2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenoneCAS# 1775-95-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1775-95-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15681 | Appearance | Powder |
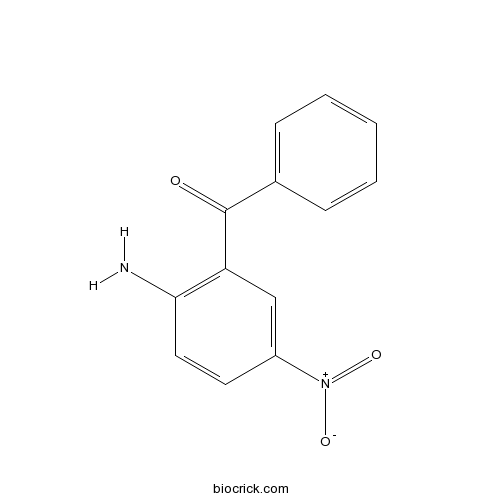
| Formula | C13H10N2O3 | M.Wt | 242 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2-amino-5-nitrophenyl)-phenylmethanone | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)[N+](=O)[O-])N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PZPZDEIASIKHPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H10N2O3/c14-12-7-6-10(15(17)18)8-11(12)13(16)9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-8H,14H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone Dilution Calculator

2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1322 mL | 20.6612 mL | 41.3223 mL | 82.6446 mL | 103.3058 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8264 mL | 4.1322 mL | 8.2645 mL | 16.5289 mL | 20.6612 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4132 mL | 2.0661 mL | 4.1322 mL | 8.2645 mL | 10.3306 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0826 mL | 0.4132 mL | 0.8264 mL | 1.6529 mL | 2.0661 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0413 mL | 0.2066 mL | 0.4132 mL | 0.8264 mL | 1.0331 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Aglain C
Catalog No.:BCN6604
CAS No.:177468-85-8
- DBeQ
Catalog No.:BCC3916
CAS No.:177355-84-9
- Aglain B
Catalog No.:BCN6636
CAS No.:177262-32-7
- 26-O-Acetylsootepin A
Catalog No.:BCN7699
CAS No.:1772588-99-4
- R 568 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7781
CAS No.:177172-49-5
- Ambrisentan
Catalog No.:BCC4887
CAS No.:177036-94-1
- 2alpha,19alpha-Dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7406
CAS No.:176983-21-4
- LY 320135
Catalog No.:BCC7346
CAS No.:176977-56-3
- CCT007093
Catalog No.:BCC5147
CAS No.:176957-55-4
- Metergoline
Catalog No.:BCC6709
CAS No.:17692-51-2
- Homoplantaginin
Catalog No.:BCN2488
CAS No.:17680-84-1
- (RS)-3,4-DCPG
Catalog No.:BCC7045
CAS No.:176796-64-8
- Flavokawain B
Catalog No.:BCN3568
CAS No.:1775-97-9
- ZK 164015
Catalog No.:BCC7272
CAS No.:177583-70-9
- Glycerol 1-(26-hydroxyhexacosanoate)
Catalog No.:BCN1131
CAS No.:177602-14-1
- MNITMT
Catalog No.:BCC7382
CAS No.:177653-76-8
- NKP608
Catalog No.:BCC1802
CAS No.:177707-12-9
- Proxyfan oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7378
CAS No.:177708-09-7
- Calystegine N1
Catalog No.:BCN1866
CAS No.:177794-03-5
- Calystegine A6
Catalog No.:BCN1886
CAS No.:177794-04-6
- Eletriptan HBr
Catalog No.:BCC5039
CAS No.:177834-92-3
- Boc-His-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3398
CAS No.:17791-52-5
- Clematichinenoside C
Catalog No.:BCN7850
CAS No.:177912-24-2
- Sauchinone
Catalog No.:BCN2299
CAS No.:177931-17-8
An approach to shortening the timeframe between the emergence of new compounds on the drugs market and the availability of reference standards: The microscale syntheses of nitrazolam and clonazolam for use as reference materials, utilizing polymer-supported reagents.[Pubmed:29542872]
Drug Test Anal. 2018 Mar 15.
Nitrazolam and clonazolam are 2 designer benzodiazepines available from Internet retailers. There is growing evidence suggesting that such compounds have the potential to cause severe adverse events. Information about tolerability in humans is scarce but typically, low doses can be difficult to administer for users when handling bulk material. Variability of the active ingredient in tablet formulations can also be of a concern. Customs, toxicology and forensic laboratories are increasingly encountering designer benzodiazepines, both in tablet and powdered form. The unavailability of reference standards can impact on the ability to identify these compounds. Therefore, the need arises for exploring in-house approaches to the preparation of new psychoactive substances (NPS) that can be carried out in a timely manner. The present study was triggered when samples of clonazolam were received in powdered and tablet form at a time when reference material for this drug was commercially unavailable. Therefore, microscale syntheses of clonazolam and its deschloro analog nitrazolam were developed utilizing polymer-supported reagents starting from 2-amino-2'-chloro-5-nitrobenzophenone (clonazolam) and 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone (nitrazolam). The final reaction step forming the 1,2,4-triazole ring moiety was performed within a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) injector. A comparison with a preparative scale synthesis of both benzodiazepine derivatives showed that microscale synthesis might be an attractive option for a forensic laboratory in terms of time and cost savings when compared with traditional methods of synthesis and when qualitative identifications are needed to direct forensic casework. The reaction by-product profiles for both the micro and the preparative scale syntheses are also presented.
Structural features of the 2-amino-5-nitrobenzophenone by means of vibrational spectroscopy HF and DFT, first order hyperpolarizability, NBO, HOMO-LUMO and theromodynamic properties.[Pubmed:24152867]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Jan 24;118:835-46.
The FT-IR and Raman spectra of 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone (ANBP) molecule have been recorded using Brucker IFS 66 V spectrometer in the range of 4000-100 cm(-1). The molecular geometry and vibrational frequencies in the ground state are calculated using the Hartree-Fock (HF) and B3LYP with 6-311+G(d) basis set. The computed values of frequencies are scaled using a suitable scale factor to yield good coherence with the observed values. The isotropic HF and DFT analysis showed good agreement with experimental observations comparison of the fundamental vibrational frequencies with calculated results by HF and B3LYP methods indicates that B3LYP/6-311+G(d) is superior to HF/6-311+G(d) for molecular vibrational problems. The electric dipole moment (mu) and first hyper polarizability (beta) values of the investigated molecule were computed using density functional theory calculations. Stability of the molecule arising from hyperconjucative interactions leading to its bioactivity, charge delocalization have been analyzed using natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis. The calculated HOMO-LUMO energies shows that charge transfer occur within the molecule. The thermodynamic functions (heat capacity, internal heat energy, Gibbs energy and entropy) from spectroscopic data by statistical methods were obtained for the range of temperature 100-1000 K. The observed and calculated frequencies are found to be in good agreement.
Studies of polymorphism in three compounds by single crystal X-ray diffraction.[Pubmed:10692639]
Int J Pharm. 2000 Jan 25;194(2):147-53.
The role of single crystal diffraction in the quantitative determination of polymorphism is demonstrated by the examination of three compounds. Two polymorphs were found for each of the compounds bis(2-nitrophenyl) trisulphide (1), 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone (2) and bis(2-nitrophenyl) sulphide (3). Only in one polymorph of (1) does molecular symmetry correspond with crystallographic symmetry. In (2) the polymorphs arise in the same crystal class and in the same crystallographic space group whereas in (3) the two polymorphs exist in different crystal classes and hence in different space groups. Crystallographic space group transformation is also discussed.
[The development of mass-screening method for benzodiazepines by radioimmunoassay].[Pubmed:8315856]
Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 1993 Feb;47(1):18-28.
For the mass-screening of benzodiazepines in urine, radioimmunoassays (RIAs) for two benzophenones (metabolites of the drugs) were established, and an animal experiment was carried out to verify their usefulness. Immunogens were prepared by condensing 2-hemisuccinyl derivatives of 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone (A-CBP) or 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone (A-NBP) to bovine serum albumin (BSA). Antisera were produced in rabbits by immunization with the individual antigens. Two kinds of RIA were established separately for A-CBP and A-NBP using each antiserum, and their sensitivities were 150 pg/tube and 30 pg/tube, respectively. The antisera had broad cross-reactivity with many chlorbenzophenone and nitrobenzophenone derivatives, respectively. Diazepam or nitrazepam was administered to rats, and the total amounts of each in urine (benzodiazepines plus their metabolites such as benzophenones) were determined relative to time using the RIAs after acid hydrolysis of the specimen. The benzophenones were positive in urine even 9 h after administration, whereas diazepam was undetectable using a RIA against diazepam. The characterization of the antisera and the results of the animal experiments indicate that these RIAs will be very useful for mass-screening of benzodiazepines.
Determination of nitrazepam and its main metabolites in urine by thin-layer chromatography and direct densitometry.[Pubmed:4019664]
J Chromatogr. 1985 Apr 12;339(1):163-9.
A method for the direct quantitative densitometry of nitrazepam and its main metabolites (7-aminonitrazepam, 7-acetamidonitrazepam and 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone) in urine was developed. The unchanged drug and its metabolites were extracted with benzene-dichloromethane (4:1), subjected to thin-layer chromatography, and determined by direct ultraviolet densitometry. Recovery experiments showed that the method was quantitative. The limit of detection was 5 ng/ml for 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone and 10 ng/ml for other compounds. The method was applied to the determination of nitrazepam and its metabolites excreted in human urine after administration of 10 mg of the drug.
Effect of temperature and relative humidity on nitrazepam stability in solid state.[Pubmed:874750]
J Pharm Sci. 1977 May;66(5):676-80.
The decomposition of a 1% dilution of nitrazepam in microcrystalline cellulose was established by quantitative determination of the two main breakdown products, 2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenone and 3-amino-6-nitro-4-phenyl-2(1H)-quinolone, using in situ diffuse reflectance measurements on thin-layer chromatograms. The decomposition and formation rate constant of nitrazepam and of the breakdown products, respectively, were determined at four temperatures and six relative humidities. By means of a three-parameter regression equation, it was possible to correlate quantitatively the decomposition constant of nitrazepam to both temperature and relative humidity.


