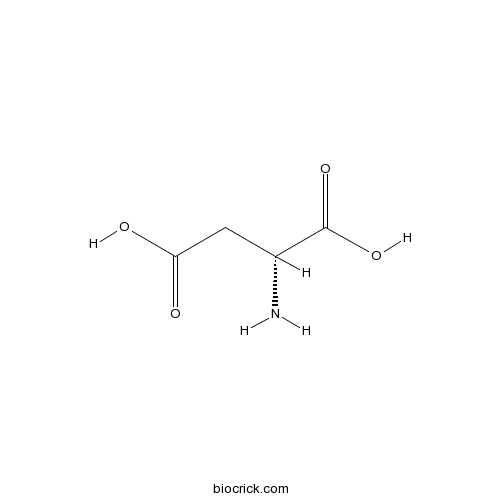
H-D-Asp-OHCAS# 1783-96-6 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1783-96-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 83887 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C4H7NO4 | M.Wt | 133.1 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 7.69 mg/mL (57.78 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-aminobutanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(C(C(=O)O)N)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-UWTATZPHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Endogenous NMDA receptor agonist with similar activity to the L-isomer (L-aspartic acid). Also a non-metabolizable substrate for EAA uptake systems. Modulates melatonin synthesis in the pineal gland. |

H-D-Asp-OH Dilution Calculator

H-D-Asp-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.5131 mL | 37.5657 mL | 75.1315 mL | 150.263 mL | 187.8287 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.5026 mL | 7.5131 mL | 15.0263 mL | 30.0526 mL | 37.5657 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7513 mL | 3.7566 mL | 7.5131 mL | 15.0263 mL | 18.7829 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1503 mL | 0.7513 mL | 1.5026 mL | 3.0053 mL | 3.7566 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0751 mL | 0.3757 mL | 0.7513 mL | 1.5026 mL | 1.8783 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H-D-Asp-OH
- Nociceptin (1-7)
Catalog No.:BCC5738
CAS No.:178249-42-8
- Orphanin FQ (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC6085
CAS No.:178249-41-7
- Calystegine B3
Catalog No.:BCN1880
CAS No.:178231-95-3
- Tetrahymanone
Catalog No.:BCN6932
CAS No.:17822-06-9
- Linderone
Catalog No.:BCN1133
CAS No.:1782-79-2
- Hardwickiic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1132
CAS No.:1782-65-6
- 6,7,4'-Trihydroxyisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2910
CAS No.:17817-31-1
- H-Asp-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2884
CAS No.:17812-32-7
- 3-Deoxyzinnolide
Catalog No.:BCN4799
CAS No.:17811-32-4
- Bacopasaponin C
Catalog No.:BCC8124
CAS No.:178064-13-6
- Nociceptin (1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5749
CAS No.:178064-02-3
- Aescigenin
Catalog No.:BCC8293
CAS No.:17806-68-7
- 12-Hydroxy-6-epi-albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7460
CAS No.:178330-78-4
- Tos-Arg-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2874
CAS No.:1784-03-8
- AR-R 17779 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7827
CAS No.:178419-42-6
- Agrostophyllidin
Catalog No.:BCN3598
CAS No.:178439-50-4
- 6-epi-Albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7342
CAS No.:178456-58-1
- Vitexin -4''-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3054
CAS No.:178468-00-3
- Hoechst 33342 analog
Catalog No.:BCC1630
CAS No.:178481-68-0
- Prilocaine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4288
CAS No.:1786-81-8
- ZD 2079
Catalog No.:BCC5878
CAS No.:178600-17-4
- Oleoside
Catalog No.:BCN1134
CAS No.:178600-68-5
- U-104
Catalog No.:BCC2312
CAS No.:178606-66-1
- CFM-2
Catalog No.:BCC6931
CAS No.:178616-26-7
D-aspartate modulates melatonin synthesis in rat pinealocytes.[Pubmed:9682837]
Neurosci Lett. 1998 Jun 19;249(2-3):143-6.
It has been known that pinealocytes contain the highest level of D-aspartate among various neuroendocrine cells in the rat. Here, we report that exogenous D-aspartate strongly inhibited norepinephrine-dependent melatonin synthesis in the rat pineal gland, the concentration required for 50% inhibition being 75 microM. This inhibition was due at least partly to decreased norepinephrine-dependent serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity. Upon incubation, D-aspartate was gradually released from pinealocytes and accumulated in the incubation medium as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography on a Pirkle-type chiral column. These results suggest that D-aspartate acts as a negative regulator for melatonin synthesis in the pineal gland.
Free D-aspartate and D-serine in the mammalian brain and periphery.[Pubmed:9247969]
Prog Neurobiol. 1997 Jul;52(4):325-53.
It has long been assumed that L-forms of amino acids exclusively constitute free amino acid pools in mammals. However, a variety of studies in the last decade has demonstrated that free D-aspartate and D-serine occur in mammals and may have important physiological function in mammals. Free D-serine is confined predominantly to the forebrain structure, and the distribution and development of D-serine correspond well with those of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type excitatory amino acid receptor. As D-serine acts as a potent and selective agonist for the strychnine-insensitive glycine site of the NMDA receptor, it is proposed that D-serine is a potential candidate for an NMDA receptor-related glycine site agonist in mammalian brain. In contrast, widespread and transient emergence of a high concentration of free D-aspartate is observed in the brain and periphery. Since the periods of maximal emergence of D-aspartate in the brain and periphery occur during critical periods of morphological and functional maturation of the organs, D-aspartate could participate in the regulation of these regulation of these developmental processes of the organs. This review deals with the recent advances in the studies of presence of free D-aspartate and D-serine and their metabolic systems in mammals. Since D-aspartate and D-serine have been shown to potentiate NMDA receptor-mediated transmission through the glutamate binding site and the strychnine-insensitive glycine binding site, respectively, and have been utilized extensively as potent and selective tools to study the excitatory amino acid system in the brain, we shall discuss also the NMDA receptor and uptake system of D-amino acids.
Structure/activity relations of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor ligands as studied by their inhibition of [3H]D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid binding in rat brain membranes.[Pubmed:2901691]
Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):17-31.
Structure/activity relations of agonists and antagonists for the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor have been investigated by measuring the ability of a large range of substances to inhibit binding of [3H]2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate to rat brain membranes. A major difference between optimum structures for agonist and antagonist activity lay in the differential effectiveness of sulphonic and phosphonic acid groups as the omega-acidic terminal in these two types of compound. The sulphonic acid moiety was an effective omega-acidic terminal in short chain agonists, but not in longer chain antagonists, while the phosphonic acid group was the most effective omega-acidic terminal in longer chain antagonists, but was only very weakly active in short chain agonists. It is proposed that the binding site of the omega-acidic terminal of antagonists is different from that for the omega-acidic group of agonists. Other structural features conducive to effective interaction of ligands with the receptor are discussed.


