Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683)HDAC inhibitor CAS# 149647-78-9 |
- Romidepsin (FK228, depsipeptide)
Catalog No.:BCC3597
CAS No.:128517-07-7
- Scriptaid
Catalog No.:BCC2163
CAS No.:287383-59-9
- Mocetinostat (MGCD0103, MG0103)
Catalog No.:BCC2146
CAS No.:726169-73-9
- ITF2357 (Givinostat)
Catalog No.:BCC2150
CAS No.:732302-99-7
- PCI-24781 (CRA-024781)
Catalog No.:BCC2155
CAS No.:783355-60-2
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 149647-78-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H20N2O3 | M.Wt | 264.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Vorinostat | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
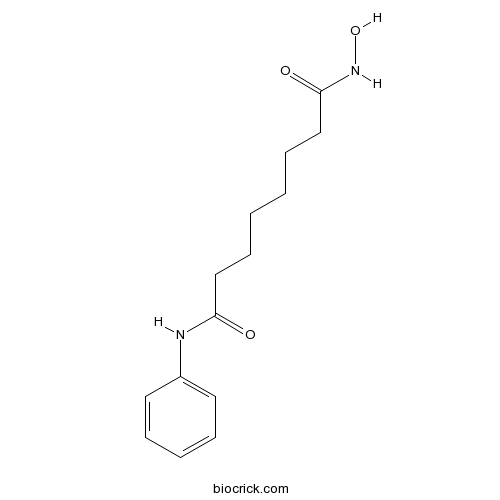
| Chemical Name | N'-hydroxy-N-phenyloctanediamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)NC(=O)CCCCCCC(=O)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WAEXFXRVDQXREF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H20N2O3/c17-13(15-12-8-4-3-5-9-12)10-6-1-2-7-11-14(18)16-19/h3-5,8-9,19H,1-2,6-7,10-11H2,(H,15,17)(H,16,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibits Class I and II histone deacetylases (HDACs); induces accumulation of acetylated histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 in transformed cultured cells. Suppresses cell growth in a range of cancer cell lines; induces apoptosis in cutaneous T cell lymphoma cells in vitro. Activates autophagy. |

Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683) Dilution Calculator

Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7836 mL | 18.9179 mL | 37.8358 mL | 75.6716 mL | 94.5895 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7567 mL | 3.7836 mL | 7.5672 mL | 15.1343 mL | 18.9179 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3784 mL | 1.8918 mL | 3.7836 mL | 7.5672 mL | 9.4589 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0757 mL | 0.3784 mL | 0.7567 mL | 1.5134 mL | 1.8918 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0378 mL | 0.1892 mL | 0.3784 mL | 0.7567 mL | 0.9459 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
The MTD, DLT and PK properties of vorinostat, an HDAC inhibitor, were determined in a study utilizing vorinostat plus temozolomide to treat children with refractory or recurrent CNS malignancies.
Abstract
The efficacy and tolerability of vorinostat plus bortezomib were assessed in multiple myeloma patients.
Abstract
Vorinostat, a class I/II HDAC inhibitor, alters the expression of target genes and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Abstract
Although it’s been used to treat advanced CTCL patients, vorinostat, a HDACi with anti-cancer activity, is currently being evaluated to treat other solid tumors and hematological malignancies.
Abstract
The effect of vorinostat, which is a HDACi capable of inducing cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis and differentiation, on biomarker modulation in women with breast cancer was evaluated.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) is a histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi), that plays key roles in epigenetic or non-epigenetic regulation, inducing growth arrest, differentiation and apoptosis of tumor cells.[1] Vorinostat is a small molecular with the formular of C14H20N2O3 and molecular weight of 264.3. The major mechanism of HDACi-induced apoptosis is the activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. HDACi can activate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway by releasing of cytochrome c from mitochondria and regulating of Bcl-2 family expression.[2]
Reference
[1] Hui-ming Z, Qian-hai D, Wei-ping C, Ru-bin L. Vorinostat, a HDAC inhibitor, showed anti-osteoarthritic activities through inhibition of iNOS and MMP expression, p38 and ERK phosphorylation and blocking NF-kB nuclear translocation. International Immunopharmacology. 2013, 17. 329-335.
[2] Norihisa U, Sayaka K, Hisanori M, Katsuhiko Y, Airo T. Requirement of p38 MAPK for a cell-death pathway triggered by vorinostat in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Letters. 2012, 315. 112-121.
- MOG (35-55)
Catalog No.:BCC3670
CAS No.:149635-73-4
- Impentamine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7197
CAS No.:149629-70-9
- Stachybotramide
Catalog No.:BCN6969
CAS No.:149598-71-0
- Marmin
Catalog No.:BCN1665
CAS No.:14957-38-1
- Ganoderic acid AM1
Catalog No.:BCN2441
CAS No.:149507-55-1
- Hypocrellin C
Catalog No.:BCN3398
CAS No.:149457-83-0
- Traxillaside
Catalog No.:BCN6917
CAS No.:149415-62-3
- Poncirin
Catalog No.:BCN2590
CAS No.:14941-08-3
- NE 100 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7573
CAS No.:149409-57-4
- Cidofovir dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4247
CAS No.:149394-66-1
- UNC2881
Catalog No.:BCC5362
CAS No.:1493764-08-1
- 1,2,3,4,6-O-Pentagalloylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN2338
CAS No.:14937-32-7
- Nafadotride
Catalog No.:BCC7025
CAS No.:149649-22-9
- Chrysosplenol D
Catalog No.:BCN1666
CAS No.:14965-20-9
- Isogambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3078
CAS No.:149655-52-7
- Isomorellinol
Catalog No.:BCN3075
CAS No.:149655-53-8
- Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5089
CAS No.:149676-40-4
- Stachybotrolide
Catalog No.:BCN6968
CAS No.:149691-31-6
- AHU-377(Sacubitril)
Catalog No.:BCC4088
CAS No.:149709-62-6
- RS 23597-190 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6767
CAS No.:149719-06-2
- H-Arg-NH2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2859
CAS No.:14975-30-5
- Tereticornate A
Catalog No.:BCN1667
CAS No.:149751-81-5
- Clemastine Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4528
CAS No.:14976-57-9
- Delaminomycin A
Catalog No.:BCN1833
CAS No.:149779-38-4
Histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683) perturb miR-9-MCPIP1 axis to block IL-1beta-induced IL-6 expression in human OA chondrocytes.[Pubmed:27404795]
Connect Tissue Res. 2017 Jan;58(1):64-75.
AIM OF THE STUDY: High levels of IL-6 are believed to contribute to osteoarthritis (OA) pathogenesis. The expression of IL-6 is regulated post-transcriptionally by the miR-9-MCPIP-1 axis in chondrocytes. Vorinostat (SAHA) inhibits the IL-6 expression in OA chondrocytes. We investigated whether SAHA suppresses the expression of IL-6 by perturbing the miR-9-MCPIP1 axis in OA chondrocytes under pathological conditions. MATERIALS AND METHODS: OA chondrocytes were isolated by enzymatic digestion and treated with IL-1beta in the absence or presence of SAHA. Genes and protein expression levels were determined by TaqMan assays and Western blotting, respectively. Secreted IL-6 was quantified by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). MCPIP1 promoter deletion mutants were generated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Promoter recruitment of transcription factors was determined by ChIP. Nuclear run-on was employed to measure the ongoing transcription. siRNA-mediated knockdown of the CEBPalpha expression was employed for loss of function studies. RESULTS: Expression of MCPIP1 was high in SAHA treated OA chondrocytes but expression of IL-6 mRNAs and secreted IL-6 were reduced by ~70%. SAHA suppressed the expression of miR-9 but enhanced the activity of the MCPIP1 promoter localized to a 156bp region which also harbors the binding site for CEBPalpha. Treatment with SAHA enhanced the recruitment of CEBPalpha to the MCPIP1 promoter. Ectopically expressed CEBPalpha enhanced the promoter activity and the expression of MCPIP1 while siRNA-mediated knockdown of CEBPalpha inhibited the expression of MCPIP1. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together our data indicate that SAHA-mediated suppression of the IL-6 expression is achieved through increased recruitment of CEBPalpha to the MCPIP1 promoter and by relieving the miR-9-mediated inhibition of MCPIP1 expression in OA chondrocytes.
Induction of pluripotent stem cells by defined factors is greatly improved by small-molecule compounds.[Pubmed:18568017]
Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Jul;26(7):795-7.
Reprogramming of mouse and human somatic cells can be achieved by ectopic expression of transcription factors, but with low efficiencies. We report that DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors improve reprogramming efficiency. In particular, valproic acid (VPA), an HDAC inhibitor, improves reprogramming efficiency by more than 100-fold, using Oct4-GFP as a reporter. VPA also enables efficient induction of pluripotent stem cells without introduction of the oncogene c-Myc.
Dimethyl sulfoxide to vorinostat: development of this histone deacetylase inhibitor as an anticancer drug.[Pubmed:17211407]
Nat Biotechnol. 2007 Jan;25(1):84-90.
In our quest to understand why dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) can cause growth arrest and terminal differentiation of transformed cells, we followed a path that led us to discover suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA; vorinostat (Zolinza)), which is a histone deacetylase inhibitor. SAHA reacts with and blocks the catalytic site of these enzymes. Extensive structure-activity studies were done along the path from DMSO to SAHA. SAHA can cause growth arrest and death of a broad variety of transformed cells both in vitro and in tumor-bearing animals at concentrations not toxic to normal cells. SAHA has many protein targets whose structure and function are altered by acetylation, including chromatin-associated histones, nonhistone gene transcription factors and proteins involved in regulation of cell proliferation, migration and death. In clinical trials, SAHA has shown significant anticancer activity against both hematologic and solid tumors at doses well tolerated by patients. A new drug application was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for vorinostat for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. More potent analogs of SAHA have shown unacceptable toxicity.
The antitumor histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid exhibits antiinflammatory properties via suppression of cytokines.[Pubmed:11867742]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):2995-3000.
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) is a hydroxamic acid-containing hybrid polar molecule; SAHA specifically binds to and inhibits the activity of histone deacetylase. Although SAHA, like other inhibitors of histone deacetylase, exhibits antitumor effects by increasing expression of genes regulating tumor survival, we found that SAHA reduces the production of proinflammatory cytokines in vivo and in vitro. A single oral administration of SAHA to mice dose-dependently reduced circulating TNF-alpha, IL-1-beta, IL-6, and IFN-gamma induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Administration of SAHA also reduced hepatic cellular injury in mice following i.v. injection of Con A. SAHA inhibited nitric oxide release in mouse macrophages stimulated by the combination of TNF-alpha plus IFN-gamma. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with LPS in the presence of SAHA released less TNF-alpha, IL-1-beta, IL-12, and IFN-gamma (50% reduction at 100-200 nM). The production of IFN-gamma stimulated by IL-18 plus IL-12 was also inhibited by SAHA (85% at 200 nM). However, SAHA did not affect LPS-induced synthesis of the IL-1-beta precursor, the IL-1 receptor antagonist, or the chemokine IL-8. In addition, IFN-gamma induced by anti-CD3 was not suppressed by SAHA. Steady-state mRNA levels for LPS-induced TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were markedly decreased, whereas IL-8 and IL-1-beta mRNA levels were unaffected. Because SAHA exhibits antiinflammatory properties in vivo and in vitro, inhibitors of histone deacetylase may stimulate the expression of genes that control the synthesis of cytokines and nitric oxide or hyperacetylate other targets.
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:11016644]
Cancer Res. 2000 Sep 15;60(18):5165-70.
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) is the prototype of a family of hybrid polar compounds that induce growth arrest in transformed cells and show promise for the treatment of cancer. SAHA induces differentiation and/or apoptosis in certain transformed cells in culture and is a potent inhibitor of histone deacetylases. In this study, we examined the effects of SAHA on the growth of human prostate cancer cells in culture and on the growth of the CWR22 human prostate xenograft in nude mice. SAHA suppressed the growth of the LNCaP, PC-3, and TSU-Pr1 cell lines at micromolar concentrations (2.5-7.5 microM). SAHA induced dose-dependent cell death in the LNCaP cells. In mice with transplanted CWR222 human prostate tumors, SAHA (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg/day) caused significant suppression of tumor growth compared with mice receiving vehicle alone; treatment with 50 mg/kg/day resulted in a 97% reduction in the mean final tumor volume compared with controls. At this dose, there was no detectable toxicity as evaluated by weight gain and necropsy examination. Increased accumulation of acetylated core histones was detected in the CWR22 tumors within 6 h of SAHA administration. SAHA induced prostate-specific antigen mRNA expression in CWR22 prostate cancer cells, resulting in higher levels of serum prostate-specific antigen than predicted from tumor volume alone. The results suggest that hydroxamic acid-based hybrid polar compounds inhibit prostate cancer cell growth and may be useful, relatively nontoxic agents for the treatment of prostate carcinoma.


