PCI-24781 (CRA-024781)Pan-HDAC inhibitor CAS# 783355-60-2 |
- Resminostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1888
CAS No.:1187075-34-8
- RG2833
Catalog No.:BCC1893
CAS No.:1215493-56-3
- Daminozide
Catalog No.:BCC1514
CAS No.:1596-84-5
- Tasquinimod
Catalog No.:BCC1987
CAS No.:254964-60-8
- CHAPS
Catalog No.:BCC1476
CAS No.:75621-03-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 783355-60-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11749858 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H23N3O5 | M.Wt | 397.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CRA 024781; CRA 24781; Abexinostat | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 3.33 mg/mL (8.38 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
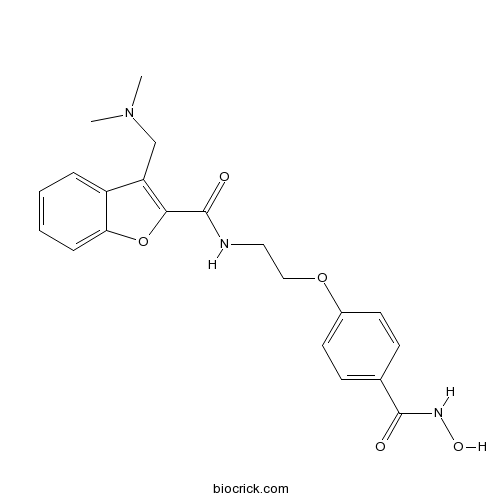
| Chemical Name | 3-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-N-[2-[4-(hydroxycarbamoyl)phenoxy]ethyl]-1-benzofuran-2-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)CC1=C(OC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NCCOC3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MAUCONCHVWBMHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H23N3O5/c1-24(2)13-17-16-5-3-4-6-18(16)29-19(17)21(26)22-11-12-28-15-9-7-14(8-10-15)20(25)23-27/h3-10,27H,11-13H2,1-2H3,(H,22,26)(H,23,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PCI-24781 is an inhibitor of HDACs with Ki values of 7 nM, 8.2 nM, 17 nM and 19 nM for HDAC1, HDAC3/SMRT, HDAC6 and HDAC2, respectively. | |||||
| Targets | HDAC1 | HDAC3/SMRT | HDAC6 | HDAC2 | HDAC10 | HDAC8 |
| IC50 | 7 nM (Ki) | 8.2 nM (Ki) | 17 nM (Ki) | 19 nM (Ki) | 24 nM | 280 nM |

PCI-24781 (CRA-024781) Dilution Calculator

PCI-24781 (CRA-024781) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5162 mL | 12.5811 mL | 25.1623 mL | 50.3246 mL | 62.9057 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5032 mL | 2.5162 mL | 5.0325 mL | 10.0649 mL | 12.5811 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2516 mL | 1.2581 mL | 2.5162 mL | 5.0325 mL | 6.2906 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0503 mL | 0.2516 mL | 0.5032 mL | 1.0065 mL | 1.2581 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0252 mL | 0.1258 mL | 0.2516 mL | 0.5032 mL | 0.6291 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CRA-024781 is a novel HDAC inhibitor targeting HDAC1, HDAC2, HADC3, HADC6, HADC8, HADC10 with IC50 value of 7 nM(Ki), 19 nM(Ki), 8.2 nM(Ki), 17 nM(Ki), 280 nM(Ki), 24 nM(Ki), respectively [1].
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly.
CRA-024781 exhibits potent antitumor activity against ten human tumor cell lines with GI50 ranging from 0.15 μM to 3.09 μM. CRA-024781 also has an antiproliferative effect on HUVEC endothelial cells with GI50 of 0.43 μM. CRA-024781 treatment causes dose-dependent accumulation of both acetylated histones and acetylated tubulin in HCT116 or DLD-1 cells suggesting that HDAC enzymes are inhibited in these cells. CRA-024781 also induces the expression of p21 (a protein playing a role in the antitumor effect) and leads to PARP cleavage and accumulation of the γH2AX, which indicate apoptosis [1].
Treatment with CRA-024781 at 200 mg/kg once daily every other day significantly inhibits the growth of HCT116 and DLD-1 xenografts in mice by 69% and 59%, respectively. In the HCT116 model, treatment with CRA-024781 at 20 mg/kg, 40 mg/kg, 80 mg/kg, or 160 mg/kg (q.d. × 4 per week) causes inhibition of tumor growth by 48%, 57%, 82.2%, or 80.0%, respectively [1].
Reference:
[1]. Buggy JJ, Cao ZA, Bass KE, et al. CRA-024781: a novel synthetic inhibitor of histone deacetylase enzymes with antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther, 2006, 5(5): 1309-1317.
.
- MLN120B
Catalog No.:BCC1772
CAS No.:783348-36-7
- MRK 016
Catalog No.:BCC6070
CAS No.:783331-24-8
- H-D-1-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3281
CAS No.:78306-92-0
- 7-Ethylcamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN2480
CAS No.:78287-27-1
- Ecliptasaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN3843
CAS No.:78285-90-2
- Nepafenac
Catalog No.:BCC1258
CAS No.:78281-72-8
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Catalog No.:BCN1049
CAS No.:78281-02-4
- [Orn5]-URP
Catalog No.:BCC5985
CAS No.:782485-03-4
- Paroxetine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5054
CAS No.:78246-49-8
- 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2
Catalog No.:BCN1070
CAS No.:78214-33-2
- Nirtetralin
Catalog No.:BCN3755
CAS No.:78185-63-4
- YM155
Catalog No.:BCC2251
CAS No.:781661-94-7
- Nocamycin I
Catalog No.:BCN1845
CAS No.:78339-49-8
- Pyranojacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN7429
CAS No.:78343-62-1
- MY-5445
Catalog No.:BCC6645
CAS No.:78351-75-4
- 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7523
CAS No.:78405-33-1
- Milrinone
Catalog No.:BCC4374
CAS No.:78415-72-2
- Trequinsin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7333
CAS No.:78416-81-6
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxy-6,4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1353
CAS No.:78417-26-2
- RGB-286638
Catalog No.:BCC5519
CAS No.:784210-87-3
- RGB-286638 free base
Catalog No.:BCC5520
CAS No.:784210-88-4
- Deacetyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN2820
CAS No.:78432-77-6
- 19-Hydroxybaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCN4330
CAS No.:78432-78-7
- 7-Epi 10-Desacetyl Paclitaxel
Catalog No.:BCC1314
CAS No.:78454-17-8
[Drug therapy of lymphomas].[Pubmed:28273193]
Magy Onkol. 2017 Mar 8;61(1):89-96. Epub 2016 Jun 15.
The therapy of lymphomas has undergone a major expansion during the last decade. Novel therapeutic targets have appeared beyond classical chemotherapeutic combinations. These novel drugs have very pronounced action across lymphoma types, and their toxicity profile is usually better tolerable compared to standard chemotherapies. These new therapies are enabling us to offer treatment to those patients who have refractory disease, and we had no option to treat them before these drugs. The author describes several new therapeutic options. New chemotherapeutic drugs are pixantrone and bendamustin. Monoclonal antibodies, like rituximab, ofatumumab, obinotuzumab are described, and conjugated antibodies like brentuximab vedotin and inotuzumab ozogamicin are also discussed. The bispecific antibody blinatumomab can modulate the immune response, and the new class of immune checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, nivolumab) is also discussed. Therapies targeting the epigenetic regulatory network are also important. Several studies reported promising results of abexinostat, vorinostat, belinostat and panobinostat. The new class of immunomodulatory drugs (imids) is also growing, results with thalidomid and lenalidomid are discussed. The proteasome inhibitors are offering new combinations, with the use of bortezomid, carfilzomib, ixazomib. All these new drugs described above offer to the physician several therapeutic options to better treat patients with lymphoma.
A phase 1 dose-escalation study of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat in combination with standard hypofractionated radiotherapy in advanced solid tumors.[Pubmed:28915584]
Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 24;8(34):56199-56209.
Current treatments for advanced solid tumors tend to be only palliative. Although radiotherapy is administered with a curative intent, radioresistance and dose-limiting toxicities pose limitations to treatment. Abexinostat, an oral pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor, demonstrated enhanced sensitivity to radiation in various solid tumor cell lines. We conducted an exploratory, phase 1, dose-escalation study of abexinostat in combination with standard hypofractionated radiotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors treated in a palliative setting. Among 58 treated patients, the median age was 61.5 years (range, 20-82); 47% of the patients had M1 stage disease, and 95% had received previous chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy in combination with surgery and/or radiotherapy. The recommended phase 2 dose was determined to be 90 mg/m(2) (140 mg). Of the 51 patients evaluable for response, best overall response was 8% (1 complete response [CR], 3 partial responses [PRs]), and best loco-regional response was 12% (1 CR and 5 PRs) at a median follow-up of 16 weeks. Of note, patients with target or non-target brain lesions showed encouraging responses, with 1 patient achieving a best loco-regional response of CR. Treatment-emergent grade >/=3 adverse events (AEs) were few, with most common being thrombocytopenia (17%), lymphopenia (12%), and hypokalemia (7%). Six patients (10%) discontinued treatment due to AEs. No grade >/=3 prolongation of the QTc interval was observed, with no treatment discontinuations due to this AE. Oral abexinostat combined with radiotherapy was well tolerated in patients with advanced solid tumors. The combination may have potential for treatment of patients with brain lesions.
Inhibiting Histone Deacetylase as a Means to Reverse Resistance to Angiogenesis Inhibitors: Phase I Study of Abexinostat Plus Pazopanib in Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies.[Pubmed:28221861]
J Clin Oncol. 2017 Apr 10;35(11):1231-1239.
Purpose This phase I trial evaluated epigenetic modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor by using a histone deacetylase abexinostat in combination with pazopanib to enhance response and reverse resistance. Patients and Methods Pazopanib was administered once a day on days 1 to 28 and abexinostat was administered orally twice a day on days 1 to 5, 8 to 12, and 15 to 19 (schedule A) or on days 1 to 4, 8 to 11, and 15 to 18 (schedule B). Dose escalation (3 + 3 design) in all solid tumors was followed by dose expansion in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Results Fifty-one patients with RCC (N = 22) were enrolled, including 30 (59%) with one or more lines of prior VEGF-targeting therapy. Five dose-limiting toxicities, including fatigue (n = 2), thrombocytopenia (n = 2), and elevated AST/ALT (n = 1), were observed with schedule A; one dose-limiting toxicity was observed (elevated AST/ALT) was observed with schedule B. Grade >/= 3 related adverse events included fatigue (16%), thrombocytopenia (16%), and neutropenia (10%). The recommended phase II dose was established as abexinostat 45 mg/m(2) twice a day administered per schedule B plus pazopanib 800 mg/d. Objective response rate was 21% overall and 27% in the RCC subset. Median duration of response was 9.1 months (1.2 to > 49 months). Eight patients (16%) had durable control of disease for > 12 months. Durable tumor regressions were observed in seven (70%) of 10 patients with pazopanib-refractory disease, including one patients with RCC with ongoing response > 3.5 years. Peripheral blood histone acetylation and HDAC2 gene expression were associated with durable response to treatment. Conclusion Abexinostat is well tolerated in combination with pazopanib, allowing prolonged exposure and promising durable responses in pazopanib- and other VEGF inhibitor-refractory tumors, which supports epigenetically mediated reversal of treatment resistance.
Time dependent modulation of tumor radiosensitivity by a pan HDAC inhibitor: abexinostat.[Pubmed:28915585]
Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 25;8(34):56210-56227.
Despite prominent role of radiotherapy in lung cancer management, there is an urgent need for strategies increasing therapeutic efficacy. Reversible epigenetic changes are promising targets for combination strategies using HDAC inhibitors (HDACi). Here we evaluated on two NSCLC cell lines, the antitumor effect of abexinostat, a novel pan HDACi combined with irradiation in vitro in normoxia and hypoxia, by clonogenic assays, demonstrating that abexinostat enhances radiosensitivity in a time dependent way with mean SER10 between 1.6 and 2.5 for A549 and H460. We found, by immunofluorescence staining, flow cytometry assays and western blotting, in abexinostat treated cells, increasing radio-induced caspase dependent apoptosis and persistent DNA double-strand breaks associated with decreased DNA damage signalling and repair. Interestingly, we demonstrated on nude mice xenografts that abexinostat potentiates tumor growth delay in combined modality treatments associating not only abexinostat and irradiation but also when adding cisplatin. Altogether, our data demonstrate in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor effect potentiation by abexinostat combined with irradiation in NSCLC. Moreover, our work suggests for the first time to our knowledge promising triple combination opportunities with HDACi, irradiation and cisplatin which deserves further investigations and could be of major interest in the treatment of NSCLC.


