Y-27632 dihydrochlorideROCK1 inhibitor CAS# 129830-38-2 |
- Fasudil (HA-1077) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2542
CAS No.:105628-07-7
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- GSK429286A
Catalog No.:BCC2532
CAS No.:864082-47-3
- SLx-2119
Catalog No.:BCC1954
CAS No.:911417-87-3
- AS 1892802
Catalog No.:BCC6335
CAS No.:928320-12-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 129830-38-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9901617 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H23Cl2N3O | M.Wt | 320.26 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 124 mg/mL (387.19 mM) DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (99.92 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
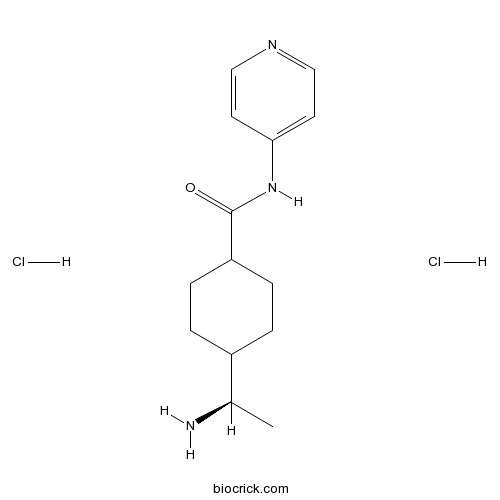
| Chemical Name | 4-[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-N-pyridin-4-ylcyclohexane-1-carboxamide;dihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC(C1CCC(CC1)C(=O)NC2=CC=NC=C2)N.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IDDDVXIUIXWAGJ-DDSAHXNVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H21N3O.2ClH/c1-10(15)11-2-4-12(5-3-11)14(18)17-13-6-8-16-9-7-13;;/h6-12H,2-5,15H2,1H3,(H,16,17,18);2*1H/t10-,11?,12?;;/m1../s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Y-27632 is a selective inhibitor of ROCK1 (p160ROCK) with Ki of 140 nM, exhibits >200-fold selectivity over other kinases, including PKC, cAMP-dependent protein kinase, MLCK and PAK. | |||||
| Targets | ROCK1 | ROCK2 | ||||
| IC50 | 140 nM (Ki) | 300 nM (Ki) | ||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human (hu) and rat(r) prostatic smooth mus-cle cells (PSM) |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 24h and 48 h; 100 μM |
| Applications | After identifying prostatic smooth muscle cells and confirming the expression of Rho-kinase in these cells we investigated whether the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 affected the viability and proliferation of these cells. In serum-free medium huPSM and rPSM were made quiescent for 24 hours. Cell viability using neutral red and MTT assays was assessed 24 and 48 hours after stimulating the cells with 1% serum in the absence and presence of Y-27632 (0.01 to 100 μM). The results of these assays showed that the number of the cells increased between the 24- and 48-hour incubation periods after re-stimulation with 1% serum. However, in the presence of Y-27632 the increase in the number of live cells was less than in the control group. This effect was concentration dependent. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | Adult Swiss male albino mice |
| Dosage form | 0.1 mg/kg/day; intrapertoneal injection |
| Application | The drug was tested by histopathological examination showed that Y-27632 administration to EAC-bearing mice diminished pathological structure, to 60–70% degree, toward to normal intact histological structure especially in pre-carcinoma inoculation regime. Respect to this, ROCK inhibition by Y-27632 decreased significantly tumor invasion and metastasis. Our immunohistochemistry results showed that ROCK2 was mainly inhibited by Y-27632 in pre-carcinoma, but not in post-carcinoma, groups. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Rees R W, Foxwell N A, Ralph D J, et al. Y-27632, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, inhibits proliferation and adrenergic contraction of prostatic smooth muscle cells[J]. The Journal of urology, 2003, 170(6): 2517-2522. [2] Isler D, Ozaslan M, Karagoz I D, et al. Antitumoral effect of a selective Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mice[J]. Pharmacological Reports, 2014, 66(1): 114-120. | |

Y-27632 dihydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Y-27632 dihydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1225 mL | 15.6123 mL | 31.2246 mL | 62.4493 mL | 78.0616 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6245 mL | 3.1225 mL | 6.2449 mL | 12.4899 mL | 15.6123 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3122 mL | 1.5612 mL | 3.1225 mL | 6.2449 mL | 7.8062 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6245 mL | 1.249 mL | 1.5612 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6245 mL | 0.7806 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Y-27632 dihydrochloride is a small-molecule inhibitor of Rho-associated protein kinase p160ROCK with the IC50 of 140 nM. Y-27632 suppresses the kinase activity of both ROCK-1 and ROCK-2 in vitro, and this compound inhibits the kinases by binding to the catalytic site of ROCK-1 and ROCK-2. Thus Y-27632 function on Rho-mediated stress fiber formation, the G1-S phase progression and cytokinesis.
References
1. Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. T Ishizaki, M Uehata, I Tamechika, J Keel Molecular Pharmacology 2000
2. A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells K Watanabe, M Ueno, D Kamiya, A Nishiyama. Nature Biotechnology. 2007
- Y-27632
Catalog No.:BCC4301
CAS No.:146986-50-7
- Fmoc-Lys(Aloc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3515
CAS No.:146982-27-6
- Fmoc-Asp(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3089
CAS No.:146982-24-3
- Codaphniphylline
Catalog No.:BCN1652
CAS No.:14694-15-6
- Ziprasidone
Catalog No.:BCC2071
CAS No.:146939-27-7
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12
Catalog No.:BCC5562
CAS No.:1469337-95-8
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 9
Catalog No.:BCC6500
CAS No.:1469337-91-4
- 1,2-Diacetoxy-4,7,8-trihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)dibenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7691
CAS No.:146905-24-0
- Triptobenzene H
Catalog No.:BCN6784
CAS No.:146900-55-2
- 1,5-Dihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7423
CAS No.:14686-65-8
- 2-Bromo-1-(3-thienyl)-1-ethanone
Catalog No.:BCN2657
CAS No.:1468-82-2
- Y-29794 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC5795
CAS No.:146794-84-5
- Atglistatin
Catalog No.:BCC5104
CAS No.:1469924-27-3
- QL47
Catalog No.:BCC3920
CAS No.:1469988-75-7
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8947
CAS No.:147-24-0
- DL-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN8541
CAS No.:147-81-9
- Proline
Catalog No.:BCN1656
CAS No.:147-85-3
- Cytarabine
Catalog No.:BCC3759
CAS No.:147-94-4
- 3'-O-Demethylarctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3544
CAS No.:147022-95-5
- Menthyl-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-[1,3]oxathiolane-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9019
CAS No.:147027-10-9
- MK591
Catalog No.:BCC1766
CAS No.:147030-01-1
- Cyclo(Phe-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN2416
CAS No.:14705-60-3
- Rocaglaol
Catalog No.:BCN1653
CAS No.:147059-46-9
- Trovafloxacin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC3931
CAS No.:147059-75-4
Effect of oxidative stress on Rho kinase II and smooth muscle contraction in rat stomach.[Pubmed:25752964]
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;93(6):405-11.
Recent studies have shown that both Rho kinase signaling and oxidative stress are involved in the pathogenesis of a number of human diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. However, very little is known about the effect of oxidative stress on the gastrointestinal (GI) smooth muscle Rho kinase pathway. The aim of the current study was to investigate the effect of oxidative stress on Rho kinase II and muscle contraction in rat stomach. The peroxynitrite donor 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and peroxynitrite were used to induce oxidative stress. Rho kinase II expression and ACh-induced activity were measured in control and oxidant-treated cells via specifically designed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and activity assay kits, respectively. Single smooth muscle cell contraction was measured via scanning micrometry in the presence or absence of the Rho kinase blocker, Y-27632 dihydrochloride. All oxidant agents significantly increased ACh-induced Rho kinase II activity without affecting its expression level. Most important, oxidative stress induced by all three agents augmented ACh-stimulated muscle cell contraction, which was significantly inhibited by Y-27632. In conclusion, oxidative stress activates Rho kinase II and enhances contraction in rat gastric muscle, suggesting an important role in GI motility disorders associated with oxidative stress.
The role of the RhoA/ROCK pathway in gender-dependent differences in gastric smooth muscle contraction.[Pubmed:26391686]
J Physiol Sci. 2016 Jan;66(1):85-92.
Gender-related differences in various gastric functions and diseases have been reported, with women having a higher prevalence of gastrointestinal disturbances than men. The aim of this study was to investigate sex-dependent differences in activation of the Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK; RhoA/Rho kinase) pathway and muscle contraction in the stomach using single gastric smooth muscle cells (GSMC) from male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. Expression of ROCK1 and ROCK2 protein and acetylcholine (ACh)-induced activation of RhoA and ROCK were measured using a specifically designed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and activity assay kits, respectively. Contraction of a single GSMC was measured by scanning micrometry in the presence or absence of the ROCK inhibitor Y27632 dihydrochloride. ACh-induced activation of RhoA and ROCK and subsequent contraction were greater in male rats than in female rats but neither was related to differences in the expression of ROCK1 or ROCK2 or total RhoA amount. Most important, Y27632 inhibited and abolished differences in ACh-induced contraction in both sexes. In conclusion, increased ACh-induced contraction in the GSMC of male rats is attributable to greater RhoA/ROCK activation independent of differences in the expression of ROCK isoforms or total RhoA.
Rosuvastatin-induced responses in calf cardiac vein.[Pubmed:26350090]
Bratisl Lek Listy. 2015;116(8):494-8.
OBJECTIVE: The effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors on vasodilatation induced by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor rosuvastatin (10-9-10-4M) on 5-HT-precontracted calf cardiac vein and the role of endothelium in these effects were analyzed. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Cardiac vein ring preparations were suspended in organ baths containing 25 ml of Krebs-Henseleit solution, maintained at 37 degrees C and continuously gassed with 95% O2-5% CO2. At the end of the resting period, the cardiac vein preparations were contracted with 10(-6) M 5-HT. After the contraction had reached a steady state, rosuvastatin was added to the organ bath cumulatively (10(-9)-10(-4) M). RESULTS: Rosuvastatin relaxed the cardiac vein rings in general while the degree of relaxation was greater in those with endothelium and lower in those without it. HA1077 [1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-homopiperazine] (Fasudil, 10(-6) M) and Y-27632 [(+)-(R)-trans-4-(1-aminoethyl)-N-(4-pyridyl) cyclohexane carboxamide dihydrochloride] (10(-6) M) incubation increased the rosuvastatin-induced relaxation only in the presence of endothelium. CONCLUSIONS: The results demonstrate for the first time that in calf cardiac vein, rosuvastatin induced endothelium-dependent relaxations while Rho-kinase inhibition increased these relaxations in the presence of endothelium layer (Fig. 3, Ref. 44).
Additive effects of the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 and vardenafil on relaxation of the corpus cavernosum tissue of patients with erectile dysfunction and clinical phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor failure.[Pubmed:27763717]
BJU Int. 2017 Feb;119(2):325-332.
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the expression of the Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) pathway in the corpus cavernosum of patients with severe erectile dysfunction (ED) compared with healthy human corpus cavernosum, and to test the functional effects of two Rho kinase inhibitors (RKIs) on erectile tissue of patients with severe ED, which did not respond to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is). PATIENTS AND METHODS: Human corpus cavernosum samples were obtained after consent from men undergoing penile prosthesis implantation (n = 7 for organ bath experiments, n = 17 for quantitative PCR [qPCR]). Potent control subjects (n = 5) underwent penile needle biopsy. qPCR was performed for the expression of RhoA and ROCK subtypes 1 and 2. Immunohistochemistry staining against ROCK and alpha smooth muscle actin (alphaSMA) was performed on the corpus cavernosum of patients with ED. Tissue strips were precontracted with phenylephrine and incubated with 1 mum of the PDE5I vardenafil or with DMSO (control). Subsequently, increasing concentrations of the RKIs azaindole or Y-27632 were added, and relaxation of tissue was quantified. RESULTS: The expression of ROCK1 was unchanged (P > 0.05), while ROCK2 (P < 0.05) was significantly upregulated in patients with ED compared with controls. ROCK1 and ROCK2 protein colocalized with alphaSMA, confirming the presence of this kinase in cavernous smooth muscle cells and/or myofibroblasts. After incubation with DMSO, 10 mum azaindole and 10 mum Y-27632 relaxed precontracted tissues with 49.5 +/- 7.42% (P = 0.1470 when compared with vehicle) and 85.9 +/- 10.3% (P = 0.0016 when compared with vehicle), respectively. Additive effects on relaxation of human corpus cavernosum were seen after preincubation with 1 mum vardenafil. CONCLUSION: The RKI Y-27632 causes a significant relaxation of corpus cavernosum in tissue strips of patients with severe ED. The additive effect of vardenafil and Y-27632 shows that a combined inhibition of Rho-kinase and phosphodiesterase type 5 could be a promising orally administered treatment for severe ED.
Early Alterations of Bile Canaliculi Dynamics and the Rho Kinase/Myosin Light Chain Kinase Pathway Are Characteristics of Drug-Induced Intrahepatic Cholestasis.[Pubmed:27538918]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Nov;44(11):1780-1793.
Intrahepatic cholestasis represents 20%-40% of drug-induced injuries from which a large proportion remains unpredictable. We aimed to investigate mechanisms underlying drug-induced cholestasis and improve its early detection using human HepaRG cells and a set of 12 cholestatic drugs and six noncholestatic drugs. In this study, we analyzed bile canaliculi dynamics, Rho kinase (ROCK)/myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) pathway implication, efflux inhibition of taurocholate [a predominant bile salt export pump (BSEP) substrate], and expression of the major canalicular and basolateral bile acid transporters. We demonstrated that 12 cholestatic drugs classified on the basis of reported clinical findings caused disturbances of both bile canaliculi dynamics, characterized by either dilatation or constriction, and alteration of the ROCK/MLCK signaling pathway, whereas noncholestatic compounds, by contrast, had no effect. Cotreatment with ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 [4-(1-aminoethyl)-N-(4-pyridyl) cyclohexanecarboxamide dihydrochloride] and MLCK activator calmodulin reduced bile canaliculi constriction and dilatation, respectively, confirming the role of these pathways in drug-induced intrahepatic cholestasis. By contrast, inhibition of taurocholate efflux and/or human BSEP overexpressed in membrane vesicles was not observed with all cholestatic drugs; moreover, examples of noncholestatic compounds were reportedly found to inhibit BSEP. Transcripts levels of major bile acid transporters were determined after 24-hour treatment. BSEP, Na(+)-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide, and organic anion transporting polypeptide B were downregulated with most cholestatic and some noncholestatic drugs, whereas deregulation of multidrug resistance-associated proteins was more variable, probably mainly reflecting secondary effects. Together, our results show that cholestatic drugs consistently cause an early alteration of bile canaliculi dynamics associated with modulation of ROCK/MLCK and these changes are more specific than efflux inhibition measurements alone as predictive nonclinical markers of drug-induced cholestasis.
Derivation of novel human ground state naive pluripotent stem cells.[Pubmed:24172903]
Nature. 2013 Dec 12;504(7479):282-6.
Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells are isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, and can be preserved in vitro in a naive inner-cell-mass-like configuration by providing exogenous stimulation with leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and small molecule inhibition of ERK1/ERK2 and GSK3beta signalling (termed 2i/LIF conditions). Hallmarks of naive pluripotency include driving Oct4 (also known as Pou5f1) transcription by its distal enhancer, retaining a pre-inactivation X chromosome state, and global reduction in DNA methylation and in H3K27me3 repressive chromatin mark deposition on developmental regulatory gene promoters. Upon withdrawal of 2i/LIF, naive mouse ES cells can drift towards a primed pluripotent state resembling that of the post-implantation epiblast. Although human ES cells share several molecular features with naive mouse ES cells, they also share a variety of epigenetic properties with primed murine epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs). These include predominant use of the proximal enhancer element to maintain OCT4 expression, pronounced tendency for X chromosome inactivation in most female human ES cells, increase in DNA methylation and prominent deposition of H3K27me3 and bivalent domain acquisition on lineage regulatory genes. The feasibility of establishing human ground state naive pluripotency in vitro with equivalent molecular and functional features to those characterized in mouse ES cells remains to be defined. Here we establish defined conditions that facilitate the derivation of genetically unmodified human naive pluripotent stem cells from already established primed human ES cells, from somatic cells through induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell reprogramming or directly from blastocysts. The novel naive pluripotent cells validated herein retain molecular characteristics and functional properties that are highly similar to mouse naive ES cells, and distinct from conventional primed human pluripotent cells. This includes competence in the generation of cross-species chimaeric mouse embryos that underwent organogenesis following microinjection of human naive iPS cells into mouse morulas. Collectively, our findings establish new avenues for regenerative medicine, patient-specific iPS cell disease modelling and the study of early human development in vitro and in vivo.
Freeze-thawing single human embryonic stem cells induce e-cadherin and actin filament network disruption via g13 signaling.[Pubmed:22227712]
Cryo Letters. 2011 Nov-Dec;32(6):516-24.
Poor adhesion of single human embryonic stem (hES) cells after freeze-thawing causes death. To investigate mechanisms responsible for this, Rho-dependent protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y-27632-treated and untreated single hES cells were analyzed for E-cadherin and F-actin distribution by immunostaining and phalloidin staining respectively and for G13 signaling pathway components by DNA microarray and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Y-27632-treated cells clustered rapidly and maintained E-cadherin and F-actin distribution without losing Oct-3/4. Immediately after thawing, E-cadherin in untreated hES cells dotted along the membrane and then displayed eccentric cytoplasmic localization. Bleb formation and early Oct-3/4 loss occurred after F-actin network condensation in the cytoplasm. Microarray analyses and quantitative PCR indicated upregulation of two actin reorganization-associated components of the G13 signaling pathway, Arhgdib and Cdc42, in untreated cells. Considering these findings and that cell death was partly interrupted by Y-27632, E-cadherin and actin cytoskeleton network disruption through the G13 signaling pathway may cause hES cell death after freeze-thawing.
Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension.[Pubmed:9353125]
Nature. 1997 Oct 30;389(6654):990-4.
Abnormal smooth-muscle contractility may be a major cause of disease states such as hypertension, and a smooth-muscle relaxant that modulates this process would be useful therapeutically. Smooth-muscle contraction is regulated by the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and by the Ca2+ sensitivity of myofilaments: the former activates myosin light-chain kinase and the latter is achieved partly by inhibition of myosin phosphatase. The small GTPase Rho and its target, Rho-associated kinase, participate in this latter mechanism in vitro, but their participation has not been demonstrated in intact muscles. Here we show that a pyridine derivative, Y-27632, selectively inhibits smooth-muscle contraction by inhibiting Ca2+ sensitization. We identified the Y-27632 target as a Rho-associated protein kinase, p160ROCK. Y-27632 consistently suppresses Rho-induced, p160ROCK-mediated formation of stress fibres in cultured cells and dramatically corrects hypertension in several hypertensive rat models. Our findings indicate that p160ROCK-mediated Ca2+ sensitization is involved in the pathophysiology of hypertension and suggest that compounds that inhibit this process might be useful therapeutically.


