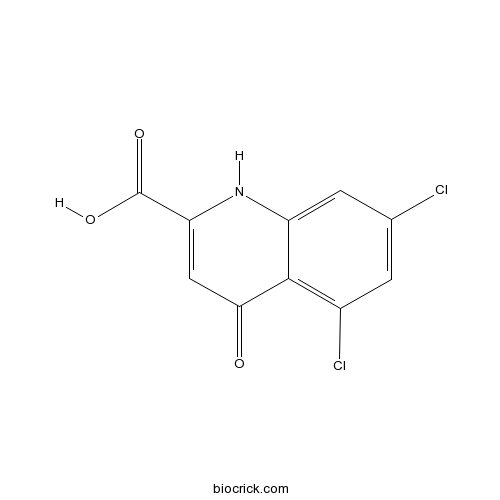
5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acidCAS# 131123-76-7 |
- Verteporfin
Catalog No.:BCC3690
CAS No.:129497-78-5
- Miglustat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5186
CAS No.:210110-90-0
- Hydrochlorothiazide
Catalog No.:BCC4786
CAS No.:58-93-5
- Miglustat
Catalog No.:BCC5187
CAS No.:72599-27-0
- TPT-260
Catalog No.:BCC5171
CAS No.:769856-81-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 131123-76-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1779 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H5Cl2NO3 | M.Wt | 258.06 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. NaOH and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dichloro-4-oxo-1H-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(C=C2C(=C1Cl)C(=O)C=C(N2)C(=O)O)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BGKFPRIGXAVYNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H5Cl2NO3/c11-4-1-5(12)9-6(2-4)13-7(10(15)16)3-8(9)14/h1-3H,(H,13,14)(H,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent antagonist at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor (Ki = 79 nM vs. [3H]-glycine). Sodium salt also available. |

5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid Dilution Calculator

5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8751 mL | 19.3753 mL | 38.7507 mL | 77.5014 mL | 96.8767 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.775 mL | 3.8751 mL | 7.7501 mL | 15.5003 mL | 19.3753 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3875 mL | 1.9375 mL | 3.8751 mL | 7.7501 mL | 9.6877 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0775 mL | 0.3875 mL | 0.775 mL | 1.55 mL | 1.9375 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0388 mL | 0.1938 mL | 0.3875 mL | 0.775 mL | 0.9688 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Miltipolone
Catalog No.:BCN3222
CAS No.:131086-61-8
- NVP-BGJ398 phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1814
CAS No.:1310746-10-1
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- NB-598
Catalog No.:BCC1786
CAS No.:131060-14-5
- GNF179 Metabolite
Catalog No.:BCC5176
CAS No.:1310455-86-7
- Boldenone undecylenate
Catalog No.:BCC8896
CAS No.:13103-34-9
- 8-Epiloganic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8956
CAS No.:82509-41-9
- Meptyldinocap
Catalog No.:BCC5468
CAS No.:131-72-6
- Oxybenzone
Catalog No.:BCC5445
CAS No.:131-57-7
- N-Acetylneuraminic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2204
CAS No.:131-48-6
- Pimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN6168
CAS No.:131-12-4
- Dimethyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN6167
CAS No.:131-11-3
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- mGlu2 agonist
Catalog No.:BCC1745
CAS No.:1311385-32-6
- Sodium Demethylcantharidate
Catalog No.:BCN8394
CAS No.:13114-29-9
- NSC 624206
Catalog No.:BCC7988
CAS No.:13116-77-3
- Cornuside
Catalog No.:BCN5007
CAS No.:131189-57-6
- PF 5081090
Catalog No.:BCC6148
CAS No.:1312473-63-4
- Antibiotic PF 1018
Catalog No.:BCN2149
CAS No.:131256-42-3
- Scutebarbatine W
Catalog No.:BCN7011
CAS No.:1312716-25-8
- Scutebarbatine X
Catalog No.:BCN6997
CAS No.:1312716-26-9
- Scutebarbatine Y
Catalog No.:BCN6994
CAS No.:1312716-27-0
- Scutebarbatine Z
Catalog No.:BCN6991
CAS No.:1312716-28-1
- Ro 25-6981 Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4159
CAS No.:1312991-76-6
Kynurenic acid and 5,7-dichlorokynurenic acids improve social and object recognition in male rats.[Pubmed:8539328]
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1995 Aug;120(4):463-9.
The present study describes the effect of kynurenic (KYNA) and 5,7-dichlorokynurenic (DCKA) acids, acting as selective antagonists at the glycine site on the NMDA receptor complex, upon short-term memory of male rats. Oxiracetam (OXIR) or pramiracetam (PRAM) were used as reference compounds. In the social recognition test, adult animals were injected SC with a drug or vehicle immediately after the first exposure to a juvenile male, 21-24 days old, and reexposed to the same or a novel juvenile 120 min later. Time spent by adults in social investigation of juveniles was measured. Animals treated with KYNA or DCKA (0.3, 3 and 30 mg/kg in both cases) and OXIR (30 and 60 mg/kg) had significantly reduced investigation time when reexposed to the same juvenile as compared to controls. No reduction of investigation time was found in those drugged animals reexposed to a novel juvenile. The findings suggest that KYNA and DCKA improved retention of memory for olfactory stimuli in adult male rats. In the object recognition test, the duration of exploration of two identical objects during the sample trial and the familiar and a new object during the choice trial, performed 60 min later, was evaluated. Drugs or vehicles were administered SC 30 min prior to the sample trial. On choice one, animals treated with KYNA or DCKA (0.6 and 30 mg/kg in both cases) and PRAM (30 mg/kg) spent more time in exploring a new object than the familiar one as compared to controls. This suggests that the drugged animals were able to remember the familiar object.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Use of [3H]5,7 dichlorokynurenic acid to identify strychnine-insensitive glycine receptors in human postmortem brain.[Pubmed:7812798]
Brain Res Bull. 1994;35(3):205-9.
[3H]5,7 Dichlorokynurenic acid ([3H]DCKA) was used to define conditions for obtaining selective binding to strychnine-insensitive glycine receptors. The parameters were established in sections of human brain prior to localizing the receptors sites by autoradiography. The binding of [3H]DCKA was of high affinity (Kd = 14.5 nM), readily reversible (K-1 = 0.216 min-1), and specific (60% specific binding determined by inhibition with 100 microM glycine or D-serine). High levels of strychnine-insensitive glycine receptors were identified in several brain areas including portions of the cerebral cortex (Bmax in middle temporal gyrus: 174.0 fmol/mg tissue), basal ganglia, hippocampal formation, and midbrain. These results identify regions where glycine receptors may be involved in modulating NMDA-mediated channel activity.
Anticonvulsant activity of 4-urea-5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid derivatives that are antagonists at the NMDA-associated glycine binding site.[Pubmed:10343967]
Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1998 Aug-Dec;35(1-3):1-12.
Twelve 4-urea-5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid derivatives were synthesized by reacting the 4-tosylimino derivative of 5,7-dichlorokynurenate methyl ester first with triphosgene and then with a secondary amine. Compounds were screened in mice for anticonvulsant activity using maximal electroshock (MES), subcutaneous pentylenetetrazole (Met), and threshold tonic extension (TTE) tests. A rotorod test was used to determine neurotoxicity. Seven of the derivatives had anticonvulsant activity in TTE testing at 100 mg/kg. One compound, 2-methyl carboxylate-5,7-dichloro-4-([ inverted question markdiphenylamino inverted question mark-carbonyl]amino)-quino line, had an ED50 value of 134 mg/kg (95% conf. int.: low-78.5, high-205.7; slope 1.9, SE = 0.44) in TTE testing. Two derivatives had MES activity. Only one compound, an N,N-diethylamino derivative, was neurotoxic in the rotorod test. Compounds were screened at a 10-microM concentration for activity in displacing 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid from synaptosomal membrane fragments. Since 9 of the 12 compounds synthesized and tested have demonstrated anticonvulsant activity, this class of chemicals offers promise for the production of useful therapeutic agents.
[3H]5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid recognizes two binding sites in rat cerebral cortex membranes.[Pubmed:9651880]
J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 1998 Mar-May;18(2-3):91-112.
Binding of [3H]5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid ([3H]DCKA), a competitive antagonist of the strychnine-insensitive glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channel complex, was characterized in synaptic plasma membranes from rat cerebral cortex. Non linear curve fitting of [3H]DCKA saturation and homologous displacement isotherms indicated the existence of two binding sites: a specific, saturable, high affinity site, with a pKD value of 7.24 (KD = 57.5 nmol/l) and a maximum binding value (Bmax) of 6.9 pmol/mg of protein and a second site, with micromolar affinity. The pharmacological profile of both binding components was determined by studying the effect on [3H]DCKA and [3H]glycine binding of a series of compounds known to interact with different excitatory and inhibitory amino acid receptors. These studies confirmed the identity of the high affinity site of [3H]DCKA binding with the strychnine-insensitive glycine site of the NMDA receptor channel complex. 3-[2-(Phenylaminocarbonyl)ethenyl]-4,6-dichloroindole-2-carb oxylic acid sodium salt (GV 150526A), a new, high affinity, selective glycine site antagonist (1), was the most potent inhibitor of this component of binding (pKi = 8.24, Ki = 5.6 nmol/l). The low affinity component of [3H]DCKA binding was insensitive to the agonists glycine and D-serine and the partial agonist (+/-)-3-amino-1-hydroxy-2-pyrrolidone (HA 966), though recognised by glycine site antagonists. The precise nature of this second, low affinity [3H]DCKA binding site remains to be elucidated.
Activity of 5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid, a potent antagonist at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-associated glycine binding site.[Pubmed:2172769]
Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;38(4):554-61.
5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid (5,7-DCKA), one of the most potent excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists yet described, binds to a strychnine-insensitive glycine binding site located on the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex (Ki = 79 nM versus [3H]glycine). 5,7-DCKA (10 microM) antagonized the ability of NMDA to stimulate the binding of the radiolabeled ion channel blocker N-[3H][1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]-piperidine ([3]TCP). Glycine was able to overcome this effect and in the presence of 5,7-DCKA enhanced [3H]TCP binding to antagonist-free levels. 5,7-DCKA completely and noncompetitively antagonized several NMDA receptor-mediated biochemical and electrophysiological responses. Thus, micromolar concentrations of 5,7-DCKA inhibited NMDA-stimulated elevation of cytosolic calcium in cultured hippocampal neurons, cGMP accumulation in cerebellar slices, and norepinephrine release from hippocampal slices. The glycine antagonist could also block the action of synaptically released agonist, as shown by its ability to inhibit the increase in the magnitude of the population spike that follows tetanic stimulation of the hippocampus in vitro (long term potentiation). Inclusion of glycine or D-serine prevented all these effects of the antagonist. 5,7-DCKA was a potent anticonvulsant when administered intracerebroventricularly to mice. As in the in vitro experiments, the dose-response curve for the antagonist was shifted rightward in a parallel fashion when D-serine was coinjected. This spectrum of activity displayed by a compound acting at the glycine binding site suggests that the therapeutic utility of glycine antagonists will be similar to those proposed for other types of glutamate receptor antagonists.


