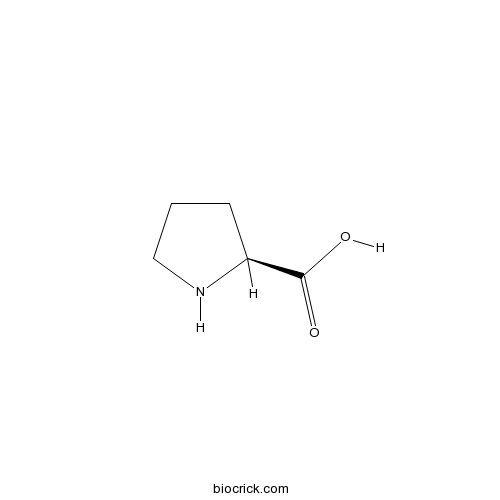
ProlineCAS# 147-85-3 |
- H-D-Pro-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3023
CAS No.:344-25-2
- H-DL-Pro-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3026
CAS No.:609-36-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 147-85-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 145742 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C5H9NO2 | M.Wt | 115.1 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (S)-2-Carboxypyrrolidine; (S)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CC(NC1)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-BYPYZUCNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H9NO2/c7-5(8)4-2-1-3-6-4/h4,6H,1-3H2,(H,7,8)/t4-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | L-Proline is one of the twenty amino acids used in living organisms as the building blocks of proteins.Proline accumulates in many plant species in response to environmental stress, it can act as a signaling molecule to modulate mitochondrial functions, influence cell proliferation or cell death and trigger specific gene expression, which can be essential for plant recovery from stress, the engineering of proline metabolism could lead to new opportunities to improve plant tolerance of environmental stresses. |
| Targets | p38MAPK | HIF |
| In vitro | HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing.[Pubmed: 11292862 ]Science. 2001 Apr 20;292(5516):464-8.HIF (hypoxia-inducible factor) is a transcription factor that plays a pivotal role in cellular adaptation to changes in oxygen availability. In the presence of oxygen, HIF is targeted for destruction by an E3 ubiquitin ligase containing the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein (pVHL). We found that human pVHL binds to a short HIF-derived peptide when a conserved Proline residue at the core of this peptide is hydroxylated. Because Proline hydroxylation requires molecular oxygen and Fe(2+), this protein modification may play a key role in mammalian oxygen sensing. |
| In vivo | Proline: a multifunctional amino acid.[Pubmed: 20036181 ]Trends Plant Sci. 2010 Feb;15(2):89-97.Proline accumulates in many plant species in response to environmental stress. Although much is now known about Proline metabolism, some aspects of its biological functions are still unclear. Here, we discuss the compartmentalization of Proline biosynthesis, accumulation and degradation in the cytosol, chloroplast and mitochondria. We also describe the role of Proline in cellular homeostasis, including redox balance and energy status. Proline can act as a signaling molecule to modulate mitochondrial functions, influence cell proliferation or cell death and trigger specific gene expression, which can be essential for plant recovery from stress. Although the regulation and function of Proline accumulation are not yet completely understood, the engineering of Proline metabolism could lead to new opportunities to improve plant tolerance of environmental stresses. |
| Structure Identification | Cell. 2006 Sep 8;126(5):905-16.Proline isomerization of histone H3 regulates lysine methylation and gene expression.[Pubmed: 16959570 ]The cis-trans isomerization of Proline serves as a regulatory switch in signaling pathways. We identify the Proline isomerase Fpr4, a member of the FK506 binding protein family in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as an enzyme which binds the amino-terminal tail of histones H3 and H4 and catalyses the isomerization of H3 Proline P30 and P38 in vitro. We show that P38 is necessary for methylation of K36 and that isomerization by Fpr4 inhibits the ability of Set2 to methylate H3 K36 in vitro. These results suggest that the conformational state of P38, controlled by Fpr4, is important for methylation of H3K36 by Set2. Consistent with such an antagonistic role, abrogation of Fpr4 catalytic activity in vivo results in increased levels of H3K36 methylation and delayed transcriptional induction kinetics of specific genes in yeast. These results identify Proline isomerization as a novel noncovalent histone modification that regulates transcription and provides evidence for crosstalk between histone lysine methylation and Proline isomerization. |

Proline Dilution Calculator

Proline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 8.6881 mL | 43.4405 mL | 86.881 mL | 173.7619 mL | 217.2024 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.7376 mL | 8.6881 mL | 17.3762 mL | 34.7524 mL | 43.4405 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.8688 mL | 4.344 mL | 8.6881 mL | 17.3762 mL | 21.7202 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1738 mL | 0.8688 mL | 1.7376 mL | 3.4752 mL | 4.344 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0869 mL | 0.4344 mL | 0.8688 mL | 1.7376 mL | 2.172 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H-Pro-OH
- DL-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN8541
CAS No.:147-81-9
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8947
CAS No.:147-24-0
- QL47
Catalog No.:BCC3920
CAS No.:1469988-75-7
- Atglistatin
Catalog No.:BCC5104
CAS No.:1469924-27-3
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Y-27632
Catalog No.:BCC4301
CAS No.:146986-50-7
- Fmoc-Lys(Aloc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3515
CAS No.:146982-27-6
- Fmoc-Asp(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3089
CAS No.:146982-24-3
- Codaphniphylline
Catalog No.:BCN1652
CAS No.:14694-15-6
- Ziprasidone
Catalog No.:BCC2071
CAS No.:146939-27-7
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12
Catalog No.:BCC5562
CAS No.:1469337-95-8
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 9
Catalog No.:BCC6500
CAS No.:1469337-91-4
- Cytarabine
Catalog No.:BCC3759
CAS No.:147-94-4
- 3'-O-Demethylarctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3544
CAS No.:147022-95-5
- Menthyl-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-[1,3]oxathiolane-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9019
CAS No.:147027-10-9
- MK591
Catalog No.:BCC1766
CAS No.:147030-01-1
- Cyclo(Phe-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN2416
CAS No.:14705-60-3
- Rocaglaol
Catalog No.:BCN1653
CAS No.:147059-46-9
- Trovafloxacin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC3931
CAS No.:147059-75-4
- Alcaftadine
Catalog No.:BCC5260
CAS No.:147084-10-4
- 5,6-Dihydro-6-methyl-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCC8722
CAS No.:147086-79-1
- Rosuvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3853
CAS No.:147098-20-2
- Maropitant
Catalog No.:BCC1728
CAS No.:147116-67-4
- Methyl (3R)-3-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-5-oxo-6-triphenylphosphoranylidenehexanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9031
CAS No.:147118-35-2
Proline: a multifunctional amino acid.[Pubmed:20036181]
Trends Plant Sci. 2010 Feb;15(2):89-97.
Proline accumulates in many plant species in response to environmental stress. Although much is now known about Proline metabolism, some aspects of its biological functions are still unclear. Here, we discuss the compartmentalization of Proline biosynthesis, accumulation and degradation in the cytosol, chloroplast and mitochondria. We also describe the role of Proline in cellular homeostasis, including redox balance and energy status. Proline can act as a signaling molecule to modulate mitochondrial functions, influence cell proliferation or cell death and trigger specific gene expression, which can be essential for plant recovery from stress. Although the regulation and function of Proline accumulation are not yet completely understood, the engineering of Proline metabolism could lead to new opportunities to improve plant tolerance of environmental stresses.
HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing.[Pubmed:11292862]
Science. 2001 Apr 20;292(5516):464-8.
HIF (hypoxia-inducible factor) is a transcription factor that plays a pivotal role in cellular adaptation to changes in oxygen availability. In the presence of oxygen, HIF is targeted for destruction by an E3 ubiquitin ligase containing the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein (pVHL). We found that human pVHL binds to a short HIF-derived peptide when a conserved Proline residue at the core of this peptide is hydroxylated. Because Proline hydroxylation requires molecular oxygen and Fe(2+), this protein modification may play a key role in mammalian oxygen sensing.
Elicitor- and wound-induced oxidative cross-linking of a proline-rich plant cell wall protein: a novel, rapid defense response.[Pubmed:1623521]
Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):21-30.
Treatment of bean or soybean cells with fungal elicitor or glutathione causes a rapid insolubilization of preexisting (hydroxy)Proline-rich structural proteins in the cell wall. This insolubilization, which involves H2O2-mediated oxidative cross-linking, is initiated within 2 min and is complete within 10 min under optimal conditions, and hence, precedes the expression of transcription-dependent defenses. Cross-linking is also under developmental control during hypocotyl growth and in tissues subject to mechanical stress such as the stem-petiole junction. Stimulus-dependent oxidative cross-linking of wall structural proteins is a novel site of cellular regulation with potentially important functions in cell maturation and toughening of cell walls in the initial stages of plant defense.
Proline isomerization of histone H3 regulates lysine methylation and gene expression.[Pubmed:16959570]
Cell. 2006 Sep 8;126(5):905-16.
The cis-trans isomerization of Proline serves as a regulatory switch in signaling pathways. We identify the Proline isomerase Fpr4, a member of the FK506 binding protein family in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as an enzyme which binds the amino-terminal tail of histones H3 and H4 and catalyses the isomerization of H3 Proline P30 and P38 in vitro. We show that P38 is necessary for methylation of K36 and that isomerization by Fpr4 inhibits the ability of Set2 to methylate H3 K36 in vitro. These results suggest that the conformational state of P38, controlled by Fpr4, is important for methylation of H3K36 by Set2. Consistent with such an antagonistic role, abrogation of Fpr4 catalytic activity in vivo results in increased levels of H3K36 methylation and delayed transcriptional induction kinetics of specific genes in yeast. These results identify Proline isomerization as a novel noncovalent histone modification that regulates transcription and provides evidence for crosstalk between histone lysine methylation and Proline isomerization.


