MK591FLAP inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 147030-01-1 |
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 147030-01-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23672584 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C34H34ClN2NaO3S | M.Wt | 609.15 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Quiflapon sodium | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (82.08 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
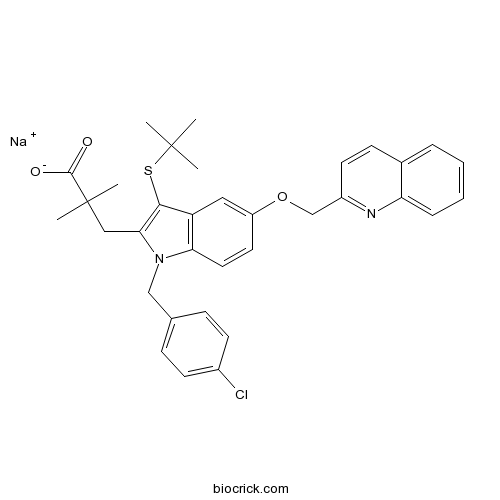
| Chemical Name | sodium;3-[3-tert-butylsulfanyl-1-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-5-(quinolin-2-ylmethoxy)indol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)SC1=C(N(C2=C1C=C(C=C2)OCC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4C=C3)CC5=CC=C(C=C5)Cl)CC(C)(C)C(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YPURUCMVRRNPHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C34H35ClN2O3S.Na/c1-33(2,3)41-31-27-18-26(40-21-25-15-12-23-8-6-7-9-28(23)36-25)16-17-29(27)37(20-22-10-13-24(35)14-11-22)30(31)19-34(4,5)32(38)39;/h6-18H,19-21H2,1-5H3,(H,38,39);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | MK591(Quiflapon sodium) is selective and specific inhibitor of 5-Lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP). | |||||
| Targets | FLAP | |||||

MK591 Dilution Calculator

MK591 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6416 mL | 8.2082 mL | 16.4163 mL | 32.8326 mL | 41.0408 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3283 mL | 1.6416 mL | 3.2833 mL | 6.5665 mL | 8.2082 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1642 mL | 0.8208 mL | 1.6416 mL | 3.2833 mL | 4.1041 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0328 mL | 0.1642 mL | 0.3283 mL | 0.6567 mL | 0.8208 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0164 mL | 0.0821 mL | 0.1642 mL | 0.3283 mL | 0.4104 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 1.6 nM in a FLAP binding assay for MK-0591, which is the acid form of MK591 [1]
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein is necessary for the activation of 5-lipoxygenase and therefore for the production of leukotrienes. MK-591 (MK-0591 sodium) is a selective and specific 5-Lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP) inhibitor.
In vitro: A series of performed inhibitor studies identified a specific inhibitor of 5-LO (MK-591), which has the ability to block JNK, MAPK and 5-LO signaling-cascades and drastically reducing the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-a. Further evaluation of MK-591 utilizing cell proliferation assays in PBMCs, human proximal tubule cells showed a decrease in cell proliferation [2].
In vivo: Amyloid β peptide (Aβ) deposition in the brains of mice receiving MK-591 was significantly reduced when compared with controls. MK-591 treatment did not cause any change in the steady-state levels ofβ-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1, amyloid-β precursor protein or disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10. By contrast, MK-591 caused a significant reduction of the γ-secretase complex, at the protein and message level [3].
Clinical trial: In an open-label and pilot study, short-term therapy with MK-591 reduces proteinuria by restoring glomerular size selectivity and thus reduces transglomerular protein trafficking. These benefits may result from glomerular leukotriene biosynthesis inhibition, but other MK-591-specific actions cannot be excluded [4].
References:
[1] Brideau C, Chan C, Charleson S, Denis D, Evans JF, Ford-Hutchinson AW, Fortin R, Gillard JW, Guay J, Guévremont D, et al. Pharmacology of MK-0591 (3-[1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-(t-butylthio)-5- (quinolin-2-yl-methoxy)-indol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid), a potent, orally active leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992;70(6):799-807.
[2] Mendis C, Campbell K, Das R, Yang D, Jett M. Effect of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor MK591 on early molecular and signaling events induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. FEBS J. 2008;275(12):3088-98.
[3] Jin Chu and Domenico Praticò. Involvement of 5-lipoxygenase activating protein in the amyloidotic phenotype of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J Neuroinflammation. 2012; 9: 127.
[4] Guasch A, Zayas CF, Badr KF. MK-591 acutely restores glomerular size selectivity and reduces proteinuria in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1999;56(1):261-7.
- Menthyl-5-(4-amino-2-oxo-2H-pyrimidin-1-yl)-[1,3]oxathiolane-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9019
CAS No.:147027-10-9
- 3'-O-Demethylarctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3544
CAS No.:147022-95-5
- Cytarabine
Catalog No.:BCC3759
CAS No.:147-94-4
- Proline
Catalog No.:BCN1656
CAS No.:147-85-3
- DL-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN8541
CAS No.:147-81-9
- Diphenhydramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8947
CAS No.:147-24-0
- QL47
Catalog No.:BCC3920
CAS No.:1469988-75-7
- Atglistatin
Catalog No.:BCC5104
CAS No.:1469924-27-3
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Y-27632
Catalog No.:BCC4301
CAS No.:146986-50-7
- Fmoc-Lys(Aloc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3515
CAS No.:146982-27-6
- Fmoc-Asp(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3089
CAS No.:146982-24-3
- Cyclo(Phe-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN2416
CAS No.:14705-60-3
- Rocaglaol
Catalog No.:BCN1653
CAS No.:147059-46-9
- Trovafloxacin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC3931
CAS No.:147059-75-4
- Alcaftadine
Catalog No.:BCC5260
CAS No.:147084-10-4
- 5,6-Dihydro-6-methyl-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCC8722
CAS No.:147086-79-1
- Rosuvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3853
CAS No.:147098-20-2
- Maropitant
Catalog No.:BCC1728
CAS No.:147116-67-4
- Methyl (3R)-3-(tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)-5-oxo-6-triphenylphosphoranylidenehexanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9031
CAS No.:147118-35-2
- 4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-[(N-methyl-N-methylsulfonyl)amino]pyrimidinyl-5-yl-formyl
Catalog No.:BCC8651
CAS No.:147118-37-4
- Tenofovir
Catalog No.:BCC2500
CAS No.:147127-20-6
- 4-Chloro-L-phenylalanine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2638
CAS No.:123053-23-6
- TT 232
Catalog No.:BCC6248
CAS No.:147159-51-1
Effect of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor MK591 on early molecular and signaling events induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.[Pubmed:18479466]
FEBS J. 2008 Jun;275(12):3088-98.
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) has been the focus of a number of studies due to its ability to promote septic shock and a massive impact on the human immune system. Even though symptoms and pathology associated with SEB is well known, early molecular events that lead to lethality are still poorly understood. Our approach was to utilize SEB induced human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) as a prototype module to further investigate the complexity of signaling cascades that may ultimately lead to lethal shock. Our study revealed the activation of multiple divergent intracellular pathways within minutes of SEB induction including components that interconnect investigated pathways. A series of performed inhibitor studies identified a specific inhibitor of 5-LO (MK591), which has the ability to block JNK, MAPK, p38kinase and 5-LO signaling-cascades and drastically reducing the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. Further evaluation of MK591 utilizing cell proliferation assays in PBMCs, human proximal tubule cells and in vivo studies (monkey) showed a decrease in cell proliferation. The inhibitory effect of MK591 was reconfirmed at a genetic level through the utilization of a set of SEB specific genes. Signaling activities, inhibitor studies, cellular analysis and gene expression analysis in unison illustrated the significance of pathway interconnectors such as 5-LO as well as inhibiting such inter-connectors (using MK591) in SEB induced human PBMCs.
5-Lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) dependent leukotriene biosynthesis inhibition (MK591) attenuates Lipid A endotoxin-induced inflammation.[Pubmed:25025775]
PLoS One. 2014 Jul 15;9(7):e102622.
The Lipid A moiety of endotoxin potently activates TLR-4 dependent host innate immune responses. We demonstrate that Lipid-A mediated leukotriene biosynthesis regulates pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP)-dependent macrophage activation. Stimulation of murine macrophages (RAW264.7) with E. coli 0111:B4 endotoxin (LPS) or Kdo2-lipid A (Lipid A) induced inflammation and Lipid A was sufficient to induce TLR-4 mediated macrophage inflammation and rapid ERK activation. The contribution of leukotriene biosynthesis was evaluated with a 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) inhibitor, MK591. MK591 pre-treatment not only enhanced but also sustained ERK activation for up to 4 hours after LPS and Lipid A stimulation while inhibiting cell proliferation and enhancing cellular apoptosis. Leukotriene biosynthesis inhibition attenuated inflammation induced by either whole LPS or the Lipid A fraction. These responses were regulated by inhibition of the key biosynthesis enzymes for the proinflammatory eicosanoids, 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) quantified by immunoblotting. Inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis differentially regulated TLR-2 and TLR-4 cell surface expression assessed by flow cytometry, suggesting a close mechanistic association between TLR expression and 5-LO associated eicosanoid activity in activated macrophages. Furthermore, MK591 pre-treatment enhanced ERK activation and inhibited cell proliferation after LPS or Lipid A stimulation. These effects were regulated in part by increased apoptosis and modulation of cell surface TLR expression. Together, these data clarify the mechanistic association between 5-lipoxygenase activating protein-mediated leukotriene biosynthesis and 5-LO dependent eicosanoid metabolites in mediating the TLR-dependent inflammatory response after endotoxin exposure typical of bacterial sepsis.
MK591, a leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor, induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells: synergistic action with LY294002, an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase.[Pubmed:19906484]
Cancer Lett. 2010 May 28;291(2):167-76.
MK591 is a synthetic compound which specifically inhibits the activity of 5-Lox and is currently under development for the treatment of asthma. We observed that human prostate cancer cells treated with MK591 undergo apoptosis within hours of treatment. Apoptosis involves severe morphological alteration, externalization of phosphatidyl-serine, cleavage of PARP, and degradation of chromatin-DNA. MK591 also induced rapid activation of the stress kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which plays an important role in the apoptosis process. The phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase-Akt/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) axis is a well-known pro-survival pathway which prevents apoptosis through defined anti-apoptotic mechanisms in a variety of cancer cells. Interestingly, we observed that MK591 triggers apoptosis in prostate cancer cells without inhibition of PI3K-Akt, or ERK. Moreover, it was observed that MK591 and LY294002 (an inhibitor of PI3K) exert synergistic effect in inducing apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Altogether, these findings indicate that 5-Lox inhibition-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells occurs without inhibition of PI3K-Akt, or ERK, and suggest for the existence of an Akt- and ERK-independent survival mechanism(s) in these cancer cells maintained via signals generated by metabolites of 5-Lox.
MK591, a second generation leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor, prevents invasion and induces apoptosis in the bone-invading C4-2B human prostate cancer cells: implications for the treatment of castration-resistant, bone-metastatic prostate cancer.[Pubmed:25875826]
PLoS One. 2015 Apr 15;10(4):e0122805.
Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is a major clinical challenge for which no cure is currently available primarily because of the lack of proper understanding about appropriate molecular target(s). Previously we observed that inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase (5-Lox) activity induces apoptosis in some types of prostate cancer cells, suggesting an important role of 5-Lox in the viability of prostate cancer cells. However, nothing is known about the role of 5-Lox in the survival of castration-resistant, metastatic prostate cancer cells. Thus, we tested the effects of MK591, a second-generation, specific inhibitor of 5-Lox activity, on the viability and metastatic characteristics of CRPC cells. We observed that MK591 effectively kills the bone-invading C4-2B human prostate cancer cells (which bear characteristics of CRPC), but does not affect normal, non-cancer fibroblasts (which do not express 5-Lox) in the same experimental conditions. We also observed that MK591 dramatically inhibits the in vitro invasion and soft-agar colony formation of C4-2B cells. Interestingly, we found that treatment with MK591 dramatically down-regulates the expression of c-Myc and its targets at sub-lethal doses. In light of frequent over-activation of c-Myc in a spectrum of aggressive cancers (including CRPC), and the challenges associated with inhibition of c-Myc (because of its non-enzymatic nature), our novel findings of selective killing, and blockade of invasive and soft-agar colony-forming abilities of the castration-resistant, bone-metastatic C4-2B prostate cancer cells by MK591, open up a new avenue to attack CRPC cells for better management of advanced prostate cancer while sparing normal, non-cancer body cells.


