Tubastatin A HClHDAC6 inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 1310693-92-5 |
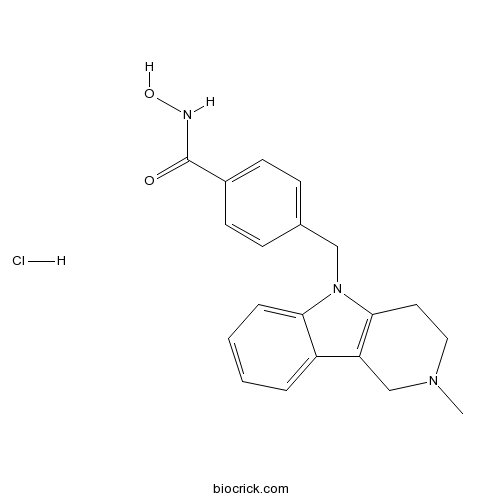
- Tubastatin A
Catalog No.:BCC2158
CAS No.:1252003-15-8
- Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)
Catalog No.:BCC2144
CAS No.:1316214-52-4
- Nexturastat A
Catalog No.:BCC5345
CAS No.:1403783-31-2
- Tubacin
Catalog No.:BCC2428
CAS No.:537049-40-4
- MC1568
Catalog No.:BCC2151
CAS No.:852475-26-4
- Resminostat (RAS2410)
Catalog No.:BCC2165
CAS No.:864814-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1310693-92-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 57336514 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H22ClN3O2 | M.Wt | 371.86 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Tubastatin A HCl; TSA HCl | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 10.8 mg/mL (29.04 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | N-hydroxy-4-[(2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-pyrido[4,3-b]indol-5-yl)methyl]benzamide;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=C(C1)C3=CC=CC=C3N2CC4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NO.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LJTSJTWIMOGKRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H21N3O2.ClH/c1-22-11-10-19-17(13-22)16-4-2-3-5-18(16)23(19)12-14-6-8-15(9-7-14)20(24)21-25;/h2-9,25H,10-13H2,1H3,(H,21,24);1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tubastatin A HCl is a potent and selective inhibitor of HDAC6 with IC50 of 15 nM. It is selective (1000-fold more) against all other isozymes except HDAC8 (57-fold more). | |||||
| Targets | HDAC6 | HDAC8 | ||||
| IC50 | 15 nM | 854 nM | ||||

Tubastatin A HCl Dilution Calculator

Tubastatin A HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6892 mL | 13.4459 mL | 26.8918 mL | 53.7837 mL | 67.2296 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5378 mL | 2.6892 mL | 5.3784 mL | 10.7567 mL | 13.4459 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2689 mL | 1.3446 mL | 2.6892 mL | 5.3784 mL | 6.723 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0538 mL | 0.2689 mL | 0.5378 mL | 1.0757 mL | 1.3446 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1345 mL | 0.2689 mL | 0.5378 mL | 0.6723 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Tubastatin A HCl is a selective inhibitor of HDAC6 with IC50 value of 15 nM [1].
HDAC6 (histone deacetylase 6) is an enzyme and plays an important role in a variety of processes, including transcriptional regulation, cell cycle preogression and developmental events. Abnormal expression of HDAC6 is correlated with many kinds of diseases, including Alzheimer's disease and cancers [1].
Tubastatin A HCl is a potent HDAC6 inhibitor and has the most selective compared with other HDAC isoforms. When tested with primary cortical neuron cells, Tubastatin A HCl treatment protected HCA-induced neuronal cell death in a dose range from 5 μM to 10 μM [1]. In HaCaT cells, administration of Tubastatin A HCl prevented sodium arsenite from inducing association of Nrf2 mRNA with ribosomes and elevation of Nrf2 protein by selectively inhibitng HDAC6 activity and had no effect on other HDACs [2]. Using atomic force microscopy study, Ketene AN et al. revealed that Tubastatin A HCl increased cell elasticity by inhibiting HDAC6 [3].
References:
[1]. Kyle V. Butler, Jay Kalin, Camille Brochier, et al. Rational Design and Simple Chemistry Yield a Superior, Neuroprotective HDAC6 Inhibitor, Tubastatin A [J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132 (31), pp 10842–10846.
[2]. Kappeler KV, Zhang J, Dinh TN, et al. Histone deacetylase 6 associates with ribosomes and regulates de novo protein translation during arsenite stress [J]. Toxicol Sci. 2012 May;127(1):246-255.
[3]. Ketene AN, Roberts PC, Shea AA, et al. Actin filaments play a primary role for structural integrity and viscoelastic response in cells [J]. Integr Biol (Camb). 2012 May;4(5):540-549.
- NB-598
Catalog No.:BCC1786
CAS No.:131060-14-5
- GNF179 Metabolite
Catalog No.:BCC5176
CAS No.:1310455-86-7
- Boldenone undecylenate
Catalog No.:BCC8896
CAS No.:13103-34-9
- 8-Epiloganic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8956
CAS No.:82509-41-9
- Meptyldinocap
Catalog No.:BCC5468
CAS No.:131-72-6
- Oxybenzone
Catalog No.:BCC5445
CAS No.:131-57-7
- N-Acetylneuraminic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2204
CAS No.:131-48-6
- Pimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN6168
CAS No.:131-12-4
- Dimethyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN6167
CAS No.:131-11-3
- alpha-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN6166
CAS No.:131-03-3
- VU 0360172 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6141
CAS No.:1309976-62-2
- 15-Methoxymkapwanin
Catalog No.:BCN6498
CAS No.:1309920-99-7
- NVP-BGJ398 phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1814
CAS No.:1310746-10-1
- Miltipolone
Catalog No.:BCN3222
CAS No.:131086-61-8
- 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6592
CAS No.:131123-76-7
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- mGlu2 agonist
Catalog No.:BCC1745
CAS No.:1311385-32-6
- Sodium Demethylcantharidate
Catalog No.:BCN8394
CAS No.:13114-29-9
- NSC 624206
Catalog No.:BCC7988
CAS No.:13116-77-3
- Cornuside
Catalog No.:BCN5007
CAS No.:131189-57-6
- PF 5081090
Catalog No.:BCC6148
CAS No.:1312473-63-4
- Antibiotic PF 1018
Catalog No.:BCN2149
CAS No.:131256-42-3
- Scutebarbatine W
Catalog No.:BCN7011
CAS No.:1312716-25-8
- Scutebarbatine X
Catalog No.:BCN6997
CAS No.:1312716-26-9
Therapeutic effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in a murine asthma model.[Pubmed:27565183]
Inflamm Res. 2016 Dec;65(12):995-1008.
OBJECTIVE AND DESIGN: To investigate the therapeutic effects of various HDAC inhibitors on the development of chronic allergic airway disease in mice with airway inflammation, airway remodeling, and airway hyperresponsiveness. SUBJECTS: Wild-type BALB/C mice (N = 72). TREATMENT: Tubastatin A HCl [TSA, a selective histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) inhibitor], PCI-34051 (a selective HDAC8 inhibitor), and givinostat (a broad-spectrum HDAC inhibitor that inhibits class I and class II HDACs and several pro-inflammatory cytokines). METHODS: Mice were divided into six groups: control, asthma, dexamethasone (positive control), TSA, PCI-34051, and givinostat (n = 12 per group). Twenty-four hours after OVA nebulization, airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and remodeling were assessed. RESULTS: The chronic asthma mouse model produced typical airway inflammation, airway remodeling, and airway hyperresponsiveness. Administration of PCI-34051 and dexamethasone reduced the eosinophilic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma to reduce the airway remodeling. Treatment with Tubastatin A HCl reduced airway inflammation and was associated with decreased IL-4, IL-5 and total inflammatory cell count, as well as goblet cell metaplasia and subepithelial fibrosis; however, this outcome was not as effective as that with dexamethasone. TGF-beta1 expression in the cytoplasm of airway epithelium of mice in the Tubastatin A HCl group was reduced and expression of alpha-SMA in the airway smooth muscle was also decreased. CONCLUSIONS: The results suggested that treatment with HDAC inhibitors can reduce airway inflammation, airway remodeling, and airway hyperresponsiveness in chronic allergic airway disease in mice.
[Therapeutic effects of Tubastatin A Hcl on airway inflammation in acute mice asthma model].[Pubmed:28648015]
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 27;97(24):1888-1892.
Objective: To investigated the therapeutic effects of Tubastatin A HCl, a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, on airway inflammation in acute mice bronchial asthma (asthma) model. Methods: A total of 48 BALB/C mice were randomly divided into control group, asthma group, dexamethasone group and Tubastatin A HCl group with 12 mice in each group. Then the airway hyperresponsiveness was assessed in each group; total cell number, different cell number, levels of Interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5 and Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were detected; the lung tissues of each group were stained with HE to observe the inflammatory cells infiltration. AB-PAS was used to observe the goblet cell metaplasia in tracheal epithelium. Masson staining was used to observe the collagen deposition in lung tissue. Results: The airway reactivity in Tubastatin A HCl group was significantly lower than that in asthma group [(4.18+/-0.94) vs (6.02+/-0.47), P<0.05]; in the Tubastatin A HCl group, the total inflammatory cells [(57.0+/-5.7)x10(4)/ml vs (87.0+/-5.6)x10(4)/ml], eosinophil cells [(6.8+/-1.7)x10(4)/ml vs (12.3+/-3.5)x10(4)/ml] and levels of IL-4 [(19.3+/-2.7) vs (26.2+/-3.2)ng/ml] in BALF were obviously lower than those of asthma group (all P<0.05); IL-5 in Tubastatin A HCl group was lower and IFN-gamma was higher than that of asthma group, while there were no significant differences (both P>0.05). The degree of inflammatory cells infiltrations around the airway and vascular, number of inflammatory cells [(9.80+/-2.42) vs (20.67+/-7.53)], score of inflammation [(2.20+/-0.70) vs (3.60+/-0.68) points, ], and percentage of goblet cell metaplasia [(50.46+/-5.03)% vs (71.06+/-5.38)%] in the lung tissue of Tubastatin A HCl group were lower than that of asthma group (all P<0.05). Although collagen deposition in the lung tissue of Tubastatin A HCl group was lower than asthma group, there were no significant differences (P>0.05). However, all of the above results in the dexamethasone group were slightly better than Tubastatin A HCl group, which had no significant differences (P>0.05). Conclusion: Tubastatin A HCl can effectively alleviate the level of airway inflammation in acute asthma, but its anti-inflammatory effect is limited, which is not as significant as dexamethasone.


