NVP-BGJ398 phosphateFGFR inhibitor CAS# 1310746-10-1 |
- SKLB610
Catalog No.:BCC3647
CAS No.:1125780-41-7
- AP26113
Catalog No.:BCC1069
CAS No.:1197958-12-5
- Pazopanib (GW-786034)
Catalog No.:BCC1286
CAS No.:444731-52-6
- Danusertib (PHA-739358)
Catalog No.:BCC2172
CAS No.:827318-97-8
- BGJ398
Catalog No.:BCC1278
CAS No.:872511-34-7
- Ponatinib (AP24534)
Catalog No.:BCC2522
CAS No.:943319-70-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1310746-10-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 56669626 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H34Cl2N7O7P | M.Wt | 658.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Infigratinib phosphate; BGJ-398 phosphate | ||
| Solubility | ≥95.7mg/ml in DMSO | ||
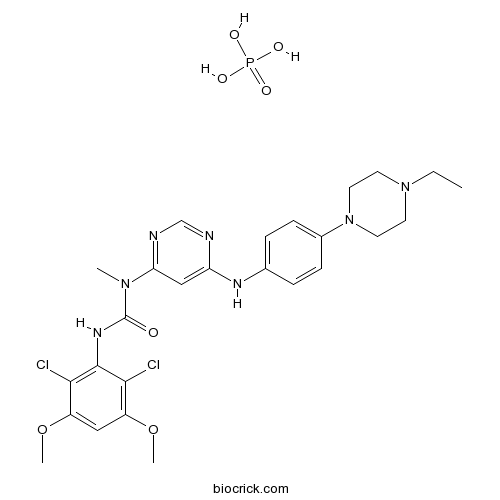
| Chemical Name | 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-[6-[4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-methylurea;phosphoric acid | ||
| SMILES | CCN1CCN(CC1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)NC3=CC(=NC=N3)N(C)C(=O)NC4=C(C(=CC(=C4Cl)OC)OC)Cl.OP(=O)(O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GUQNHCGYHLSITB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H31Cl2N7O3.H3O4P/c1-5-34-10-12-35(13-11-34)18-8-6-17(7-9-18)31-21-15-22(30-16-29-21)33(2)26(36)32-25-23(27)19(37-3)14-20(38-4)24(25)28;1-5(2,3)4/h6-9,14-16H,5,10-13H2,1-4H3,(H,32,36)(H,29,30,31);(H3,1,2,3,4) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | NVP-BGJ398 phosphate is a potent inhibitor of the FGFR family with IC50 of 0.9 nM, 1.4 nM, 1 nM, and 60 nM for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4, respectively.In Vitro:NVP-BGJ398 inhibits FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 with IC50=~1 nM, FGFR3K650E with IC50=4.9 nM, and FGFR4 with IC50=60 nM. IC50 values for all other kinases are in the μM range (FYN, LCK, YES, and ABL, IC50=1.9, 2.5, 1.1, and 2.3 μM, respectively) except for VEGFR2, KIT, and LYN, which are inhibited at submicromolar concentrations (IC50=0.18, 0.75, and 0.3 μM, respectively). NVP-BGJ398 inhibits the proliferation of the FGFR1-, FGFR2-, and FGFR3-dependent BaF3 cells with IC50 values which are in the low nanomolar range and comparable to those observed for the inhibition of the receptors kinase activity in the enzymatic assay. For the remaining cells, all IC50 values are greater than 1.5 μM except for VEGFR2 (IC50 1449 and 938 nM), for which there is at least a 400-fold selectivity versus FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3[1]. NVP-BGJ398 (ranging between 1 nM and 10 μM) is potent at inhibiting cell growth of FGFR2-mutant endometrial cancer cells[2].In Vivo:NVP-BGJ398 is administered to athymic nude mice implanted subcutaneously with RT112/luc1 tumors: either as a 5 mg/kg intravenous bolus in NMP/PEG200 (1:9, v/v) or orally by gavage as a suspension in PEG300/D5W (2:1, v/v) at a 20 mg/kg dose. The relevant pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters indicate that the oral bioavailability of NVP-BGJ398 in this study is 32%. After intravenous dosing, NVP-BGJ398 shows a rapid distribution from the vascular compartment into the peripheral tissues, translating into a high volume of distribution (26 L/kg). The plasma clearance is high at 3.3 L/h/kg (61% of liver blood flow). The ratio of tumor to plasma after oral dosing based on AUC is determined to be 10[1]. NVP-BGJ398 (30 mg/kg) significantly inhibits the growth of FGFR2-mutated endometrial cancer xenograft models[2]. References: | |||||

NVP-BGJ398 phosphate Dilution Calculator

NVP-BGJ398 phosphate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5187 mL | 7.5934 mL | 15.1867 mL | 30.3734 mL | 37.9668 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3037 mL | 1.5187 mL | 3.0373 mL | 6.0747 mL | 7.5934 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1519 mL | 0.7593 mL | 1.5187 mL | 3.0373 mL | 3.7967 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0304 mL | 0.1519 mL | 0.3037 mL | 0.6075 mL | 0.7593 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0152 mL | 0.0759 mL | 0.1519 mL | 0.3037 mL | 0.3797 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Description: IC50 Value: 0.9 nM (FGFR1); 1.4 nM (FGFR2); 1 nM (FGFR2) [1] NVP-BGJ398 is a novel selective, pan-specific FGFR inhibitor currently in Phase I clinical trials for cancer therapy. in vitro: NVP-BGJ398 is a novel and selective fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor. NVP-BGJ398 inhibit FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 with IC50 of 0.9 nM, 1.4 nM and 1 nM. NVP-BGJ398 inhibited FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 with single digit nmol/L IC50 in biochemical and cellular autophosphorylation assays and FGFR4 with 38- to 60-fold lower potency. NVP-BGJ398 significantly inhibits proliferation of cancer cell lines bearing FGF/FGFR genetic alterations across various cancer types.Among the 35 cell lines selected from the high-throughput assays, 28 were confirmed as sensitive to NVP-BGJ398 with IC50s ranging from 0.001 to 500 nM. Cancer cell lines harboring FGF19 copy number gain at the 11q13 amplicon are sensitive to NVP-BGJ398 only when concomitant expression of beta-klotho occurs [1]. Cell lines with activating FGFR2 mutations (S252W, N550K) were more sensitive to dovitinib or NVP-BGJ398 when compared with their FGFR2 wild-type counterparts (P = 0.073 and P = 0.021, respectively). Both agents inhibited FGFR2 signaling, induced cell-cycle arrest, and significantly increased apoptosis in FGFR2-mutant lines. In vitro, dovitinib and NVP-BGJ398 were both potent at inhibiting cell growth of FGFR2-mutant endometrial cancer cells, but the activity of dovitinib was less restricted to FGFR2-mutant lines when compared with NVP-BGJ398 [2]. in vivo: In tumor tissues from primary tumor model GAM033 treated with 15 mg/kg NVP-BGJ398, NVP-BGJ398 shows inhibition to FGFR and ERK1/2 [1].NVP-BGJ398 significantly inhibited the growth of FGFR2-mutated endometrial cancer xenograft models [2]. Toxicity: N/A Clinical trial: Phase 1
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- NB-598
Catalog No.:BCC1786
CAS No.:131060-14-5
- GNF179 Metabolite
Catalog No.:BCC5176
CAS No.:1310455-86-7
- Boldenone undecylenate
Catalog No.:BCC8896
CAS No.:13103-34-9
- 8-Epiloganic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8956
CAS No.:82509-41-9
- Meptyldinocap
Catalog No.:BCC5468
CAS No.:131-72-6
- Oxybenzone
Catalog No.:BCC5445
CAS No.:131-57-7
- N-Acetylneuraminic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2204
CAS No.:131-48-6
- Pimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN6168
CAS No.:131-12-4
- Dimethyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN6167
CAS No.:131-11-3
- alpha-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN6166
CAS No.:131-03-3
- VU 0360172 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6141
CAS No.:1309976-62-2
- Miltipolone
Catalog No.:BCN3222
CAS No.:131086-61-8
- 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6592
CAS No.:131123-76-7
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- mGlu2 agonist
Catalog No.:BCC1745
CAS No.:1311385-32-6
- Sodium Demethylcantharidate
Catalog No.:BCN8394
CAS No.:13114-29-9
- NSC 624206
Catalog No.:BCC7988
CAS No.:13116-77-3
- Cornuside
Catalog No.:BCN5007
CAS No.:131189-57-6
- PF 5081090
Catalog No.:BCC6148
CAS No.:1312473-63-4
- Antibiotic PF 1018
Catalog No.:BCN2149
CAS No.:131256-42-3
- Scutebarbatine W
Catalog No.:BCN7011
CAS No.:1312716-25-8
- Scutebarbatine X
Catalog No.:BCN6997
CAS No.:1312716-26-9
- Scutebarbatine Y
Catalog No.:BCN6994
CAS No.:1312716-27-0
FGF23 is elevated in multiple myeloma and increases heparanase expression by tumor cells.[Pubmed:25944690]
Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 14;6(23):19647-60.
Multiply myeloma (MM) grows in and destroys bone, where osteocytes secrete FGF23, a hormone which affects phosphate homeostasis and aging. We report that multiple myeloma (MM) cells express receptors for and respond to FGF23. FGF23 increased mRNA for EGR1 and its target heparanase, a pro-osteolytic factor in MM. FGF23 signals through a complex of klotho and a classical FGF receptor (FGFR); both were expressed by MM cell lines and patient samples. Bone marrow plasma cells from 42 MM patients stained positively for klotho, while plasma cells from 8 patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and 6 controls were negative. Intact, active FGF23 was increased 2.9X in sera of MM patients compared to controls. FGF23 was not expressed by human MM cells, but co-culture with mouse bone increased its mRNA. The FGFR inhibitor NVP-BGJ398 blocked the heparanase response to FGF23. NVP-BGJ398 did not inhibit 8226 growth in vitro but significantly suppressed growth in bone and induction of the osteoclast regulator RANK ligand, while decreasing heparanase mRNA. The bone microenvironment provides resistance to some anti-tumor drugs but increased the activity of NVP-BGJ398 against 8226 cells. The FGF23/klotho/heparanase signaling axis may offer targets for treatment of MM in bone.
FGFR Inhibitor Ameliorates Hypophosphatemia and Impaired Engrailed-1/Wnt Signaling in FGF2 High Molecular Weight Isoform Transgenic Mice.[Pubmed:26762209]
J Cell Biochem. 2016 Sep;117(9):1991-2000.
High molecular weight FGF2 transgenic (HMWTg) mouse phenocopies the Hyp mouse, homolog of human X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets with hypophosphatemis, and abnormal FGF23, FGFR, Klotho signaling in kidney. Since abnormal Wnt signaling was reported in Hyp mice we assessed whether Wnt signaling was impaired in HMWTg kidneys and the effect of blocking FGF receptor (FGFR) signaling. Bone mineral density and bone mineral content in female HMWTg mice were significantly reduced. HMWTg mice were gavaged with FGFR inhibitor NVP-BGJ398, or vehicle and were euthanized 24 h post treatment. Serum phosphate was significantly reduced and urine phosphate was significantly increased in HMWTg and was rescued by NVP-BGJ398. Analysis of kidneys revealed a significant reduction in Npt2a mRNA in HMWTg that was significantly increased by NVP-BGJ398. Increased FGFR1, KLOTHO, P-ERK1/2, and decreased NPT2a protein in HMWTg were rescued by NVP-BGJ398. Wnt inhibitor Engrailed-1 mRNA and protein was increased in HMWTg and was decreased by BGJ398. Akt mRNA and protein was decreased in HMWTg and was increased by NVP-BGJ398. The active form of glycogen synthase 3 beta (pGSK3-beta) and phosphor-beta-catenin were increased in HMWTg and were both decreased by NVP-BGJ398 while decreased active-beta-catenin in HMWTg was increased by NVP-BGJ398. We conclude that FGFR blockade rescued hypophosphatemia by regulating FGF and WNT signaling in HMWTg kidneys. J. Cell. Biochem. 117: 1991-2000, 2016. (c) 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Inhibition of FGFR Signaling Partially Rescues Hypophosphatemic Rickets in HMWFGF2 Tg Male Mice.[Pubmed:28938491]
Endocrinology. 2017 Oct 1;158(10):3629-3646.
Transgenic mice harboring high molecular weight fibroblast growth factor (FGF)2 isoforms (HMWTg) in osteoblast lineage cells phenocopy human X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH) and Hyp murine model of XLH demonstrating increased FGF23/FGF receptor signaling and hypophosphatemic rickets. Because HMWFGF2 was upregulated in bones of Hyp mice and abnormal FGF receptor (FGFR) signaling is important in XLH, HMWTg mice were used to examine the effect of the FGFR inhibitor NVP-BGJ398, now in clinical trials for cancer therapy, on hypophosphatemic rickets. Short-term treatment with NVP-BGJ398 rescued abnormal FGFR signaling and hypophosphatemia in HMWTg. Long-term treatment with NVP-BGJ398 normalized tail, tibia, and femur length. Four weeks NVP-BGJ398 treatment significantly increased total body bone mineral density (BMD) and bone mineral content (BMC) in HMWTg mice; however, at 8 weeks, total body BMD and BMC was indistinguishable among groups. Micro-computed tomography revealed decreased vertebral bone volume, trabecular number, and increased trabecular spacing, whereas femur trabecular tissue density was increased; however, NVP-BGJ398 rescued defective cortical bone mineralization, increased thickness, reduced porosity, and increased endosteal perimeter and cortical tissue density in HMWTg. NVP-BGJ398 improved femur cancellous bone, cortical bone structure, growth plate, and double labeling in cortical bone and also increased femur trabeculae double labeled surface, mineral apposition rate, bone formation rate, and osteoclast number and surface in HMWTg. The decreased NPT2a protein that is important for renal phosphate excretion was rescued by NVP-BGJ398 treatment. We conclude that NVP-BGJ398 partially rescued hypophosphatemic rickets in HMWTg. However, long-term treatment with NVP-BGJ398 further increased serum FGF23 that could exacerbate the mineralization defect.
Pharmacological inhibition of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor signaling ameliorates FGF23-mediated hypophosphatemic rickets.[Pubmed:23129509]
J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Apr;28(4):899-911.
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a circulating factor secreted by osteocytes that is essential for phosphate homeostasis. In kidney proximal tubular cells FGF23 inhibits phosphate reabsorption and leads to decreased synthesis and enhanced catabolism of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25[OH]2 D3 ). Excess levels of FGF23 cause renal phosphate wasting and suppression of circulating 1,25(OH)2 D3 levels and are associated with several hereditary hypophosphatemic disorders with skeletal abnormalities, including X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH) and autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets (ARHR). Currently, therapeutic approaches to these diseases are limited to treatment with activated vitamin D analogues and phosphate supplementation, often merely resulting in partial correction of the skeletal aberrations. In this study, we evaluate the use of FGFR inhibitors for the treatment of FGF23-mediated hypophosphatemic disorders using NVP-BGJ398, a novel selective, pan-specific FGFR inhibitor currently in Phase I clinical trials for cancer therapy. In two different hypophosphatemic mouse models, Hyp and Dmp1-null mice, resembling the human diseases XLH and ARHR, we find that pharmacological inhibition of FGFRs efficiently abrogates aberrant FGF23 signaling and normalizes the hypophosphatemic and hypocalcemic conditions of these mice. Correspondingly, long-term FGFR inhibition in Hyp mice leads to enhanced bone growth, increased mineralization, and reorganization of the disturbed growth plate structure. We therefore propose NVP-BGJ398 treatment as a novel approach for the therapy of FGF23-mediated hypophosphatemic diseases.


