HydrochlorothiazideCAS# 58-93-5 |
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- Semagacestat (LY450139)
Catalog No.:BCC3610
CAS No.:425386-60-3
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 58-93-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3639 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H8ClN3O4S2 | M.Wt | 297.74 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | HCTZ | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (167.93 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
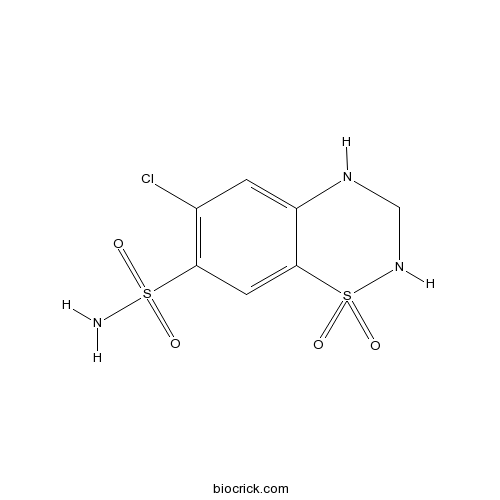
| Chemical Name | 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | C1NC2=CC(=C(C=C2S(=O)(=O)N1)S(=O)(=O)N)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JZUFKLXOESDKRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H8ClN3O4S2/c8-4-1-5-7(2-6(4)16(9,12)13)17(14,15)11-3-10-5/h1-2,10-11H,3H2,(H2,9,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic drug of the thiazide class.
Target: Others
Hydrochlorothiazide belongs to thiazide class of diuretics. It reduces blood volume by acting on the kidneys to reduce sodium (Na) reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. The major site of action in the nephron appears on an electroneutral Na+-Cl? co-transporter by competing for the chloride site on the transporter. By impairing Na transport in the distal convoluted tubule, hydrochlorothiazide induces a natriuresis and concomitant water loss. Thiazides increase the reabsorption of calcium in this segment in a manner unrelated to sodium transport. Additionally, by other mechanisms, Hydrochlorothiazide is believed to lower peripheral vascular resistance [1]. References: | |||||

Hydrochlorothiazide Dilution Calculator

Hydrochlorothiazide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3586 mL | 16.7932 mL | 33.5864 mL | 67.1727 mL | 83.9659 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6717 mL | 3.3586 mL | 6.7173 mL | 13.4345 mL | 16.7932 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3359 mL | 1.6793 mL | 3.3586 mL | 6.7173 mL | 8.3966 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0672 mL | 0.3359 mL | 0.6717 mL | 1.3435 mL | 1.6793 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0336 mL | 0.1679 mL | 0.3359 mL | 0.6717 mL | 0.8397 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic drug of the thiazide class.
- D-(+)-Xylose
Catalog No.:BCN1010
CAS No.:58-86-6
- Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3585
CAS No.:58-85-5
- Papaverine
Catalog No.:BCC8230
CAS No.:58-74-2
- Inosine
Catalog No.:BCN3841
CAS No.:58-63-9
- Adenosine
Catalog No.:BCN5796
CAS No.:58-61-7
- Puromycin aminonucleoside
Catalog No.:BCC1873
CAS No.:58-60-6
- Puromycin dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7860
CAS No.:58-58-2
- Pyridoxine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4835
CAS No.:58-56-0
- Theophylline
Catalog No.:BCN1258
CAS No.:58-55-9
- Tetrabenazine
Catalog No.:BCC5277
CAS No.:58-46-8
- Prochlorperazine
Catalog No.:BCC3846
CAS No.:58-38-8
- Promethazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5480
CAS No.:58-33-3
- Chlorothiazide
Catalog No.:BCC3752
CAS No.:58-94-6
- alpha-Tocopherol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5803
CAS No.:58-95-7
- Uridine
Catalog No.:BCN4090
CAS No.:58-96-8
- 6-Aminoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8766
CAS No.:580-15-4
- 3-Aminoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8620
CAS No.:580-17-6
- 2-Aminoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8555
CAS No.:580-22-3
- Matairesinol
Catalog No.:BCN5789
CAS No.:580-72-3
- Epicorynoxidine
Catalog No.:BCN7554
CAS No.:58000-48-9
- HOKU-81
Catalog No.:BCC1634
CAS No.:58020-43-2
- Averantin
Catalog No.:BCN7027
CAS No.:5803-62-3
- 24, 25-Dihydroxy VD2
Catalog No.:BCC1302
CAS No.:58050-55-8
- Miltefosine
Catalog No.:BCC4360
CAS No.:58066-85-6
Comparison of efficacy and safety between benidipine and hydrochlorothiazide in fosinopril-treated hypertensive patients with chronic kidney disease: protocol for a randomised controlled trial.[Pubmed:28237959]
BMJ Open. 2017 Feb 24;7(2):e013672.
INTRODUCTION: Co-administration of a diuretic or calcium channel blocker with an ACE inhibitor are both preferred combinations in patients with hypertensive chronic kidney disease (CKD). According to the available evidence, it is still unknown which combination plays a more active role in renal protection. We hypothesised that a combination of fosinopril and benidipine may delay the progression of CKD more effectively than a combination of fosinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ). METHODS AND ANALYSIS: This study will be a multicentred, prospective, double-blind, randomised parallel controlled trial for hypertensive CKD patients in China. Patients will be randomised to one of two treatment groups: a combination of benidipine 4-8 mg/day and fosinopril 20 mg/day; or a combination of HCTZ 12.5-25 mg/day and fosinopril 20 mg/day. Patients will be followed up for 24 months after a month's fosinopril run-in. There will be dose-titration after 1 and 2 months. The primary endpoint is changes in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from baseline to month 24. Secondary endpoints include changes in home blood pressure (BP), ambulatory BP, proteinuria, urinary albumin/creatinine ratio, and composite renal events in 24 months. Inclusion criteria are: age 18-80 years, non-dialysis CKD patients with eGFR >30 mL/min/1.73 m(2), home BP >130 mm Hg systolic or BP >80 mm Hg diastolic at the screening and randomisation, and 24 hour proteinuria <3.5 g. Principal exclusions are hypertensive crisis, transplantation, cancer, severe diabetes complications, hyperkalaemia and severe allergy. The required sample size was 511 patients for detecting a difference in the change of eGFR (one sided alpha=0.025, power 1-beta=0.90). ETHICS AND DISSEMINATION: BEAHIT (Benidipine and Hydrochlorothiazide in Fosinopril Treated Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Hypertension) was approved by Changzheng Hospital Ethics Committee (CZ-20160504-16). The outcomes will be published in a peer-reviewed journal. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: NCT02646397.
Hydrochlorothiazide treatment increases the abundance of the NaCl cotransporter in urinary extracellular vesicles of essential hypertensive patients.[Pubmed:28274929]
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):F1063-F1072.
The thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter (NCC), located apically in distal convoluted tubule epithelia, regulates the fine-tuning of renal sodium excretion. Three isoforms of NCC are generated through alternative splicing of the transcript, of which the third isoform has been the most extensively investigated in pathophysiological conditions. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of different anti-hypertensive treatments on the abundance and phosphorylation of all three NCC isoforms in urinary extracellular vesicles (uEVs) of essential hypertensive patients. In uEVs isolated from patients (n = 23) before and after Hydrochlorothiazide or valsartan treatment, the abundance and phosphorylation of the NCC isoforms was determined. Additionally, clinical biochemistry and blood pressure of the patients was assessed. Our results show that NCC detected in human uEVs has a glycosylated and oligomeric structure, comparable to NCC present in human kidney membrane fractions. Despite the inhibitory action of Hydrochlorothiazide on NCC activity, immunoblot analysis of uEVs showed significantly increased abundance of NCC isoforms 1 and 2 (NCC1/2), total NCC (NCC1-3), and the phosphorylated form of total NCC (pNCC1-3-T55/T60) in essential hypertensive patients treated with Hydrochlorothiazide but not with valsartan. This study highlights that NCC1/2, NCC1-3, and pNCC1-3-T55/T60 are upregulated by Hydrochlorothiazide, and the increase in NCC abundance in uEVs of essential hypertensive patients correlates with the blood pressure response to Hydrochlorothiazide.
Multicriteria Optimization Methodology in Stability-Indicating Method Development of Cilazapril and Hydrochlorothiazide.[Pubmed:28334985]
J Chromatogr Sci. 2017 Jul 1;55(6):625-637.
Multicriteria optimization methodology was applied in development of UHPLC-UV-MS method for separation of cilazapril, Hydrochlorothiazide and their degradation products. This method is also applicable for analysis of cilazapril, Hydrochlorothiazide and their degradation products in combined tablet formulation. Prior to method optimization forced degradation studies were conducted. Cilazapril and Hydrochlorothiazide were subjected to acidic (0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 M HCl), basic (0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 M NaOH), thermal (70 degrees C), oxidative (3-30% H2O2) degradation and photodegradation (day light). Cilazapril appeared to be unstable toward acid and base and resulted in formation of cilazaprilat. Hydrochlorothiazide significantly degraded after acid, base and thermal hydrolysis and formed degradation product was 4-amino-6-chlorobenzene-1.3-disulfonamide. For both substances, after oxidative degradation unknown products have arisen. Initial percentage of acetonitrile in mobile phase, final percentage of acetonitrile in mobile phase, time of gradient elution and column temperature were defined as variables to be optimized toward two chromatographic responses by means of central composite design and Derringer's desirability function. The satisfactory chromatographic analysis was achieved on Kinetex C18 (2.6 microm, 50 x 2.1 mm) column with temperature set at 25 degrees C. The final mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile and 20 mM ammonium formate buffer (pH adjusted to 8.5). The flow rate of the mobile phase was 400 muL min-1 and it was pumped in a gradient elution mode.
Development and in vivo evaluation of an innovative "Hydrochlorothiazide-in Cyclodextrins-in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles" formulation with sustained release and enhanced oral bioavailability for potential hypertension treatment in pediatrics.[Pubmed:28229944]
Int J Pharm. 2017 Apr 15;521(1-2):73-83.
An innovative pediatric oral formulation of Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) (2mg/mL), endowed with improved bioavailability and sustained release properties and suitable for the hypertension treatment in pediatric patients, was developed by combining the drug-cyclodextrin complexation and the incorporation of the complex into Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN). Precirol((R))ATO5-based SLN, with two different surfactants (Pluronic((R))F68 and Tween((R))80) loaded with the drug as such or as binary system with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPbetaCd) and sulfobutyl-ether-beta-cyclodextrin (SBEbetaCd) both as physical mixture (P.M.) or coground product (GR), were prepared using the hot high-shear homogenization followed by ultrasonication method. Loading of the drug:HPbetaCd both as P.M. and GR gave rise to nanoparticle formation, differently from the HCT:SBEbetaCd ones, with an entrapment efficiency of about 65%. Such SLN formulations showed an improvement of the drug release rate compared both to the drug suspension and to the free drug-loaded SLN. In all cases the SLN containing the GR systems exhibited better performances than the corresponding with P.M. However, the presence of Tween((R))80 gave rise to the complete drug release after only 150min, without providing a sustained release, whereas Pluronic((R))F68-based SLN containing GR were able to assure a sustained release over the time achieving more than 75% drug released at the end of the test, maintaining a constant 1.8-fold increase respect to simple drug suspension. Pluronic((R))F68-based SLN showed a pharmaceutically acceptable stability up to three months. In vivo studies highlighted the effectiveness of such formulations, enabling a concomitant increased diuretic effect and a sustained drug release and, consequently, enhanced HCT oral bioavailability.


