6,7,4'-TrihydroxyisoflavoneCAS# 17817-31-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 17817-31-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5284649 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H10O5 | M.Wt | 270.2 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
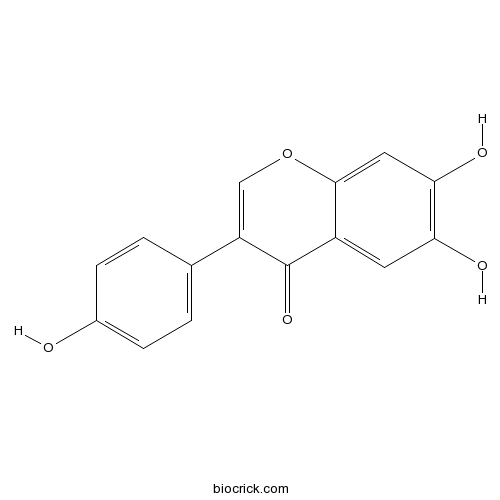
| Chemical Name | 6,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=COC3=CC(=C(C=C3C2=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GYLUFQJZYAJQDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone has antioxidant activity. 2. 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone, is a novel inhibitor of PKCα in suppressing solar UV-induced matrix metalloproteinase 1. 3. 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone, suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via ATP-competitive inhibition of PI3K. 4. 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone inhibits HCT-116 human colon cancer cell proliferation by targeting CDK1 and CDK2. |
| Targets | ERK | MEK | JNK | p38MAPK | PKC | CDK | PI3K |

6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone Dilution Calculator

6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.701 mL | 18.5048 mL | 37.0096 mL | 74.0192 mL | 92.5241 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7402 mL | 3.701 mL | 7.4019 mL | 14.8038 mL | 18.5048 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3701 mL | 1.8505 mL | 3.701 mL | 7.4019 mL | 9.2524 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.3701 mL | 0.7402 mL | 1.4804 mL | 1.8505 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.3701 mL | 0.7402 mL | 0.9252 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-Asp-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2884
CAS No.:17812-32-7
- 3-Deoxyzinnolide
Catalog No.:BCN4799
CAS No.:17811-32-4
- Bacopasaponin C
Catalog No.:BCC8124
CAS No.:178064-13-6
- Nociceptin (1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5749
CAS No.:178064-02-3
- Aescigenin
Catalog No.:BCC8293
CAS No.:17806-68-7
- Fmoc-D-Phe(4-NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3278
CAS No.:177966-63-1
- Allopurinol Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4886
CAS No.:17795-21-0
- Sauchinone
Catalog No.:BCN2299
CAS No.:177931-17-8
- Clematichinenoside C
Catalog No.:BCN7850
CAS No.:177912-24-2
- Boc-His-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3398
CAS No.:17791-52-5
- Eletriptan HBr
Catalog No.:BCC5039
CAS No.:177834-92-3
- Calystegine A6
Catalog No.:BCN1886
CAS No.:177794-04-6
- Hardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1132
CAS No.:1782-65-6
- Linderone
Catalog No.:BCN1133
CAS No.:1782-79-2
- Tetrahymanone
Catalog No.:BCN6932
CAS No.:17822-06-9
- Calystegine B3
Catalog No.:BCN1880
CAS No.:178231-95-3
- Orphanin FQ (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC6085
CAS No.:178249-41-7
- Nociceptin (1-7)
Catalog No.:BCC5738
CAS No.:178249-42-8
- H-D-Asp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2894
CAS No.:1783-96-6
- 12-Hydroxy-6-epi-albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7460
CAS No.:178330-78-4
- Tos-Arg-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2874
CAS No.:1784-03-8
- AR-R 17779 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7827
CAS No.:178419-42-6
- Agrostophyllidin
Catalog No.:BCN3598
CAS No.:178439-50-4
- 6-epi-Albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7342
CAS No.:178456-58-1
A metabolite of daidzein, 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone, suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via ATP-competitive inhibition of PI3K.[Pubmed:23737351]
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Aug;57(8):1446-55.
SCOPE: Daidzein is one of the major soy isoflavones. Following ingestion, daidzein is readily metabolized in the liver and converted into hydroxylated metabolites. One such metabolite is 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone (6,7,4'-THIF), which has been the focus of recent studies due to its various health benefits, however, its anti-adipogenic activity has not been investigated. Our objective was to determine the effects of 6,7,4'-THIF on adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and elucidate the mechanisms of action involved. METHODS AND RESULTS: Adipogenesis was stimulated in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Both 6,7,4'-THIF and daidzein were treated in the presence and absence of mixture of isobutylmethylxanthine, dexamethasone, and insulin (MDI). We observed that 6,7,4'-THIF, but not daidzein, inhibited MDI-induced adipogenesis significantly at 40 and 80 muM, associated with decreased peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and C/EBP-alpha protein expression. 6,7,4'-THIF significantly suppressed MDI-induced lipid accumulation in the early stage of adipogenesis, attributable to a suppression of cell proliferation and the induction of cell cycle arrest. We also determined that 6,7,4'-THIF, but not daidzein, attenuated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. 6,7,4'-THIF was found to inhibit PI3K activity via direct binding in an ATP-competitive manner. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that 6,7,4'-THIF suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by directly targeting PI3K. Soy isoflavones like 6,7,4'-THIF may have potential for development into novel treatment strategies for chronic obesity.
The daidzein metabolite, 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone, is a novel inhibitor of PKCalpha in suppressing solar UV-induced matrix metalloproteinase 1.[Pubmed:25415304]
Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 19;15(11):21419-32.
Soy isoflavone is an attractive source of functional cosmetic materials with anti-wrinkle, whitening and skin hydration effects. After consumption, the majority of soy isoflavones are converted to their metabolites in the human gastrointestinal tract. To understand the physiological impact of soy isoflavone on the human body, it is necessary to evaluate and address the biological function of its metabolites. In this study, we investigated the effect of 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone (6,7,4'-THIF), a major metabolite of daidzein, against solar UV (sUV)-induced matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in normal human dermal fibroblasts. MMPs play a critical role in the degradation of collagen in skin, thereby accelerating the aging process of skin. The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MKK)3/6/p38 and MKK4/c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) signaling pathways are known to modulate MMP-1 function, and their activation by sUV was significantly reduced by 6,7,4'-THIF pretreatment. Our results also indicated that the enzyme activity of protein kinase C (PKC)alpha, an upstream regulator of MKKs signaling, is suppressed by 6,7,4'-THIF using the in vitro kinase assay. Furthermore, the direct interaction between 6,7,4'-THIF and endogenous PKCalpha was confirmed using the pull-down assay. Not only sUV-induced MMP-1 expression, but also sUV-induced signaling pathway activation were decreased in PKCalpha knockdown cells. Overall, we elucidated the inhibitory effect of 6,7,4'-THIF on sUV-induced MMPs and suggest PKCalpha as its direct molecular target.
6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone inhibits HCT-116 human colon cancer cell proliferation by targeting CDK1 and CDK2.[Pubmed:21258042]
Carcinogenesis. 2011 Apr;32(4):629-35.
Colon cancer is a common epithelial malignancies worldwide. Epidemiologic evidence has shown that nutrition and dietary components are important environmental factors involved in the development of this disease. We investigated the biological activity of 6,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavone (6,7,4'-THIF, a metabolite of daidzein) in in vitro and in vivo models of human colon cancer. 6,7,4'-THIF suppressed anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of HCT-116 and DLD1 human colon cancer cells more effectively than daidzein. In addition, 6,7,4'-THIF induced cell cycle arrest at the S and G2/M phases in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells. Western blot analysis revealed that 6,7,4'-THIF effectively suppressed the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2, but had no effect on other S- or G2/M-phase regulatory proteins such as cyclin A, cyclin B1 or CDK1. Daidzein did not affect the expression of any of these proteins. In kinase and pull-down assays, 6,7,4'-THIF, but not daidzein, inhibited CDK1 and CDK2 activities in HCT-116 cells by directly interacting with CDK1 and CDK2. In a xenograft mouse model, 6,7,4'-THIF significantly decreased tumor growth, volume and weight of HCT-116 xenografts. 6,7,4'-THIF bound directly to CDK1 and CDK2 in vivo, resulting in the suppression of CDK1 and CDK2 activity in tumors corresponding with our in vitro results. Collectively, these results suggest that CDK1 and CDK2 are potential molecular targets of 6,7,4'-THIF to suppress HCT-116 cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. These findings provide insight into the biological actions of 6,7,4'-THIF and might establish a molecular basis for the development of new cancer therapeutic agents.


