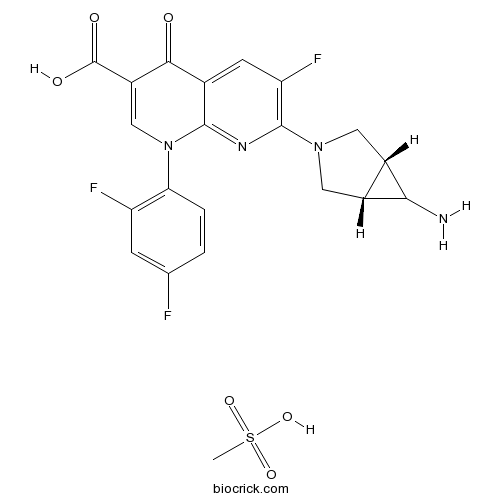
Trovafloxacin mesylateFluoroquinolone antibiotic CAS# 147059-75-4 |
- Daptomycin
Catalog No.:BCC1057
CAS No.:103060-53-3
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Clofarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1078
CAS No.:123318-82-1
- Ifosfamide
Catalog No.:BCC1164
CAS No.:3778-73-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 147059-75-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 62960 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H19F3N4O6S | M.Wt | 512.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CP 99219 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 7-[(1S,5R)-6-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-3-yl]-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid;methanesulfonic acid | ||
| SMILES | CS(=O)(=O)O.C1C2C(C2N)CN1C3=C(C=C4C(=O)C(=CN(C4=N3)C5=C(C=C(C=C5)F)F)C(=O)O)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DYNZICQDCVYXFW-GIPYJWDTSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H15F3N4O3.CH4O3S/c21-8-1-2-15(13(22)3-8)27-7-12(20(29)30)17(28)9-4-14(23)19(25-18(9)27)26-5-10-11(6-26)16(10)24;1-5(2,3)4/h1-4,7,10-11,16H,5-6,24H2,(H,29,30);1H3,(H,2,3,4)/t10-,11+,16?; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Inhibits bacterial DNA topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase and forms a stable quinolone-DNA complex with these enzymes which reversibly inhibits DNA synthesis. Displays potent activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Increases the production of mitochondrial NO in immortalized hepatocytes; also increases mitochondrial Ca2+. Inhibits Panx-1 (IC50 ~ 4μM). |

Trovafloxacin mesylate Dilution Calculator

Trovafloxacin mesylate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9514 mL | 9.7569 mL | 19.5137 mL | 39.0274 mL | 48.7843 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3903 mL | 1.9514 mL | 3.9027 mL | 7.8055 mL | 9.7569 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1951 mL | 0.9757 mL | 1.9514 mL | 3.9027 mL | 4.8784 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.039 mL | 0.1951 mL | 0.3903 mL | 0.7805 mL | 0.9757 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0195 mL | 0.0976 mL | 0.1951 mL | 0.3903 mL | 0.4878 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Inhibits bacterial DNA topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase and forms a stable quinolone-DNA complex with these enzymes which reversibly inhibits DNA synthesis. Displays potent activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacter
- Rocaglaol
Catalog No.:BCN1653
CAS No.:147059-46-9
- Cyclo(Phe-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN2416
CAS No.:14705-60-3
- MK591
Catalog No.:BCC1766
CAS No.:147030-01-1
- Menthyl-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-[1,3]oxathiolane-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9019
CAS No.:147027-10-9
- 3'-O-Demethylarctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3544
CAS No.:147022-95-5
- Cytarabine
Catalog No.:BCC3759
CAS No.:147-94-4
- Proline
Catalog No.:BCN1656
CAS No.:147-85-3
- DL-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN8541
CAS No.:147-81-9
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8947
CAS No.:147-24-0
- QL47
Catalog No.:BCC3920
CAS No.:1469988-75-7
- Atglistatin
Catalog No.:BCC5104
CAS No.:1469924-27-3
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Alcaftadine
Catalog No.:BCC5260
CAS No.:147084-10-4
- 5,6-Dihydro-6-methyl-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCC8722
CAS No.:147086-79-1
- Rosuvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3853
CAS No.:147098-20-2
- Maropitant
Catalog No.:BCC1728
CAS No.:147116-67-4
- Methyl (3R)-3-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-5-oxo-6-triphenylphosphoranylidenehexanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9031
CAS No.:147118-35-2
- 4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-[(N-methyl-N-methylsulfonyl)amino]pyrimidinyl-5-yl-formyl
Catalog No.:BCC8651
CAS No.:147118-37-4
- Tenofovir
Catalog No.:BCC2500
CAS No.:147127-20-6
- 4-Chloro-L-phenylalanine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2638
CAS No.:123053-23-6
- TT 232
Catalog No.:BCC6248
CAS No.:147159-51-1
- N-6-Methyl-7,7-dioxo-2-sulfamoyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-4-yl]acetamide
Catalog No.:BCC9077
CAS No.:147200-03-1
- Arecaidine propargyl ester tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC6628
CAS No.:147202-94-6
- Delavirdine mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4069
CAS No.:147221-93-0
Stability of an oral liquid dosage form of trovafloxacin mesylate and its quantitation in tablets using high-performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:23986008]
Int J Pharm Compd. 2000 May-Jun;4(3):233-5.
A high-performance liquid chromatographic assay method for the quantitation of trovafloxacin in film-coated tablets and an oral liquid dosage form (10 mg/mL) prepared from tablets has been developed. The assay method is very simple, precise and accurate, with a percent relative standard deviation of 1.8 based on five injections. The recovery from the tablets and the oral liquid dosage form was very close to the label claims. The method is stablilty indicating, since the peak from a degraded sample (using sodium hydroxide) did not interfere with the assay procedure. Furthermore, a number of excipients present in the tablets and the oral liquid dosage form did not interfere with the developed method. The oral liquid dosage form gave uniform results and the drug was stable for at least 14 days when stored in an amber-colored glass bottle at 25 deg C(+/-1). The pH of the formulation did not change.
Unexpected link between an antibiotic, pannexin channels and apoptosis.[Pubmed:24646995]
Nature. 2014 Mar 20;507(7492):329-34.
Plasma membrane pannexin 1 channels (PANX1) release nucleotide find-me signals from apoptotic cells to attract phagocytes. Here we show that the quinolone antibiotic trovafloxacin is a novel PANX1 inhibitor, by using a small-molecule screen. Although quinolones are widely used to treat bacterial infections, some quinolones have unexplained side effects, including deaths among children. PANX1 is a direct target of trovafloxacin at drug concentrations seen in human plasma, and its inhibition led to dysregulated fragmentation of apoptotic cells. Genetic loss of PANX1 phenocopied trovafloxacin effects, revealing a non-redundant role for pannexin channels in regulating cellular disassembly during apoptosis. Increase in drug-resistant bacteria worldwide and the dearth of new antibiotics is a major human health challenge. Comparing different quinolone antibiotics suggests that certain structural features may contribute to PANX1 blockade. These data identify a novel linkage between an antibiotic, pannexin channels and cellular integrity, and suggest that re-engineering certain quinolones might help develop newer antibacterials.
Activity of the new fluoroquinolone trovafloxacin (CP-99,219) against DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae selected in vitro.[Pubmed:9124824]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996 Dec;40(12):2691-7.
The MICs of trovafloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and sparfloxacin at which 90% of isolates are inhibited for 55 isolates of pneumococci were 0.125, 1, 4, and 0.5 microgram/ml, respectively. Resistant mutants of two susceptible isolates were selected in a stepwise fashion on agar containing ciprofloxacin at 2 to 10 times the MIC. While no mutants were obtained at the highest concentration tested, mutants were obtained at four times the MIC of ciprofloxacin (4 micrograms/ml) at a frequency of 1.0 x 10(-9). Ciprofloxacin MICs for these first-step mutants ranged from 4 to 8 micrograms/ml, whereas trovafloxacin MICs were 0.25 to 0.5 microgram/ml. Amplification of the quinolone resistance-determining region of the grlA (parC; topoisomerase IV) and gyrA (DNA gyrase) genes of the parents and mutants revealed that changes of the serine at position 80 (Ser80) to Phe or Tyr (Staphylococcus aureus coordinates) in GrlA were associated with resistance to ciprofloxacin. Second-step mutants of these isolates were selected by plating the isolates on medium containing ciprofloxacin at 32 micrograms/ml. Mutants for which ciprofloxacin MICs were 32 to 256 micrograms/ml and trovafloxacin MICs were 4 to 16 micrograms/ml were obtained at a frequency of 1.0 x 10(-9). Second-step mutants also had a change in GyrA corresponding to a substitution in Ser84 to Tyr or Phe or in Glu88 to Lys. Trovafloxacin protected from infection mice whose lungs were inoculated with lethal doses of either the parent strain or the first-step mutant. These results indicate that resistance to fluoroquinolones in S. pneumoniae occurs in vitro at a low frequency, involving sequential mutations in topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase. Trovafloxacin MICs for wild-type and first-step mutants are within clinically achievable levels in the blood and lungs of humans.
In vitro activity of the new fluoroquinolone CP-99,219.[Pubmed:7872757]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Nov;38(11):2615-22.
The in vitro activity of the new fluoroquinolone CP-99,219 [7-(3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexyl)naphthyridone] was compared with those of four other quinolones against 541 gram-negative, 283 gram-positive, and 70 anaerobic bacterial isolates. CP-99,219 inhibited 90% of many isolates in the family Enterobacteriaceae at a concentration of < or = 0.25 micrograms/ml (range, < 0.008 to 1 microgram/ml), an activity comparable to those of tosufloxacin and sparfloxacin and two times greater than that of temafloxacin. Ninety percent of the Proteus vulgaris, Providencia rettgeri, Providencia stuartii, and Serratia marcescens isolates were inhibited by 0.5 to 2 micrograms of CP-99,219 per ml. CP-99,219 inhibited 90% of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Haemophilus influenzae isolates at 1 and 0.015 micrograms/ml, respectively. The compound inhibited methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus at 0.06 micrograms/ml, whereas a ciprofloxacin concentration of 1 microgram/ml was required to inhibit these organisms. CP-99,219 inhibited 90% of methicillin-resistant S. aureus isolates at a concentration of < or = 4 micrograms/ml, while ciprofloxacin and temafloxacin had MICs against these isolates of > 16 micrograms/ml. Streptococci were inhibited by < or = 0.25 micrograms/ml, an activity comparable to that of tosufloxacin. CP-99,219 was eight times more active than ciprofloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Bacteroides species were inhibited by CP-99,219 at a concentration of 2 micrograms/ml, whereas inhibition of these species required 4- and 16-microgram/ml concentrations of tosufloxacin and ciprofloxacin, respectively. The MBCs of CP-99,219 ranged from two to four times the MICs, and inoculum size had a minimal effect on MIC. CP-99,219 was active against P. aeruginosa at pH 5.5, with only a fourfold increase in MIC compared with values obtained at pH 7.5. The addition of up to 9 mM Mg(2+) increased the MIC range from 0.03 to 0.06 microgram/ml to 0.12 to 0.5 microgram/ml. In view of its excellent in vitro activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, CP-99,219 merits further study to determine it's clinical pharmacologic properties and potential for therapeutic use.


