MC1568Class II HDAC inhibitor,potent and CAS# 852475-26-4 |
- Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683)
Catalog No.:BCC2145
CAS No.:149647-78-9
- Mocetinostat (MGCD0103, MG0103)
Catalog No.:BCC2146
CAS No.:726169-73-9
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
- Pracinostat (SB939)
Catalog No.:BCC2152
CAS No.:929016-96-6
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
- Droxinostat
Catalog No.:BCC2157
CAS No.:99873-43-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 852475-26-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11381449 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H15FN2O3 | M.Wt | 314.31 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 18.5 mg/mL (58.86 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
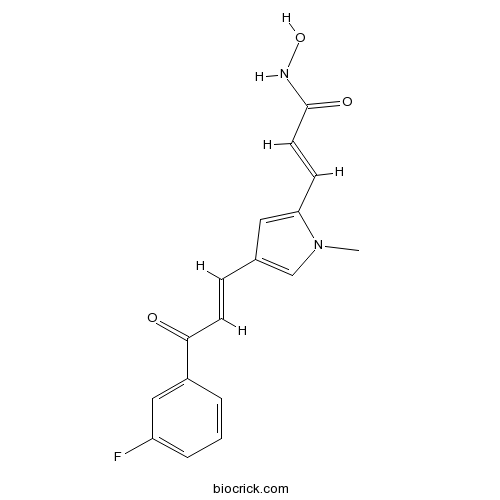
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-[4-[(E)-3-(3-fluorophenyl)-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]-1-methylpyrrol-2-yl]-N-hydroxyprop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | CN1C=C(C=C1C=CC(=O)NO)C=CC(=O)C2=CC(=CC=C2)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QRDAPCMJAOQZSU-KQQUZDAGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H15FN2O3/c1-20-11-12(9-15(20)6-8-17(22)19-23)5-7-16(21)13-3-2-4-14(18)10-13/h2-11,23H,1H3,(H,19,22)/b7-5+,8-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs). Exhibits tissue-selective inhibition between members of class II deacetylases in vivo; inhibits HDAC4 and HDAC5 in skeletal muscle and the heart without affecting HDAC3 activity. Arrests myogenesis through the stabilization of myocyte enhancer factor 2D (MEF2D)-HDAC3/4 complex. Displays no inhibition of class I HDAC activity or expression. |

MC1568 Dilution Calculator

MC1568 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1816 mL | 15.9079 mL | 31.8157 mL | 63.6314 mL | 79.5393 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6363 mL | 3.1816 mL | 6.3631 mL | 12.7263 mL | 15.9079 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3182 mL | 1.5908 mL | 3.1816 mL | 6.3631 mL | 7.9539 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0636 mL | 0.3182 mL | 0.6363 mL | 1.2726 mL | 1.5908 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0318 mL | 0.1591 mL | 0.3182 mL | 0.6363 mL | 0.7954 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
MC1568, an HDACi, inhibited IL-8 levels and cell proliferation in unstimulated or PMA-stimulated GR-M and OCM-3 melanoma cell lines through suppressing c-Jun binding to the IL-8 promoter, recruitment of histones 3&4, Rna polymerase II and TFIIB to the IL-8 promoter and c-Jun expression.
Abstract
MC1568, an inhibitor of class IIa HDAC has been described in terms of synthesis and structural reassignment.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MC1568, a derivative of (Aryloxopropenyl)pyrrolyl hydroxyamide, is a novel, potent and specific inhibitor of class II histone deacetylase (HDAC), including two subclasses IIa (HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC6, HDAC7 and HDAC9) and IIb (HDAC6 and HDAC 10), that exhibits strong inhibition against maize class II HDAC with 50% inhibition concentration IC50 value of 22 μM. MC1568 has been found to tissue-selectively inhibits HDAC and arrest myogenesis in cultured muscle cells through three possible mechanisms, including decreasing the expression of myocyte enhancer factor 2D, stabilizing the HDAC-HDAC3-MEF2D complex and inhibiting the acetylation of differentiation-induced MEF2D. Moreover, MC1568 is able to interfere with RAR- and PPARγ-mediated differentiation-inducing signaling pathways.
Reference
Mai A, Massa S, Pezzi R, Simeoni S, Rotili D, Nebbioso A, Scognamiglio A, Altucci L, Loidl P, Brosch G. Class II (IIa)-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors. 1. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel (aryloxopropenyl)pyrrolyl hydroxyamides. J Med Chem. 2005 May 5;48(9):3344-53.
Nebbioso A, Dell'Aversana C, Bugge A, Sarno R, Valente S, Rotili D, Manzo F, Teti D, Mandrup S, Ciana P, Maggi A, Mai A, Gronemeyer H, Altucci L. HDACs class II-selective inhibition alters nuclear receptor-dependent differentiation. J Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Oct;45(4):219-28. doi: 10.1677/JME-10-0043. Epub 2010 Jul 16.
Nebbioso A, Manzo F, Miceli M, Conte M, Manente L, Baldi A, De Luca A, Rotili D, Valente S, Mai A, Usiello A, Gronemeyer H, Altucci L. Selective class II HDAC inhibitors impair myogenesis by modulating the stability and activity of HDAC-MEF2 complexes. EMBO Rep. 2009 Jul;10(7):776-82. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.88. Epub 2009 Jun 5.
- Futokadsurin C
Catalog No.:BCN6402
CAS No.:852459-91-7
- Dovitinib Dilactic acid
Catalog No.:BCC3771
CAS No.:852433-84-2
- Necrostatin 2 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC2078
CAS No.:852391-20-9
- Necrostatin 2
Catalog No.:BCC1793
CAS No.:852391-19-6
- Necrostatin 2 racemate
Catalog No.:BCC2077
CAS No.:852391-15-2
- 6-Methyl-7-O-methylaromadendrin
Catalog No.:BCN4010
CAS No.:852385-13-8
- BAPTA
Catalog No.:BCC7483
CAS No.:85233-19-8
- TOK-001
Catalog No.:BCC3910
CAS No.:851983-85-2
- RuBi-4AP
Catalog No.:BCC6044
CAS No.:851956-02-0
- ADX-47273
Catalog No.:BCC4598
CAS No.:851881-60-2
- 3-(3-Chloropropyl)-1,3-dihydro-7,8-dimethoxy-2H-3-benzazepin-2-one
Catalog No.:BCC8587
CAS No.:85175-59-3
- PF 514273
Catalog No.:BCC7746
CAS No.:851728-60-4
- Heteronoside
Catalog No.:BCN4401
CAS No.:852638-61-0
- (±)-LY 395756
Catalog No.:BCC7623
CAS No.:852679-66-4
- ABT-737
Catalog No.:BCC3613
CAS No.:852808-04-9
- TP-808
Catalog No.:BCC6450
CAS No.:852821-06-8
- Sculponeatin A
Catalog No.:BCN4402
CAS No.:85287-60-1
- 2,3-Dihydropodocarpusflavone A
Catalog No.:BCN6668
CAS No.:852875-96-8
- TCN 201
Catalog No.:BCC6122
CAS No.:852918-02-6
- 20(21)-Dehydrolucidenic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN2940
CAS No.:852936-69-7
- Dehydroepiandrosterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8929
CAS No.:853-23-6
- Anthraquinone-1,5-disulfonic acid disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC8833
CAS No.:853-35-0
- PG 01
Catalog No.:BCC7820
CAS No.:853138-65-5
- Ajugalide C
Catalog No.:BCN8015
CAS No.:853247-64-0
MC1568 Inhibits Thimerosal-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death by Preventing HDAC4 Up-Regulation in Neuronal Cells and in Rat Prefrontal Cortex.[Pubmed:27660204]
Toxicol Sci. 2016 Dec;154(2):227-240.
Ethylmercury thiosalicylate (thimerosal) is an organic mercury-based compound commonly used as an antimicrobial preservative that has been found to be neurotoxic. In contrast, histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibition has been found to be neuroprotective against several environmental contaminants, such as polychlorinated biphenyls, di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, and methylmercury. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of HDAC inhibition on thimerosal-induced neurotoxicity in neuroblastoma cells and cortical neurons. Interestingly, we found that thimerosal, at 0.5 muM in SH-SY5Y cells and at 1 muM in neurons, caused cell death by activation of apoptosis, which was prevented by the HDAC class IIA inhibitor MC1568 but not the class I inhibitor MS275. Furthermore, thimerosal specifically increased HDAC4 protein expression but not that of HDACs 5, 6, 7, and 9. Western blot analysis revealed that MC1568 prevented thimerosal-induced HDAC4 increase. In addition, both HDAC4 knocking-down and MC1568 inhibited thimerosal-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells and cortical neurons. Importantly, intramuscular injection of 12 mug/kg thimerosal on postnatal days 7, 9, 11, and 15 increased HDAC4 levels in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), which decreased histone H4 acetylation in infant male rats, in parallel increased motor activity changes. In addition, coadministration of 40 mg/kg MC1568 (intraperitoneal injection) moderated the HDAC4 increase which reduced histone H4 deacetylation and caspase-3 cleavage in the PFC. Finally, open-field testing showed that thimerosal-induced motor activity changes are reduced by MC1568. These findings indicate that HDAC4 regulates thimerosal-induced cell death in neurons and that treatment with MC1568 prevents thimerosal-induced activation of caspase-3 in the rat PFC.
Improved synthesis and structural reassignment of MC1568: a class IIa selective HDAC inhibitor.[Pubmed:24450497]
J Med Chem. 2014 Feb 13;57(3):1132-5.
An improved synthesis and structural reassignment of the class IIa selective histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor MC1568 are described.
MC1568 inhibits HDAC6/8 activity and influenza A virus replication in lung epithelial cells: role of Hsp90 acetylation.[Pubmed:27739328]
Future Med Chem. 2016 Nov;8(17):2017-2031.
AIM: Histone deacetylases (HDACs) regulate the life cycle of several viruses. We investigated the ability of different HDAC inhibitors, to interfere with influenza virus A/Puerto Rico/8/34/H1N1 (PR8 virus) replication in Madin-Darby canine kidney and NCI cells. RESULTS: 3-(5-(3-Fluorophenyl)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-N-hydroxyacry lamide (MC1568) inhibited HDAC6/8 activity and PR8 virus replication, with decreased expression of viral proteins and their mRNAs. Such an effect may be related to a decrease in intranuclear content of viral polymerases and, in turn, to an early acetylation of Hsp90, a major player in their nuclear import. Later, the virus itself induced Hsp90 acetylation, suggesting a differential and time-dependent role of acetylated proteins in virus replication. CONCLUSION: The inhibition of HDAC6/8 activity during early steps of PR8 virus replication could lead to novel anti-influenza strategy.
Class II-specific histone deacetylase inhibitors MC1568 and MC1575 suppress IL-8 expression in human melanoma cells.[Pubmed:23176534]
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Mar;26(2):193-204.
Here, we explored the effects of the novel class II-specific histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) MC1568 and MC1575 on interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression and cell proliferation in cutaneous melanoma cell line GR-M and uveal melanoma cell line OCM-3 upon stimulation with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). We found that PMA upregulated IL-8 transcription via the AP-1 binding site and identified c-Jun as the transcription factor involved in this eventS. MC1568 and MC1575 inhibited IL-8 levels and cell proliferation in either unstimulated or PMA-stimulated melanoma cells. They acted by suppressing (i) c-Jun binding to the IL-8 promoter, (ii) recruitment of histones 3 and 4, RNA polymerase II and TFIIB to the c-Jun promoter, and (iii) c-Jun expression. Our findings provide new insights into mechanisms underlying anti-tumoral activities of class II-specific HDACis in human melanoma and suggest that they may constitute a novel therapeutic strategy for improving the treatment of this cancer.
Identification of two new synthetic histone deacetylase inhibitors that modulate globin gene expression in erythroid cells from healthy donors and patients with thalassemia.[Pubmed:17666592]
Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;72(5):1111-23.
We have identified two new histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors (9 and 24) capable of inducing the expression of gamma-globin and/or beta-globin promoter-driven reporter genes in a synthetic model of Hb switch. Both compounds also increased, with different mechanisms, the gamma/(gamma+beta) ratio expressed in vitro by normal human erythroblasts. Compound 9 increased the levels of gamma-globin mRNA and the gamma/(gamma+beta) ratio (both by 2-fold). Compound 24 increased by 3-fold the level of gamma-globin and decreased by 2-fold that of beta-globin mRNA, increasing the gamma/(gamma+beta) ratio by 6-fold, and raising (by 50%) the cell HbF content. Both compounds raised the acetylation state of histone H4 in primary cells, an indication that their activity was mediated through HDAC inhibition. Compounds 9 and 24 were also tested as gamma/(gamma+beta) mRNA inducers in erythroblasts obtained from patients with beta(0) thalassemia. Progenitor cells from patients with beta(0) thalassemia generated in vitro morphologically normal proerythroblasts that, unlike normal cells, failed to mature in the presence of EPO and expressed low beta-globin levels but 10 times higher-than-normal levels of the alpha hemoglobin-stabilizing protein (AHSP) mRNA. Both compounds ameliorated the impaired in vitro maturation in beta(0) thalassemic erythroblasts, decreasing AHSP expression to normal levels. In the case of two patients (of five analyzed), the improved erythroblast maturation was associated with detectable increases in the gamma/(gamma+beta) mRNA ratio. The low toxicity exerted by compounds 9 and 24 in all of the assays investigated suggests that these new HDAC inhibitors should be considered for personalized therapy of selected patients with beta(0) thalassemia.
Class II (IIa)-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors. 1. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel (aryloxopropenyl)pyrrolyl hydroxyamides.[Pubmed:15857140]
J Med Chem. 2005 May 5;48(9):3344-53.
Chemical manipulations performed on aroyl-pyrrolyl-hydroxyamides (APHAs) led to (aryloxopropenyl)pyrrolyl hydroxamates 2a-w, and their inhibition against maize HDACs and their class I or class II HDAC selectivity were determined. In particular, from these studies some benzene meta-substituted compounds emerged as highly class II (IIa)-selective HDAC inhibitors, the most selective being the 3-chloro- and 3-fluoro-substituted compounds 2c (SI = 71.4) and2f (SI = 176.4). The replacement of benzene with a 1-naphthyl ring afforded 2s, highly active against the class II homologue HD1-A (IC(50) = 10 nM) but less class II-selective than 2c,f. When tested against human HDAC1 and HDAC4, 2f showed no inhibitory activity against HDAC1 but was able to inhibit HDAC4. Moreover, in human U937 acute myeloid leukaemia cells 2f did not produce any effect on apoptosis, granulocytic differentiation, and the cell cycle, whereas 2s (that retain class I HDAC inhibitory activity) was 2-fold less potent than SAHA used as reference.


