NepafenacAnti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) CAS# 78281-72-8 |
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- Docetaxel Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1535
CAS No.:148408-66-6
- Colchicine
Catalog No.:BCN6271
CAS No.:64-86-8
- D-64131
Catalog No.:BCC1510
CAS No.:74588-78-6
- 7-Xylosyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN5341
CAS No.:90332-66-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 78281-72-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 151075 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14N2O2 | M.Wt | 254.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AHR 9434; AL 6515 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (125.85 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
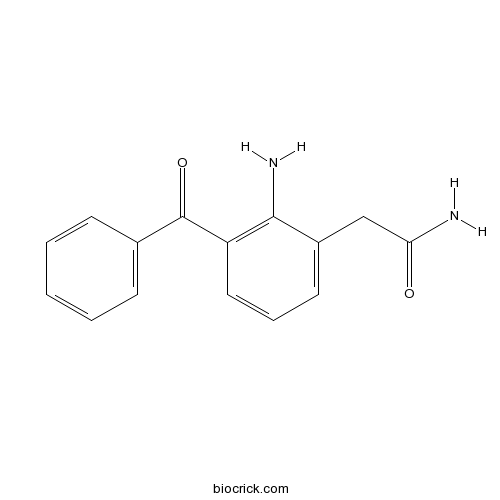
| Chemical Name | 2-(2-amino-3-benzoylphenyl)acetamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=C(C(=CC=C2)CC(=O)N)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QEFAQIPZVLVERP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14N2O2/c16-13(18)9-11-7-4-8-12(14(11)17)15(19)10-5-2-1-3-6-10/h1-8H,9,17H2,(H2,16,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nepafenac(AHR 9434; AL 6515; Nevanac) is a selective COX-2 inhibitor; is prodrug of Amfenac.
IC50 value:
Target: COX-2
Nepafenac is a NSAID (nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drug) that is routinely used in opthamology to control pain following cataract surgery. References: | |||||

Nepafenac Dilution Calculator

Nepafenac Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9327 mL | 19.6634 mL | 39.3267 mL | 78.6535 mL | 98.3168 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7865 mL | 3.9327 mL | 7.8653 mL | 15.7307 mL | 19.6634 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3933 mL | 1.9663 mL | 3.9327 mL | 7.8653 mL | 9.8317 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0787 mL | 0.3933 mL | 0.7865 mL | 1.5731 mL | 1.9663 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0393 mL | 0.1966 mL | 0.3933 mL | 0.7865 mL | 0.9832 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Nepafenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). The IC50 values of nepafenac for (cyclooxygenase-1) COX-1 and COX-2 are 250 nM and 150 nM, respectively [1].
Nepafenac showed to significantly decrease the retinal levels of PGE2 in LPS-induced rats when administrated topically. However, nepafenac has revealed no significant effect on BRB permeability in LPS-induced rat model [1].
Nepafenac significantly reduced proliferation rate of human uveal melanoma cell lines including SP6.5, 92.1, OCM-1, MKT-BR and of human transformed uveal melanocyte cell line UW-1. Compared to rofecoxib, nepafenac might reveal a better systemic safety profile [2].
References:
[1] Bucolo C1, Marrazzo G, Platania CB, Romano GL, Drago F, Salomone S. Effects of topical indomethacin, bromfenac and nepafenac on lipopolysaccharide-induced ocular inflammation. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;66(7):954-60.
[2] Marshall JC1, Caissie AL, Cruess SR, Cools-Lartigue J, Burnier MN Jr. The effects of a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and inhibition on human uveal melanoma cell proliferation and macrophage nitric oxide production. J Carcinog. 2007 Nov 27;6:17.
- Hydroxysafflor yellow A
Catalog No.:BCN1049
CAS No.:78281-02-4
- [Orn5]-URP
Catalog No.:BCC5985
CAS No.:782485-03-4
- Paroxetine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5054
CAS No.:78246-49-8
- 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2
Catalog No.:BCN1070
CAS No.:78214-33-2
- Nirtetralin
Catalog No.:BCN3755
CAS No.:78185-63-4
- YM155
Catalog No.:BCC2251
CAS No.:781661-94-7
- 4-Hydroxyisoleucine
Catalog No.:BCN1211
CAS No.:781658-23-9
- CDPPB
Catalog No.:BCC7610
CAS No.:781652-57-1
- MK-0974
Catalog No.:BCC1756
CAS No.:781649-09-0
- DAMGO
Catalog No.:BCC6958
CAS No.:78123-71-4
- Okadaic acid
Catalog No.:BCC2464
CAS No.:78111-17-8
- Aztreonam
Catalog No.:BCC2557
CAS No.:78110-38-0
- Ecliptasaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN3843
CAS No.:78285-90-2
- 7-Ethylcamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN2480
CAS No.:78287-27-1
- H-D-1-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3281
CAS No.:78306-92-0
- MRK 016
Catalog No.:BCC6070
CAS No.:783331-24-8
- MLN120B
Catalog No.:BCC1772
CAS No.:783348-36-7
- PCI-24781 (CRA-024781)
Catalog No.:BCC2155
CAS No.:783355-60-2
- Nocamycin I
Catalog No.:BCN1845
CAS No.:78339-49-8
- Pyranojacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN7429
CAS No.:78343-62-1
- MY-5445
Catalog No.:BCC6645
CAS No.:78351-75-4
- 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7523
CAS No.:78405-33-1
- Milrinone
Catalog No.:BCC4374
CAS No.:78415-72-2
- Trequinsin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7333
CAS No.:78416-81-6
Comparison of the efficacy and patients' tolerability of Nepafenac and Ketorolac in the treatment of ocular inflammation following cataract surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.[Pubmed:28253334]
PLoS One. 2017 Mar 2;12(3):e0173254.
As a new ophthalmic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with prodrug structure, Nepafenac was supposed to have a better efficacy than conventional NSAIDs both in patients' tolerability and ocular inflammation associated with cataract surgery. However, many current studies reached contradictory conclusions on the superiority of Nepafenac over Ketorolac. The objective of our study is to evaluate the efficacy and patients' tolerability of Nepafenac and Ketorolac following cataract surgery. To clarify this, we conducted a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eleven articles were included in this study. The dataset consisted of 1165 patients, including 1175 cataract surgeries. Among them, 574 patients were in the Nepafenac group and 591 in the Ketorolac group. Our analysis indicated that these two drugs were equally effective in controlling post cataract surgery ocular inflammation, reducing macular edema, achieving a better visual ability and maintaining intraoperative mydriasis during cataract surgery. However, Nepafenac was more effective than Ketorolac in reducing the incidence of postoperative conjunctival hyperemia and ocular discomfort. This meta-analysis indicated that topical Nepafenac is superior to Ketorolac in patients' tolerability following cataract surgery. However, these two drugs are equally desirable in the management of anterior chamber inflammation, visual rehabilitation and intraoperative mydriasis. Given the limitations in our study, more researches with larger sample sizes and focused on more specific indicators such as peak aqueous concentrations of drugs or PEG2 levels are required to reach a firmer conclusion.
Nepafenac 0.3% after Cataract Surgery in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: Results of 2 Randomized Phase 3 Studies.[Pubmed:28268098]
Ophthalmology. 2017 Jun;124(6):776-785.
PURPOSE: To demonstrate the efficacy and safety of once-daily Nepafenac 0.3% ophthalmic suspension versus vehicle, based on clinical outcomes, after cataract surgery in patients with diabetes. DESIGN: Two prospective, randomized, multicenter, double-masked, vehicle-controlled phase 3 studies. PARTICIPANTS: Total, 615 patients in study 1 and 605 patients in study 2. METHODS: Patients were randomized (1:1) to topical Nepafenac 0.3% or vehicle once-daily starting the day before surgery and continuing for 90 days thereafter. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: Key efficacy variables were: patients (%) in whom macular edema (ME) developed (>/=30% increase from preoperative baseline central subfield macular thickness) within 90 days after cataract surgery and the patients (%) with a best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) improvement of >/=15 letters from preoperative baseline through day 14 maintained through day 90. Secondary end points included: patients (%) with a BCVA improvement of >/=15 letters from preoperative baseline through days 90 and 60 and safety over 3 months. RESULTS: A significantly lower percentage of patients demonstrated ME within 90 days after surgery with Nepafenac 0.3% versus vehicle (study 1: 2.3% vs. 17.3%; P < 0.001; study 2: 5.9% vs. 14.3%; P = 0.001; pooled: 4.1% vs. 15.9%; P < 0.001). The percentage of patients achieving a >/=15-letter improvement from baseline through day 14 maintained through day 90 with Nepafenac 0.3% versus vehicle was 61.7% versus 43.0% (P < 0.001) in study 1, 48.8% versus 50.5% (P = 0.671) in study 2, and 55.4% versus 46.7% (P = 0.003) in the pooled analysis. A greater percentage of patients treated with Nepafenac 0.3% versus vehicle in study 1 and similar percentage in study 2 had a BCVA improvement of >/=15 letters from preoperative baseline through day 90 (77.2% vs. 67.7% [P = 0.009] and 65.4% vs. 65.9% [P = 0.888]) and through day 60 (76.2% vs. 64.7% [P = 0.002] and 68.9% vs. 62.1% [P = 0.092]). No unanticipated adverse events were observed. CONCLUSIONS: These studies demonstrated the clinical benefits of Nepafenac 0.3% over vehicle in reducing the risk of postoperative ME, with the integrated analysis showing improved BCVA after cataract surgery in patients with diabetic retinopathy, with no unanticipated safety events.
Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema prevention and risk factors; prospective study with adjunctive once daily topical nepafenac 0.3% versus placebo.[Pubmed:28219426]
BMC Ophthalmol. 2017 Feb 20;17(1):16.
BACKGROUND: Define the effectiveness of a topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) added to topical steroid use after uncomplicated phacoemulsification for the prevention of pseudophakic cystoid macular edema (PCME) using a prospective, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled clinical study. METHODS: Eyes (1000) were randomized to placebo (497) or Nepafenac 0.3% (503) used once daily, post-operatively for 5 weeks at two ophthalmology clinics. Diagnosis of PCME was made by clinical, ocular coherence tomography (OCT), and with fluorescein angiography confirmation. Correlation of PCME to NSAID use and the presence of pre-operative risk factors for PCME were assessed including, contralateral PCME, diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, macular hole, epiretinal membrane, macular degeneration, retinal detachment repair, and prostaglandin use. RESULTS: PCME was the most common complication associated with routine cataract surgery (4.2% with PCME risk factors, 2.0% with risk factors excluded). Topical Nepafenac 0.3% significantly reduces the incidence of PCME compared to placebo when used after routine cataract surgery (p = .0001). When patients with pre-operative risk factors are excluded, the incidence of PCME between treatment and placebo groups is equivalent (p = 0.31). PCME relative risk (RR) was most significant in contralateral PCME (RR 19.5), diabetic retinopathy (RR 13.1), retinal vein occlusion (RR 12.9), macular hole (RR 7.7), and epiretinal membrane (RR 5.7). Prostaglandin use and previous retinal detachment were not shown to increase risk. CONCLUSION: Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema is common after phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Topical Nepafenac 0.3% reduces PCME in patients with pre-operative risk factors for PCME compared to placebo but shows no benefit in patients without pre-operative risk factors. TRIAL REGISTRATION: NIH ClincalTrials.gov retrospectively registered January 15, 2017, NCT03025945 .
Effect of topical nepafenac in prevention of macular edema after cataract surgery in patients with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy.[Pubmed:28367202]
Pak J Med Sci. 2017 Jan-Feb;33(1):210-214.
OBJECTIVE: To determine the efficacy of topical Nepafenac (0.1%), administered post-operatively in prevention of Macular Edema (ME), after cataract surgery in patients with Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR). METHODS: This randomized control trial was conducted at Armed Forces Institute of Ophthalmology (AFIO), Rawalpindi from Sep 2015 to Sep 2016. Sixty eyes of 60 patients with NPDR underwent phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation. Group 1 received 0.1% Nepafenac, 8-hourly, in operated eye after cataract surgery for three months, along with routine post-operative medications. Group-2 received only routine post-operative medications. ME was defined as increase in Central Macular Thickness (CMT) of >10% from pre-operative baseline, measured using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. RESULTS: Mean age of study population was 60.97+/-4.91 years. Out of 60 patients, 34 (56.7%) were males and 24 (43.3%) were females. Mean pre-operative CMT, 3 months post-operative CMT, mean change in CMT and mean frequency change in CMT of Group-1 was 226.5+/-10.86microm, 228.83+/-14.56 microm, 2.33+/-10.45 microm and 1.05% respectively. Mean pre-operative CMT, three months post-operative CMT, mean change in CMT and mean frequency change in CMT in Group-2 was 223.93+/-11.69microm, 236.17+/-16.16 microm, 12.23+/-12.40microm and 5.51% respectively. ME was observed in one patient (3.3%) in Group-1, and seven patients (23.3%) in Group 2. The difference of mean change in CMT and frequency change in CMT between groups was statistically significant (p<0.05). CONCLUSION: 0.1% topical Nepafenac is effective in prevention of macular edema after cataract surgery in patients with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR).


