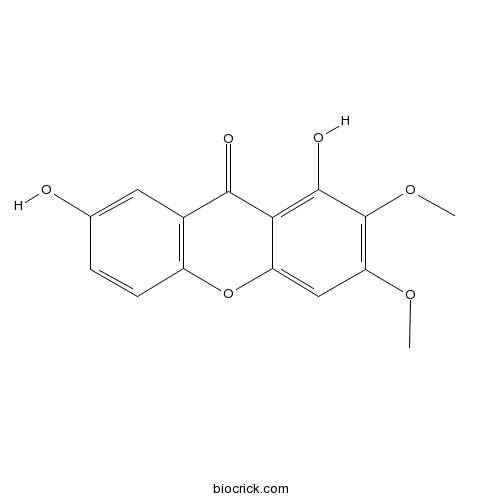
1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthoneCAS# 78405-33-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 78405-33-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10039726 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H12O6 | M.Wt | 288.25 |
| Type of Compound | Xanthones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthen-9-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C(=C2C(=C1)OC3=C(C2=O)C=C(C=C3)O)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BLXIZCDWQXDWQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H12O6/c1-19-11-6-10-12(14(18)15(11)20-2)13(17)8-5-7(16)3-4-9(8)21-10/h3-6,16,18H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone shows significant inhibitory effects on LPS-induced NO production in BV2 microglia cells. 2. 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone antagonises in a non competitive but, reversible manner the contractions induced by chemical inflammatory mediators in the guinea pig trachea in vitro, thus, it may have medicinal use in the management of inflammation, asthma and allergy. |
| Targets | NO |

1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone Dilution Calculator

1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4692 mL | 17.3461 mL | 34.6921 mL | 69.3842 mL | 86.7303 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6938 mL | 3.4692 mL | 6.9384 mL | 13.8768 mL | 17.3461 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3469 mL | 1.7346 mL | 3.4692 mL | 6.9384 mL | 8.673 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0694 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.6938 mL | 1.3877 mL | 1.7346 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0347 mL | 0.1735 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.6938 mL | 0.8673 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- MY-5445
Catalog No.:BCC6645
CAS No.:78351-75-4
- Pyranojacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN7429
CAS No.:78343-62-1
- Nocamycin I
Catalog No.:BCN1845
CAS No.:78339-49-8
- PCI-24781 (CRA-024781)
Catalog No.:BCC2155
CAS No.:783355-60-2
- MLN120B
Catalog No.:BCC1772
CAS No.:783348-36-7
- MRK 016
Catalog No.:BCC6070
CAS No.:783331-24-8
- H-D-1-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3281
CAS No.:78306-92-0
- 7-Ethylcamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN2480
CAS No.:78287-27-1
- Ecliptasaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN3843
CAS No.:78285-90-2
- Nepafenac
Catalog No.:BCC1258
CAS No.:78281-72-8
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Catalog No.:BCN1049
CAS No.:78281-02-4
- [Orn5]-URP
Catalog No.:BCC5985
CAS No.:782485-03-4
- Milrinone
Catalog No.:BCC4374
CAS No.:78415-72-2
- Trequinsin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7333
CAS No.:78416-81-6
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxy-6,4',5'-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1353
CAS No.:78417-26-2
- RGB-286638
Catalog No.:BCC5519
CAS No.:784210-87-3
- RGB-286638 free base
Catalog No.:BCC5520
CAS No.:784210-88-4
- Deacetyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN2820
CAS No.:78432-77-6
- 19-Hydroxybaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCN4330
CAS No.:78432-78-7
- 7-Epi 10-Desacetyl Paclitaxel
Catalog No.:BCC1314
CAS No.:78454-17-8
- Enterolakton
Catalog No.:BCC8170
CAS No.:78473-71-9
- Praeruptorin E
Catalog No.:BCN2591
CAS No.:78478-28-1
- 7-Epi-10-deacetylcephalomannine
Catalog No.:BCN7673
CAS No.:78479-12-6
- N-trans-Feruloyl-3-methoxytyramine
Catalog No.:BCN4331
CAS No.:78510-19-7
Xanthones from Polygala alpestris (Rchb.).[Pubmed:18998397]
Z Naturforsch C. 2004 May-Jun;59(5-6):335-8.
Bioactivity-guided fractionation of Polygala alpestris L. (Rchb.) extracts led to the identification of two new xanthones, 1,3,7-trihydroxy-2,6-dimethoxyxanthone (1) and 2,3-methylenedioxy-4,7-dihydroxyxanthone (2). In addition five known compounds 3,4-dimethoxy-1,7-dihydroxyxanthone (3), 1,3-dihydroxy-7-methoxyxanthone (4), 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone (5), 3',6-O-disinapoyl sucrose (6) and 3',5'-dimethoxybiphenyl-4-olo (7) were isolated. The structures of the isolated compounds were established by means of high resolution mass spectrometry, mono- and bi-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. All isolated compounds were tested for cytotoxic activity against three tumor cell lines (LoVo, HL-60, K 562).
Role of gastric mucus secretion, oxinitrergic system and sulfhydryl groups on the gastroprotection elicited by Polygala cyparissias (Polygalaceae) in mice.[Pubmed:23600395]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013 May;65(5):767-76.
OBJECTIVES: This study has aimed to assess the mechanisms of action for the gastroprotective effect of the acetone extract (PCAE) and methanol fraction (PCMF) of Polygala cyparissias, as well as to evaluate the activity of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-2,7-dimethoxyxanthone (1), 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone (2) and astragalin (3). METHODS: Gastric secretion and mucus content were determined by pylorus ligation in mice. Nitric oxide (NO) and sulfhydryl group participation were observed by the pretreatment of mice with L-NAME or NEM. Acute ulcer was induced by ethanol/HCl and chronic ulcer by acetic acid. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity was evaluated by the agar solid dilution assay. KEY FINDINGS: Neither PCAE nor PCMF had the ability to reduce H(+) concentration. However, both of them enhanced mucus secretion. PCAE demonstrated its gastroprotection in a NO-dependent manner, while PCMF exerted the activity depending on the sulfhydryl group. In chronic ulcer, the curative ratios for the PCAE and PCMF were 67.5 and 58.4%, respectively. No effect over H. pylori was detected. Compounds 1, 2 and 3 were able to reduce lesions in the order of 79.6, 73.8 and 67.6%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: The data suggested that PCAE and PCMF displayed antiulcer activity due to different mechanisms and with the participation of phenolic compounds obtained from the plant.
In vitro effect of the extract and the 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy xanthone from Polygala cyparissias on the contractions induced by inflammatory mediators and ovalbumin in normal and actively sensitised trachea from guinea pig.[Pubmed:10344473]
Inflamm Res. 1999 Apr;48(4):218-23.
OBJECTIVE: This study describes the in vitro action of the hydroalcoholic extract and the 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy xanthone isolated from P. cyparissias on agonist and ovalbumin induced contractions in trachea, from normal and actively sensitised guinea pigs. RESULTS: The hydroalcoholic extract of P. cyparissias (0.125 to 1 mg/ml), incubated with the guinea-pig trachea for 20 min, had no effect on the resting tone of the preparations, but caused a concentration-dependent, reversible and non competitive inhibition of contractions induced by acetylcholine, histamine, compound 48/80, bradykinin, substance P, prostaglandin E2 and the stable analogue of thromboxane A2 mimetic U 46619. The calculated mean IC50 values for the hydroalcoholic extract were: 0.37, 0.51, 0.06, 0.32, 0.48, 0.3 and 0.17 mg/ml, respectively. Also, the extract of P. cyparissias (0.125 to 0.5 mg/ml) antagonised, in a graded manner (IC50 of 0.46 mg/ml) ovalbumin-induced contractions in guinea-pig trachea obtained from animals which had been actively sensitised to this antigen. Pre-incubation of the preparations with the purifed xanthone isolated from P. cyparssias (2.5 to 80 microg/ml; 10.0 to 310.0 microM) caused significant and concentration-dependent, reversible and noncompetitive inhibition of the contractile responses elicited by acetylcholine, histamine, bradykinin, substance P, U 46619 and prostaglandin E2. The calculated mean IC50 values for these effects were: 132.0, 73.0, 9.2, 32.0, 110.6 and 66.0 microM, respectively. At very high concentrations (I55.0-620.0 microM) the xanthone also antagonised contraction induced by KCl in guinea-pig trachea (IC50 of 190.0 microM). CONCLUSIONS: Taken together these and our previous in vivo results are consistent with the view that the active principles present in P. cyparissias, including the 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy xanthone, antagonise, in a non competitive but, reversible manner the contractions induced by chemical inflammatory mediators in the guinea pig trachea in vitro. Thus, these results might explain at least in part, the medicinal use of this plant in the management of inflammation, asthma and allergy.
Chemical constituents of Polygala tenuifolia roots and their inhibitory activity on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglia.[Pubmed:21740104]
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2012 Feb;27(1):1-4.
A methanolic extract of the roots of Polygala tenuifolia (Polygalaceae) significantly attenuated nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV2 microglia cells. Five xanthones, 1-hydroxy-7-methoxyxanthone (1), 3,6-dihydroxy-1,2,7-trimethoxyxanthone (2), 1,3,6-trihydroxy-2,7-dimethoxyxanthone (3), 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone (4) and 1,7-dihydroxy-3-methoxyxanthone (5), and five phenylpropanoids, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxypropiophenone (6), methyl 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid (7), 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid (8), 4-methoxycinnamic acid (9) and beta-d-(3-O-sinapoyl) fructofuranosyl-alpha-d-(6-O-sinapoyl)glucopyranoside (10), were isolated from CHCl(3) fraction using bioactivity-guided fractionation. Among these compounds, compounds 1, 2, 4, 5 and 7 showed significant inhibitory effects on LPS-induced NO production in BV2 microglia cells at the concentration ranging from 10.0 to 100.0 muM.


