
| Chemical Name | (Z)-but-2-enedioic acid;(1S,2R)-5-methoxy-1-methyl-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-amine | ||
| SMILES | CCCN(CCC)C1CCC2=C(C1C)C=CC=C2OC.C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MEQAJDYHKYAPJE-GUUGRXDUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H29NO.C4H4O4/c1-5-12-19(13-6-2)17-11-10-16-15(14(17)3)8-7-9-18(16)20-4;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h7-9,14,17H,5-6,10-13H2,1-4H3;1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b;2-1-/t14-,17+;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | D2 antagonist (Ki = 72.7 nM in a ligand binding assay; apparent KB = 14.5 nM in a cAMP accumulation assay); displays preferential activity at central dopamine autoreceptors. Stimulates a marked acceleration of dopamine synthesis and turnover. Produces locomotor stimulation. Exhibits little or no activity at central noradrenalin and 5-HT receptors. Also D3 partial agonist. |

(+)-UH 232 maleate Dilution Calculator

(+)-UH 232 maleate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5542 mL | 12.7711 mL | 25.5421 mL | 51.0843 mL | 63.8553 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5108 mL | 2.5542 mL | 5.1084 mL | 10.2169 mL | 12.7711 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2554 mL | 1.2771 mL | 2.5542 mL | 5.1084 mL | 6.3855 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0511 mL | 0.2554 mL | 0.5108 mL | 1.0217 mL | 1.2771 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1277 mL | 0.2554 mL | 0.5108 mL | 0.6386 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Isochandalone
Catalog No.:BCN4767
CAS No.:121747-90-8
- Isoderrone
Catalog No.:BCN3698
CAS No.:121747-89-5
- Ro 26-4550 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC5813
CAS No.:1217448-66-2
- VD2-D3
Catalog No.:BCC2034
CAS No.:1217448-46-8
- A 350619 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5939
CAS No.:1217201-17-6
- CP 31398 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2406
CAS No.:1217195-61-3
- 6-O-p-Methoxycinnamoylcatalpol
Catalog No.:BCN6109
CAS No.:121710-02-9
- GYKI 47261 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7566
CAS No.:1217049-32-5
- BU 239 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5668
CAS No.:1217041-98-9
- PTC209 HBr
Catalog No.:BCC5640
CAS No.:1217022-63-3
- Moluccanin diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6108
CAS No.:121700-27-4
- Moluccanin
Catalog No.:BCN6107
CAS No.:121700-26-3
- NAS-181
Catalog No.:BCC7056
CAS No.:1217474-40-2
- threo-1-C-Syringylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN6110
CAS No.:121748-11-6
- BYL-719
Catalog No.:BCC3707
CAS No.:1217486-61-7
- SB 205607 dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC5687
CAS No.:1217628-73-3
- SB 258719 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5937
CAS No.:1217674-10-6
- RS 16566 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6890
CAS No.:1217788-97-0
- 5-Iodo-A-85380 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7099
CAS No.:1217837-17-6
- Ac-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3109
CAS No.:1218-34-4
- Xylometazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4879
CAS No.:1218-35-5
- Pidotimod
Catalog No.:BCC4823
CAS No.:121808-62-6
- CAY10505
Catalog No.:BCC4990
CAS No.:1218777-13-9
- LDE225 Diphosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1693
CAS No.:1218778-77-8
Evidence that antipsychotic drugs are inverse agonists at D2 dopamine receptors.[Pubmed:9208141]
Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;121(4):731-6.
1. The effects of a number of D2-like dopamine receptor antagonists have been determined on forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing the human D2short dopamine receptor (CHO-D2S cells). 2. Dopamine inhibited the effect of forskolin (as expected for a D2 receptor). However, all of the antagonists tested, apart from UH232 and (-)-butaclamol, were able to increase cyclic AMP accumulation above the forskolin control level. (+)-Butaclamol elicited a similar stimulation of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in a CHO cell line expressing human D2long dopamine receptors whereas it exhibited no stimulating effect on forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in untransfected CHO-K1 cells. 3. There was a strong correlation between the EC50 values of these compounds for potentiation of cyclic AMP accumulation and their Ki values from radioligand binding experiments in CHO-D2S cells. 4. The effects of both (+)-butaclamol and dopamine in CHO-D2S cells were inhibited by pre-treatment with pertussis toxin indicating a role for Gi/Go proteins. 5. UH232 did not significantly affect forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation but this substance was able to inhibit the effects of both dopamine and (+)-butaclamol in a concentration-dependent manner. Thus the effects of (+)-butaclamol on forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation are mediated directly via the D2 receptor rather than by reversal of the effects of an endogenous agonist. 6. These data suggest that the D2 dopamine receptor antagonists tested here, many of which are used clinically as antipsychotic drugs, are in fact inverse agonists at human D2 dopamine receptors.
The preferential dopamine D3 receptor ligand, (+)-UH232, is a partial agonist.[Pubmed:7498261]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Aug 25;282(1-3):R3-4.
In a NG 108 15 hybrid cell line stably expressing a recombinant dopamine D3 receptor, (+)-UH 232 (cis-(+)-1S,2R)-5-methoxy-1-methyl-2-(di-n- propylamino)tetralin), a partially selective D3 receptor ligand, stimulates mitogenesis, as measured by incorporation of [3H]thymidine, with an EC50 of 7.6 nM and a maximal increase corresponding to 23% of the response elicited by quinpirole, a full agonist. This effect was antagonised by nafadotride, a D3 receptor-selective antagonist. (+)-UH 232 also antagonised quinpirole-induced mitogenesis with a Ki value of 9.4 nM. (+)-UH 232 (1 microM) inhibited by 22% the forskolin-induced accumulation of cAMP, whilst the inhibition by quinpirole (100 nM) was 53%. These results indicate that (+)-UH 232 is a partial agonist at the D3 receptor with an intrinsic activity of 0.2-0.4.
(+)-AJ 76 and (+)-UH 232: central stimulants acting as preferential dopamine autoreceptor antagonists.[Pubmed:2880302]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;334(3):234-45.
The biochemical and behavioral effects of the putative dopamine autoreceptor antagonists cis-(+)-5-methoxy-1-methyl-2-(n-propylamino)tetralin, (+)-AJ 76 and cis-(+)-5-methoxy-1-methyl-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, (+)-UH 232, were evaluated in various in vivo models in rats. Both compounds produced a marked elevation in brain dopamine synthesis and turnover with only slight effects on the synthesis and turnover of serotonin (5-HT) and noradrenaline being noted. (+)-AJ 76 and (+)-UH 232 also failed to antagonize the decrease in cortical noradrenaline synthesis rate caused by the alpha 2 agonist clonidine. The apomorphine-induced decrease in dopamine synthesis rate in gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) treated animals was completely blocked by (+)-AJ 76 and (+)-UH 232 but not by d-amphetamine or methylphenidate. In activity experiments using habituated animals, (+)-AJ 76 and (+)-UH 232 produced locomotor stimulation and weak stereotypies and antagonized the sedative effects of low doses of apomorphine. Locomotor hyperactivity induced by apomorphine or the dopamine agonist DiPr-5,6-ADTN was antagonized by (+)-UH 232 and to a lesser degree by (+)-AJ 76. The locomotor hyperactivity produced by (+)-AJ 76, (+)-UH 232 and methylphenidate was completely prevented by reserpine pretreatment and partially blocked by the tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine (alpha-MT), whereas d-amphetamine-induced hyperactivity was only antagonized by alpha-MT pretreatment. It is concluded that (+)-AJ 76 and (+)-UH 232 produce behavioral stimulation via a preferential antagonism on central dopamine autoreceptors, an action different from that of all known stimulants including apomorphine, d-amphetamine and methylphenidate. (+)-AJ 76 and (+)-UH 232 possess but weak antagonistic effects on postsynaptic dopamine receptors and only the latter compound is able to induce sedation in rats.
Novel dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists with preferential action on autoreceptors.[Pubmed:3927002]
J Med Chem. 1985 Aug;28(8):1049-53.
The enantiomers of cis-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin and its methyl ether have been synthesized. The compounds were tested for central dopamine (DA) receptor activity, by using biochemical and behavioral tests in rats. The (1R,2S)-(-) enantiomers of 1 and 2 are characterized as centrally acting DA-receptor agonists while the corresponding (1S,2R)-(+) enantiomers are characterized as centrally acting DA-receptor antagonists. Compounds (+)-1 and (+)-2 differ from classical neuroleptics in being able to increase DA synthesis rate in a wide dose range without reducing locomotor activity, suggesting a pronounced selectivity for DA autoreceptors. Also the (-) enantiomers seem to act preferentially on DA autoreceptors.


