Tubastatin AHDAC6 inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 1252003-15-8 |
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)
Catalog No.:BCC2144
CAS No.:1316214-52-4
- Nexturastat A
Catalog No.:BCC5345
CAS No.:1403783-31-2
- Tubacin
Catalog No.:BCC2428
CAS No.:537049-40-4
- MC1568
Catalog No.:BCC2151
CAS No.:852475-26-4
- Resminostat (RAS2410)
Catalog No.:BCC2165
CAS No.:864814-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1252003-15-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 49850262 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H21N3O2 | M.Wt | 335.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 12.5 mg/mL (37.27 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
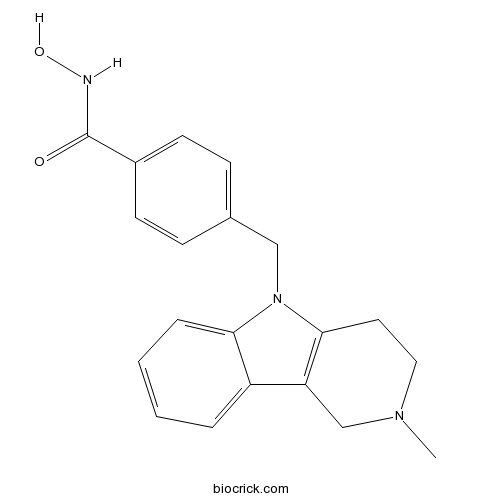
| Chemical Name | N-hydroxy-4-[(2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5-yl)methyl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=C(C1)C3=CC=CC=C3N2CC4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GOVYBPLHWIEHEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H21N3O2/c1-22-11-10-19-17(13-22)16-4-2-3-5-18(16)23(19)12-14-6-8-15(9-7-14)20(24)21-25/h2-9,25H,10-13H2,1H3,(H,21,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tubastatin A is a potent and selective inhibitor of HDAC6 with an IC50 value of 15 nM. | |||||
| Targets | HDAC6 | |||||
| IC50 | 15 nM | |||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). |
| Preparation method | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 15, 30 μM; 48 h. |
| Applications | In MCF-7 cells, tubastatin A inhibits cell proliferation in a dose-dependent way with IC50 value of 15 μM and increases the acetylation of cytoplasmic microtubules. Also, tubastatin A reduces the microtubule depolymerization rate induced by cold and 200 nM nocodazole, which is mediated by the inhibition of HDAC6. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | Wistar rats; DBA1 mice |
| Dosage form | Rats: 30 mg/kg/day i.p. for 5 days; mice: 30 mg/kg, q.d. from day 21 to day 36. |
| Preparation method | Solubilized in 10% Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) 10% Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400 and 80% (40% of hydroxy propyl beta cyclodextrin). |
| Application | In FCA injected rats, tubastatin significantly reduces paw volume by 71.9% at 2 h. In DBA1 arthritis mouse induced by semi-therapeutic collagen, tubastatin (30 mg/kg/day, i.p.) significantly reduces arthritic clinical scores by 73% and inhibits the production of IL-6 in paw tissues by 59%. Tubastatin treated mice shows insignificant changes in body weight. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1]. Asthana J, Kapoor S, Mohan R, et al. Inhibition of HDAC6 deacetylase activity increases its binding with microtubules and suppresses microtubule dynamic instability in MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(31): 22516-22526. [2]. Vishwakarma S, Iyer LR, Muley M, et al. Tubastatin, a selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor shows anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic effects. Int Immunopharmacol, 2013, 16(1): 72-78. | |

Tubastatin A Dilution Calculator

Tubastatin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9815 mL | 14.9076 mL | 29.8151 mL | 59.6303 mL | 74.5379 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5963 mL | 2.9815 mL | 5.963 mL | 11.9261 mL | 14.9076 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2982 mL | 1.4908 mL | 2.9815 mL | 5.963 mL | 7.4538 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0596 mL | 0.2982 mL | 0.5963 mL | 1.1926 mL | 1.4908 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0298 mL | 0.1491 mL | 0.2982 mL | 0.5963 mL | 0.7454 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Tubastatin A is a potent and selective inhibitor of HDAC6 with IC50 value of 15 nM [1].
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) and histone acetyltransferases (HATs) mediates the balance between histone deacetylation and acetylation. HDACs also regulate the acetylation status of signaling molecules, chaperones, and transcription factors that are non-histone proteins [2]. HDAC6 interacts with the HSP90 which is a molecular chaperone. The deacetylation of HSP90 by HDAC6 is important for the stability and of many client proteins including Bcr-Abl, c-Raf, and AKT. So, HDAC inhibitors have anti-cancer function [2].
Tubastatin A is a selective inhibitor of HDAC6 compared with other HDACs. Tubastatin A maintained an average 200-fold selectivity compared with class I HDACs. Tubastatin A displayed selectivity against all isoforms excluding HDAC8
over 1000-fold. Tubastatin A protected against HCA induced neuronal cell death in a dose-dependent manner. Tubastatin A induced the hyperacetylationof -tubulin at 2.5 μM[1]. In LPS stimulated human THP-1 macrophages, Tubastatin A displayed significant inhibition of IL-6and TNF with an IC50 of 712 nM and 212 nM [3]. Tubastatin A showed the inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) secretion with an IC50 of 4.2μM in murine Raw 264.7 macrophages [3]. Tubastatin-A also significantly inhibit cell proliferation at 10μM in KMCH cells [4].
Tubastatin A showed inhibition of paw volume at 30 mg/kg in an animal model of inflammation[3]. Tubastatin-A treatment reduced tumor growth and induces ciliogenesis in rat orthotopic model of cholangiocarcinoma at 10 mg/kg [4].
References:
1.Butler KV, Kalin J, Brochier C, Vistoli G, Langley B, Kozikowski AP: Rational design and simple chemistry yield a superior, neuroprotective HDAC6 inhibitor, tubastatin A. J Am Chem Soc 2010, 132(31):10842-10846.
2.Kim HJ, Bae SC: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action and clinical trials as anti-cancer drugs. Am J Transl Res 2011, 3(2):166-179.
3.Vishwakarma S, Iyer LR, Muley M, Singh PK, Shastry A, Saxena A, Kulathingal J, Vijaykanth G, Raghul J, Rajesh N et al: Tubastatin, a selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor shows anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic effects. Int Immunopharmacol 2013, 16(1):72-78.
4.Gradilone SA, Radtke BN, Bogert PS, Huang BQ, Gajdos GB, LaRusso NF: HDAC6 inhibition restores ciliary expression and decreases tumor growth. Cancer Res 2013, 73(7):2259-2270.
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-6-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN6597
CAS No.:1251830-57-5
- Rosthornin B
Catalog No.:BCN6133
CAS No.:125181-21-7
- N-Methoxyanhydrovobasinediol
Catalog No.:BCN4856
CAS No.:125180-42-9
- Vibralactone D
Catalog No.:BCN6747
CAS No.:1251748-32-9
- Rosthornin A
Catalog No.:BCN6132
CAS No.:125164-55-8
- 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN8163
CAS No.:2040-20-2
- 26-Nor-8-oxo-alpha-onocerin
Catalog No.:BCN6131
CAS No.:125124-68-7
- XL388
Catalog No.:BCC2059
CAS No.:1251156-08-7
- Epinortrachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN3719
CAS No.:125072-69-7
- 8-(3-Ethoxy-2-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-7-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN1594
CAS No.:125072-68-6
- Fmoc-D-Ala-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3037
CAS No.:125043-04-1
- 8-Prenylluteone
Catalog No.:BCN4771
CAS No.:125002-91-7
- (1beta,3beta,25S)-3-Hydroxyspirost-5-en-1-yl 2-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-beta-D-xylopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8164
CAS No.:125225-63-0
- Rubiprasin A
Catalog No.:BCN7138
CAS No.:125263-65-2
- Rubiprasin B
Catalog No.:BCN7137
CAS No.:125263-66-3
- Spiranthesol
Catalog No.:BCN7915
CAS No.:125263-69-6
- Kihadanin A
Catalog No.:BCN3440
CAS No.:125276-62-2
- 2,4,6-Trimethoxyphenol 1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1593
CAS No.:125288-25-7
- Wallichinine
Catalog No.:BCN6602
CAS No.:125292-97-9
- 21,24-Epoxycycloartane-3,25-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4718
CAS No.:125305-73-9
- Chlorantholide D
Catalog No.:BCN4825
CAS No.:1253106-58-9
- Ro 31-8220
Catalog No.:BCC4295
CAS No.:125314-64-9
- CD 437
Catalog No.:BCC7110
CAS No.:125316-60-1
- Vinorelbine Tartrate
Catalog No.:BCN2288
CAS No.:125317-39-7
A novel HDAC6 inhibitor Tubastatin A: Controls HDAC6-p97/VCP-mediated ubiquitination-autophagy turnover and reverses Temozolomide-induced ER stress-tolerance in GBM cells.[Pubmed:28131906]
Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 10;391:89-99.
Temozolomide (TMZ) is the cornerstone of therapy for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). However, its efficacy is limited due to the development of multidrug resistance (MDR). In this study, we first identified the occurrence of ER stress-tolerance (ERST) in glioma cells and confirmed that ERST was positively correlated with TMZ resistance. We further showed that the seesaw-effect of HDAC6-p97/VCP (increased HDAC6 and decreased p97/VCP) in glioma cells was crucial to ERST-associated TMZ resistance. Moreover, the combination treatment of Tubastatin A (TUB, a selective inhibitor of HDAC6) and TMZ synergistically overcame ERST, reduced cell viability and induced apoptosis in TMZ-resistant glioma cells. TUB and TMZ triggered pro-apoptotic signals of the unfolded protein response (UPR) and ER stress and reversed the ratio between HDAC6 and p97/VCP, which potentially attenuated the activation of heat shock proteins and mediated the reversal of ERST. The combination treatment also triggered the dissociation of Dynein-HDAC6 and attenuation of the Dynein-Dynactin motor complex. In addition, this treatment induced HDAC6-p97/VCP-mediated ubiquitination-autophagy turnover, which was involved in the degradation and clearance of ubiquitinated misfolded proteins. This effect could be partially reversed by HDAC6 KO and/or p97/VCP overexpression. Therefore, we proposed that glioma cells optimized the clearance of ubiquitinated misfolded proteins via the reinforcement of HDAC6-facilitated autophagy and attenuation of the p97/VCP-mediated ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). In conclusion, our findings showed that the balance of HDAC6-p97/VCP was crucial to ERST-associated TMZ resistance and that HDAC6 inhibition might be a synergistic target and strategy along with TMZ for the improvement of clinical glioma treatment.
Exploration of the labeling of [11C]tubastatin A at the hydroxamic acid site with [11C]carbon monoxide.[Pubmed:26647018]
J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2016 Jan;59(1):9-13.
We aimed to label Tubastatin A (1) with carbon-11 (t1/2 = 20.4 min) in the hydroxamic acid site to provide a potential radiotracer for imaging histone deacetylase 6 in vivo with positron emission tomography. Initial attempts at a one-pot Pd-mediated insertion of [(11)C]carbon monoxide between the aryl iodide (2) and hydroxylamine gave low radiochemical yields (<5%) of [(11) C]1. Labeling was achieved in useful radiochemical yields (16.1 +/- 5.6%, n = 4) through a two-step process based on Pd-mediated insertion of [(11)C]carbon monoxide between the aryl iodide (2) and p-nitrophenol to give the [(11)C]p-nitrophenyl ester ([(11)C]5), followed by ultrasound-assisted hydroxyaminolysis of the activated ester with excess hydroxylamine in a DMSO/THF mixture in the presence of a strong phosphazene base P1-t-Bu. However, success in labeling the hydroxamic acid group of [(11)C]Tubastatin A was not transferable to the labeling of three other model hydroxamic acids.
Tubastatin A, an HDAC6 inhibitor, alleviates stroke-induced brain infarction and functional deficits: potential roles of alpha-tubulin acetylation and FGF-21 up-regulation.[Pubmed:26790818]
Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 21;6:19626.
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 6 exists exclusively in cytoplasm and deacetylates cytoplasmic proteins such as alpha-tubulin. HDAC6 dysfunction is associated with several pathological conditions in the central nervous system. This study investigated the beneficial effects of Tubastatin A (TubA), a novel specific HDAC6 inhibitor, in a rat model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and an in vitro model of excitotoxicity. Post-ischemic TubA treatment robustly improved functional outcomes, reduced brain infarction, and ameliorated neuronal cell death in MCAO rats. These beneficial effects lasted at least three days after MCAO. Notably, when given at 24 hours after MCAO, TubA still exhibited significant protection. Levels of acetylated alpha-tubulin were decreased in the ischemic hemisphere on Days 1 and 3 after MCAO, and were significantly restored by TubA. MCAO markedly downregulated fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF-21) and TubA significantly reversed this downregulation. TubA also mitigated impaired FGF-21 signaling in the ischemic hemisphere, including up-regulating beta-Klotho, and activating ERK and Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathways. In addition, both TubA and exogenous FGF-21 conferred neuroprotection and restored mitochondrial trafficking in rat cortical neurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Our findings suggest that the neuroprotective effects of TubA likely involve HDAC6 inhibition and the subsequent up-regulation of acetylated alpha-tubulin and FGF-21.
Tubastatin A suppresses renal fibrosis via regulation of epigenetic histone modification and Smad3-dependent fibrotic genes.[Pubmed:25921924]
Vascul Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;72:130-40.
Inflammation and fibrosis are implicated in the pathogenesis of hypertensive kidney damage. We previously demonstrated that a nonspecific histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor attenuates cardiac fibrosis in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats, which induces HDAC6 protein and enzymatic activity. However, the HDAC inhibitor's effect and mechanism have not yet been demonstrated. We sought to determine whether an HDAC6-selective inhibitor could treat hypertension and kidney damage in angiotensin II-infused mice. Hypertension was induced by infusion of ANG in mice. Tubastatin A, an HDAC6 selective inhibitor, did not regulate blood pressure. Hypertensive stimuli enhanced the expression of HDAC6 in vivo and in vitro. We showed that the inhibition of HDAC6 prevents fibrosis and inflammation as determined by quantitative real-time PCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) against HDAC6 or Smad3 attenuated hypertensive stimuli-induced fibrosis and inflammation, whereas Smad2 siRNA failed to inhibit fibrosis. Interestingly, the combination of the HDAC6 inhibitor and Smad3 knockdown synergistically blocked transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) or ANG-induced fibrosis. We also demonstrated for the first time, to our knowledge, that acetylation of collagen type I can be regulated by HDAC6/p300 acetyltransferase. The chromatin immunoprecipitation assay revealed that the HDAC6 inhibitor suppressed TGF-beta-induced acetylated histone H4 or phospho-Smad2/3 to Smad3 binding elements in the fibrosis-associated gene promoters including collagen type I. These results suggest that HDAC6 may be a valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of hypertension-induced kidney fibrosis and inflammation.


